World Time Zones
Local
Time in Different Locales
It’s easy to know what time it is in your classroom right
now — just look at the clock. But do you know what time it is in another
classroom across the world? How can you figure this out?
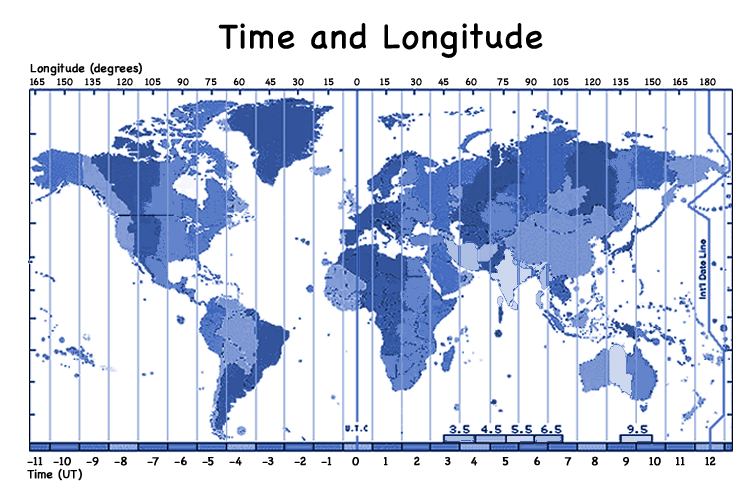
Calculating
Local Time Using World Time Zones
One way is to use world time zones to count how many hours different a location
is from you. The twenty-four time zones correspond to meridians of longitude.
Specifically, the zones are spaced 15 degrees apart, and each time zone
differs from its adjacent time zone by one hour (earlier or later). That
way, the times in each zone align with the local solar times of sunrise
and sunset.
But
using the time zones can be confusing for several reasons. First, some
countries have several different time zones, and those local zones don’t
always align perfectly with specific longitude lines. Also, remember that
with 24 time zones the local time at another location can be anywhere
from 0 to 24 hours different from you, and it can even be a different
date!
Calculating Local Time Using Universal Time
What if you could somehow use just one single uniform time zone all around
the world, would that make it easier to know what the time is at another
location? That’s exactly what Universal Time or “UT”
was designed to do–to provide a single time keeping method,
a single time zone, that everyone would understand, and which would avoid
the confusion of local time zones. UT is also called Greenwich Mean Time (“GMT”).
What
is UT Based On?
UT is based on the local time in Greenwich, England. That means that
UT time keeping is the same time as it is in Greenwich England. Because
UT is based on this single time zone, it is a uniform standard time keeping
method. Therefore, if you are using UT to designate a specific time,
your own local time no longer matters.
- Check
the Universal Time
Clock
What
is UT Used For?
Because UT is an international time keeping standard, it is used in important
applications such as official international matters, railroads, other
mass transit, in military time keeping, and also in scientific applications
such as satellites, weather, or astronomy.
In addition,
UT was used long ago in sea navigation, in order for sailors to estimate
their approximate longitude coordinate.
Try
This! Plan an International Call Using UT and Time Zones
>>















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


