Why Electrical Conductivity of Water is Important for Industrial Applications – Sensorex
The conductivity of water refers to the ability of water to conduct an electrical current. A material like copper has a high electrical conductivity, which is why it’s typically used as electrical wiring in a home. The high conductivity of copper allows an electrical current to travel through the wiring and over to a light bulb or ceiling fan. While pure water has very low conductivity, sea water comes with much higher conductivity. Different water types need to be measured for different reasons. For instance, the measurement of the electrical conductivity of water is very important for numerous industrial applications like cooling towers and boilers.
The reason that the conductivity of water is important is because it can tell you how much dissolved substances, chemicals, and minerals are present in the water. Higher amounts of these impurities will lead to a higher conductivity. Even a small amount of dissolved salts and chemicals can heighten the conductivity of water. In the event that you’re in charge of a wastewater treatment facility, significant changes in the conductivity of water might indicate that a pollutant has entered the water. It’s also possible that it could be the sign of a sewage leak. The following article acts as a guide that will help you understand all there is to know about the electrical conductivity of water and what it can mean for you.
What Is the Electrical Conductivity of Water?
The electrical conductivity of water is a term that refers to how well or otherwise water is able to conduct electricity. When the EC of water is higher, electricity will be more attracted to water, which is why it can be dangerous to use a smartphone while taking a bath or to go for a swim while a thunderstorm is ongoing. Pure water has an extremely low electrical conductivity because of the lack of impurities within it. For water to properly conduct electricity, there must be ions contained within it.
When various chemicals and salts dissolve into the water, they will turn into negatively charged and positively charged ions. The positively charged ions that can affect water include potassium, magnesium, and sodium. On the other hand, negatively charged ions include carbonate, chloride, and sulfate. A higher amount of a substance like sulfate can cause scale buildup to occur, which can damage boilers and other pieces of industrial equipment. For environmental and industrial applications, measuring the electrical conductivity of water is a very straightforward and inexpensive method of identifying how many ions are present in the water. Once these measurements have been taken, the water can be properly treated if necessary.

It’s important to understand that the electrical conductivity of water should be measured for a variety of different reasons. If you produce drinking water, the electrical conductivity should be less than 1 mS/cm. When working in the pharmaceutical industry, the EC of water will need to be even lower and should be less than 1 uS/cm. Because seawater has an ample amount of salt and other chemicals within it, the measurements of this water will typically come in at 45-72 mS/cm.
The main measurements of electrical conductivity are uS/cm and mS/cm, the former of which is considered to be less than the latter. The uS/cm unit stands for micro-Siemens, of which there are 100,000 in a standard SI unit of S/cm. As for mS/cm, this unit is essentially equivalent to 100 micro-Siemens per one S/CM. No matter what application you’re using it for, measuring the electrical conductivity of your water will allow you to identify if the EC levels are too high or too low. Once you have this information, you can take the appropriate measurements that will address the changes.
