What is Strategy? Definition, Components & Examples Explained
The success of any business is determined by the effectiveness of the strategy it follows. A strategy explains how a company plans to compete in a market and how it intends to grow at a profit.
Businesses worldwide sell goods and services in competitive markets that require them to increase the value for owners and shareholders to secure their future existence.
This calls for a plan that helps managers guide their decisions and use resources effectively to achieve key objectives. This plan is also known as a business strategy.
This article will cover:
Mục Lục
What is a business strategy?
The definition is as straight forward as it can be confusing when reading it first:
A business strategy outlines the plan of action to achieve the vision and set objectives of an organization and guides the decision-making processes to improve the company’s financial stability in a competing market.
In an attempt to reduce complexity, many online sources refer to a simpler definition of strategy as:
A high-level plan that helps a business achieve its goals.
While this is still accurate, it does not give a good understanding of how these goals are actually achieved.
To allow for a better and more granular understanding, I will refer to the former definition in the following chapters.
How is strategy different from tactics?
Before we get into the details of building a strategy, it is vital to understand how a strategy differs from a tactic.
While both terms are often interchangeably confused, they are two entirely different things:
A strategy refers to an organization’s long-term goals and how it plans to reach them. In other words, it shows the path to achieve the defined vision.
A tactic refers to the specific actions taken to reach the set goals in line with the strategy.
For example, company A’s strategy might be to become the cheapest provider in the smartphone market. Their managers then need to negotiate with suppliers to reduce the costs of the electronic components used in production. This is a tactic to achieve the set strategy.
Or, as the English comedian and writer Frank Muir put it:
Strategy is buying a bottle of fine wine when you take someone out for dinner. Tactics is getting them to drink it.
Frank Muir
Levels of business strategies
There are three levels at which strategies are typically used: The corporate, business and functional level.
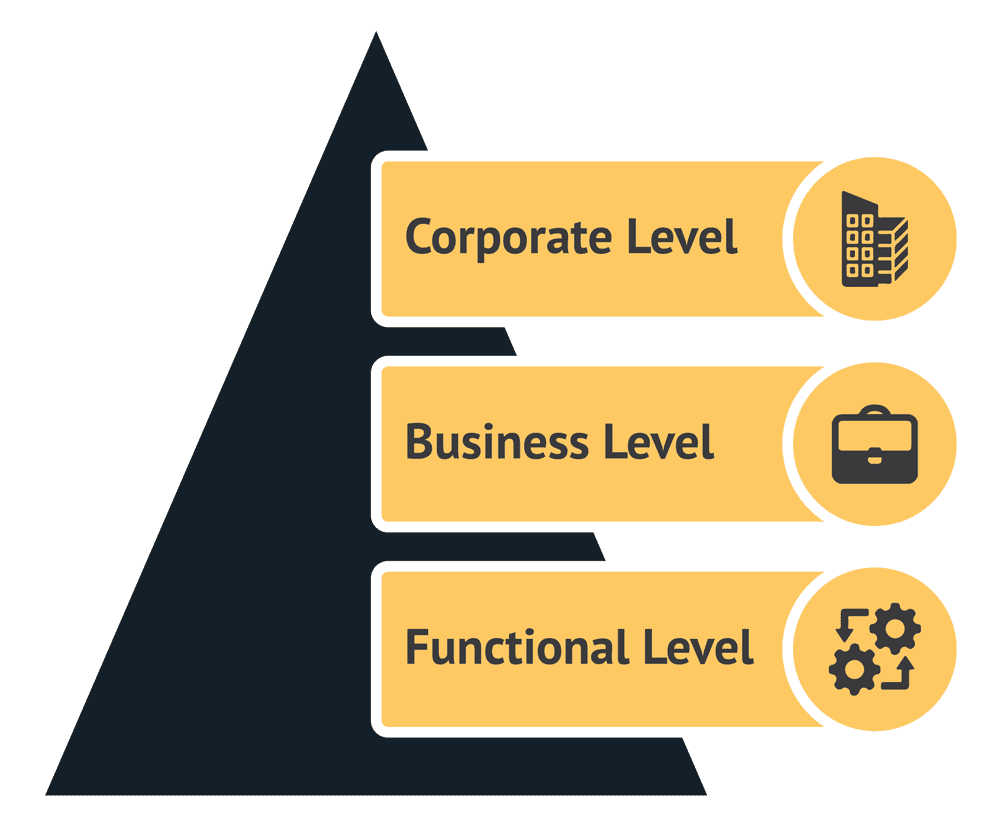
All three levels form the strategic framework of an organization:
1. Corporate Level: Corporate level strategies are the strategic plans of an organisation’s top management. They form the mission and vision statement and have a fundamental impact on the firm’s long-term performance. They guide decisions around growth, acquisitions, diversification and investments.