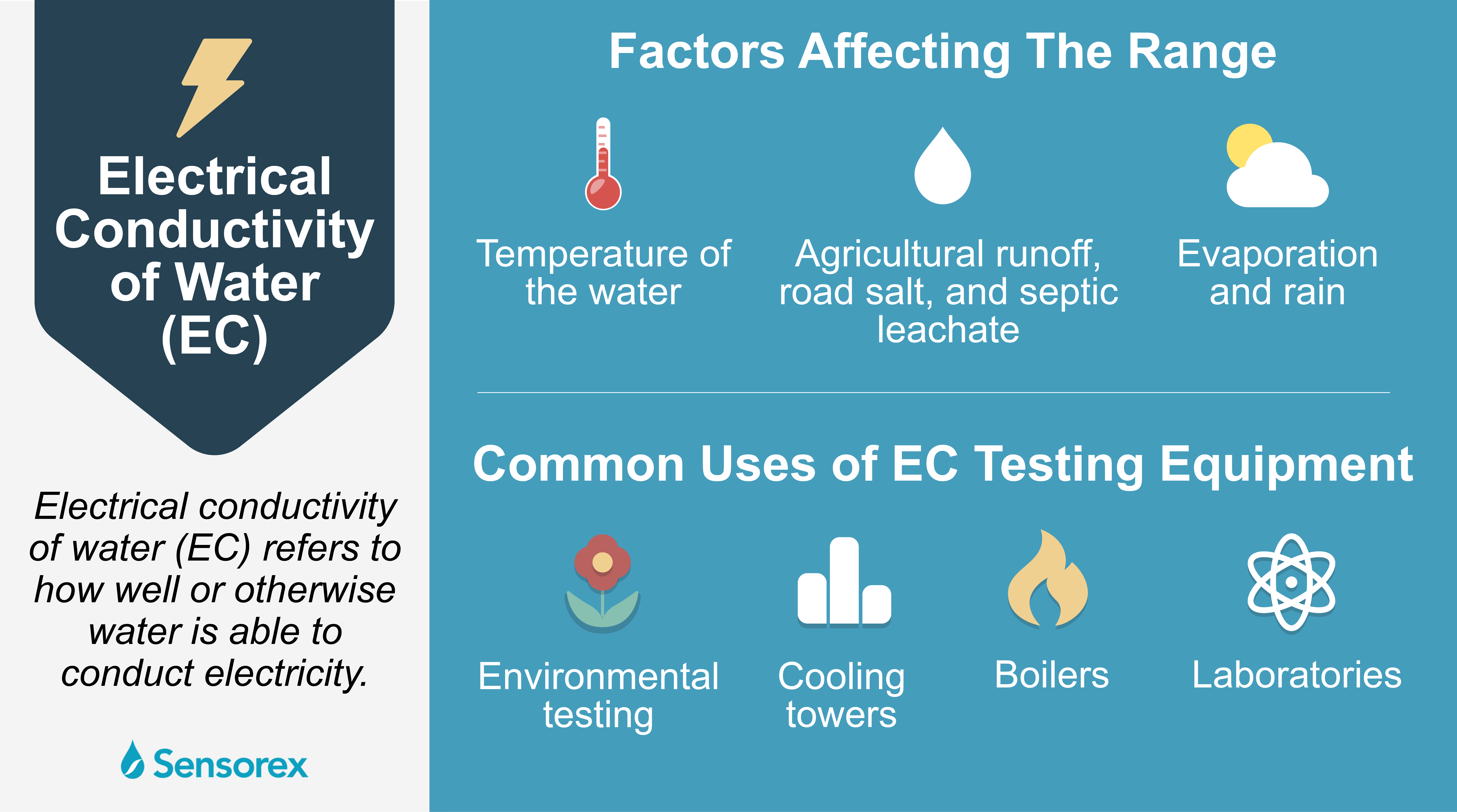
Factors Affecting The Range of Electrical Conductivity of Water

There are many distinct factors that can affect the EC of water, the primary of which involves the temperature of the water. In most cases, higher temperatures will equate to higher electrical conductivity. An increase in the temperature of the water by just one degree Celsius will cause an increase of electrical conductivity by 2-3 percent, which is why it’s so important to measure the electrical conductivity of your water. If you need the EC of your water to be at a certain level, even minor temperature changes can cause significant EC fluctuations.
The other factors that dictate how the EC fluctuates include natural impacts and human impacts. The natural factors that impact the EC of water include evaporation and rain. Some of the human impacts on water EC include agricultural runoff, road salt, and septic leachate. You can actually change the electrical conductivity of water by understanding what elements are able to change the EC of water. The easiest way to change the EC is by increasing or decreasing the temperature of the water. While there are other treatment methods that you might need to look into for significant EC alterations, changing the temperature of the water should be enough for now.
Sensorex Electrical Conductivity Testing Equipment
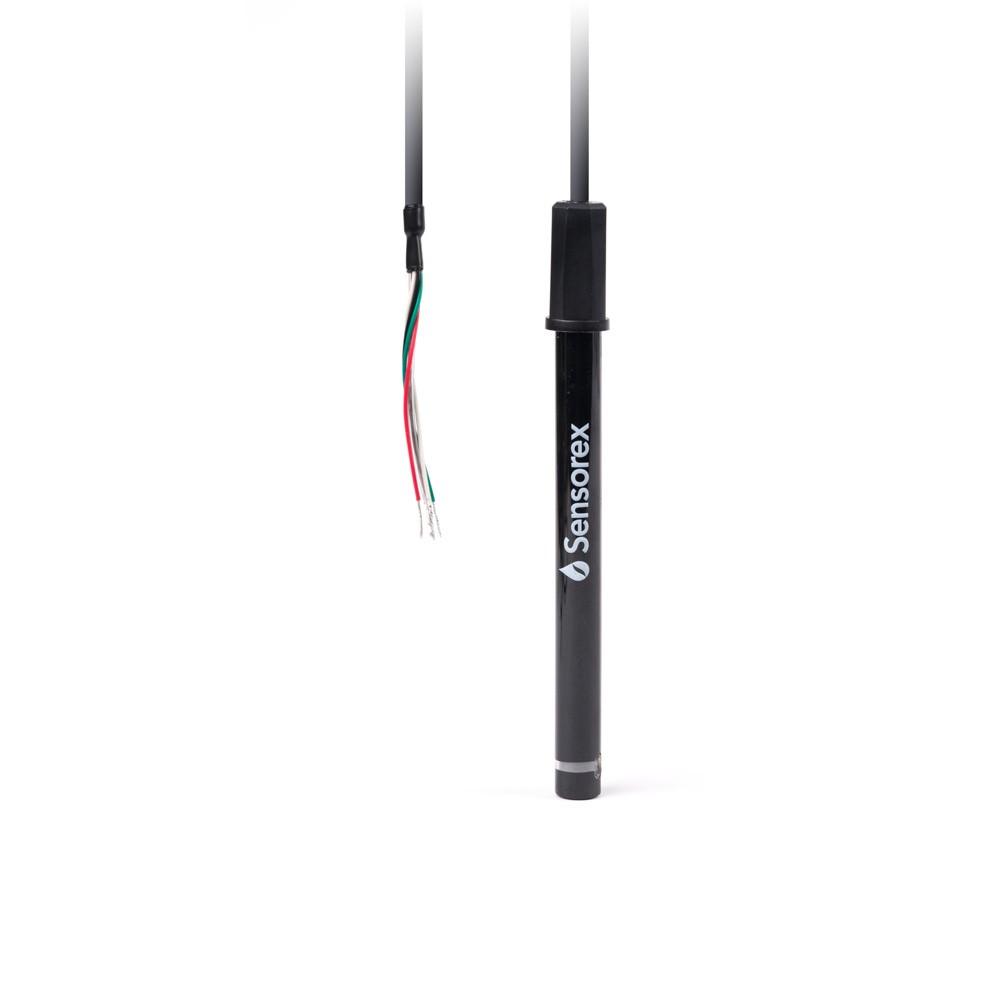 There are many fantastic equipment sensors at Sensorex that you can use to help measure the EC of water. Keep in mind that these sensors can provide you with measurements in micro-Siemens, milli-Siemens, or TDS, the latter of which stands for total dissolved solids. If you use TDS to measure the electrical conductivity of water, the measurement will be relayed to you as parts per million or PPM. Higher readings equate to a higher conductivity.
There are many fantastic equipment sensors at Sensorex that you can use to help measure the EC of water. Keep in mind that these sensors can provide you with measurements in micro-Siemens, milli-Siemens, or TDS, the latter of which stands for total dissolved solids. If you use TDS to measure the electrical conductivity of water, the measurement will be relayed to you as parts per million or PPM. Higher readings equate to a higher conductivity.
There are two basic types of sensors that can measure the electrical conductivity of water, which include contacting conductivity sensors and toroidal conductivity sensors. A contacting conductivity sensor is unique in that it places two separate surfaces into the water, which can be made from such materials as graphite and platinum. A voltage waveform is sent from one surface to the other, which means that it needs to pass through the water. Once the second surface obtains the signal, the EC readings are then sent to a digital display. Constant monitoring is recommended so that you can compare one reading to another. If a significant change has occurred, you will be able to react accordingly.
As for toroidal conductivity sensors, these use a 2-coil system that’s situated in a plastic case. The coil that sends a signal will produce a magnetic field in order to create an electric current. The flow of this current will be identified by the receiving coil. A high current flow means that there are many ions in the water, which indicates a high electrical conductivity. These sensors are notable for being fully resistant to fouling issues. As such, toroidal sensors are commonly used in applications that call for high water conductivity, which include seawater monitoring, cooling towers, and chemical processing.

The benefits that you’ll be provided with from an EC sensor depend on the exact sensor that you choose. For instance, the CS150TC sensor can be used in environmental and laboratory applications. This specific sensor can be mounted within a pipe, used in combination with a benchtop meter, or submerged directly into a tank, which makes it a highly versatile sensor. If the sensor needs to be used in a boiler with hot temperatures, the CS675HTTC is the best option for you. These models come with a heavy-duty, stainless-steel body and can accommodate a maximum temperature of 200 degrees Celsius.
If you require a sensor to measure the water in a cooling tower, the CS8300TC model is designed specifically for this application. This model is able to resist fouling and comes with digital communication. As for the standard toroidal sensor, this option is ideal for industrial and chemical use. These sensors are known to be extremely precise and come with very little maintenance requirements. No matter which of these sensors you choose, you’ll be able to measure the electrical conductivity of your water with ease.
Why Use Electrical Conductivity Testing Equipment for Water Testing?

It’s important to use EC testing equipment for the measurement of your water for many notable reasons. Since significant changes in the electrical conductivity of water indicate that a pollutant may have entered the water or that other issues are taking place, the readings that you’re provided with will help you determine if you need to treat the water. Identifying these changes will also help you keep issues like scaling and biocide at bay, the former of which will almost certainly make your boiler or cooling tower less efficient.
This testing can be done in a wide array of different environments and settings, many of which are industrial in nature. Some of the more common uses of EC testing equipment occur with environmental testing, in cooling towers, in boilers, and in laboratories with pharmaceutical testing. If the testing equipment is set to be used at a wastewater treatment facility, it can control the activated sludge process. While the testing of the EC of water is very important for companies, it’s also beneficial for individuals in certain situations. If you have an outdoor pool at your home, the use of EC testing equipment will allow you to identify the TDS levels in the pool water. If the levels reach higher than 2,000 PPM, the water will need to be filtered or drained to prevent scale buildup.
No matter which industry you work in, this measurement will be able to help you determine if you need to treat the water. If you want to get an ideal EC measurement for your water, it’s recommended that you first test the water with an EC sensor. The readings that you obtain will help you determine if the EC levels are too high or too low. While there are some scenarios where the water might need to be removed and replaced entirely, it’s also possible that you could obtain optimal readings by reducing or increasing the water temperature by a few degrees Celsius. Making these changes immediately will prevent such problems as scale buildup and cloudy water.
Why Should You Know the Electrical Conductivity of Water

Being able to effectively measure the electrical conductivity of water is absolutely essential in many industries and for numerous applications. Since fish can only tolerate a specific electrical conductivity range, assessing the EC of water can be very beneficial for fisheries. Some of the other applications that call for the measurement of the EC of water include environmental monitoring, boiler protection, the monitoring of chemical concentration, and the monitoring of reverse osmosis. In order to create an ideal measurement, you should obtain a conductivity sensor that matches the specific application you need it for. Once you’re provided with the EC readings, you can filter the water for a better reading or change the temperatures of the water altogether.
Keep it mind that you can customize the sensor to ensure that it meets the needs of your specific system. The main customization options include measurement range, body size, construction materials, connector type, and cable length. Whether you work at a wastewater treatment facility or cooling tower, there are also a wide range of additional Sensorex products that will provide for all of your water measurement needs. If you want to measure the acidity of your water, you can do so with a pH sensor, of which there are several different types. No matter what tool you require for water measurement purposes, you’re certain to find it at Sensorex.















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