2. Business Level: Business level strategies integrate into the corporate vision, but with a focus on a specific business. At this level, the vision and objectives are turned into concrete strategies that inform how a business is going to compete in the market.
3. Functional Level: Functional level strategies are designed to answer how functional departments like Marketing, HR or R&D can support the defined business and corporate strategies of an organization.
It’s not uncommon for a firm to have multiple strategies at each level. In fact, this is essential to ensure that the different needs of each layer are accurately reflected.
Although multiple strategies carry the risk of conflicting priorities and objectives, these risks can be reduced if managed correctly. We will come back to this point in a second.
Why is having a business strategy important?
The existence of a strategy is a critical success factor for any business.
Essentially, it reflects the strengths and weaknesses of the company and answers how the company plans to respond to the threats and opportunities in the market in which it operates.
A strategy takes into account the resources at hand and how to best deploy them to achieve its set objectives.
That’s why a strategy is often called the lighthouse for a company’s management: It aligns the efforts of all functional departments and gives its employees a Northstar that guides their daily decision making.
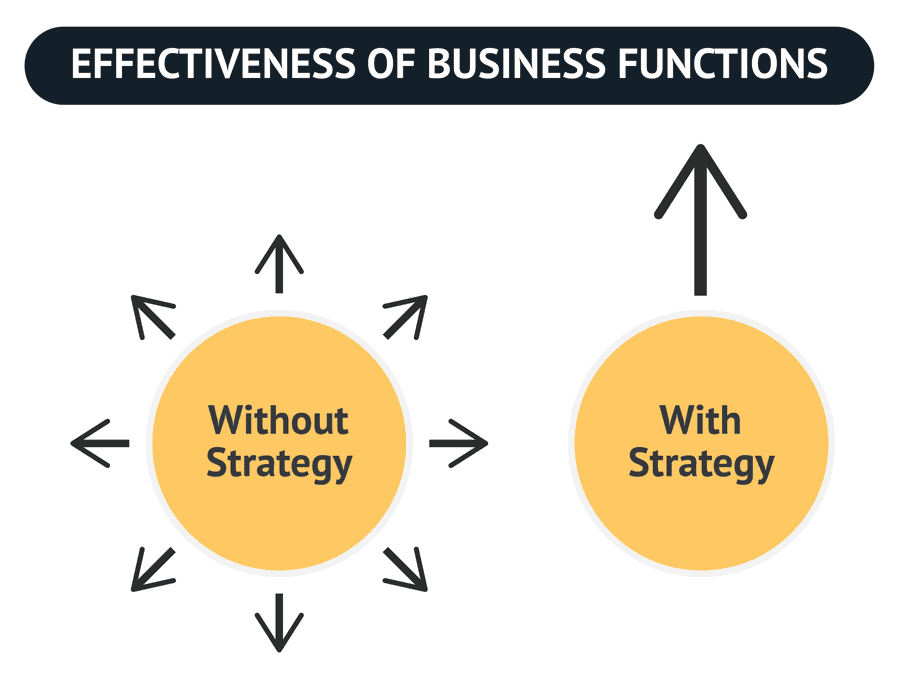
To make this point even clearer, let’s say a business would not have a strategy on how it will compete in a market:
The absence of such a blueprint would lead to disordered actions in each department, limiting the organisation’s effectiveness as a whole. This incoherence always results in a loss of competitive power that will be exploited in the market.
How do you formulate a business strategy?
A business strategy outlines the plan of action to achieve the vision and set objectives of an organization and guides the decision-making processes to improve the company’s financial stability in a competing market.
The above definition already gives some practical advice on how to build an effective strategy:
A strategy needs to outline the vision of a business, define its targets and how it is going to grow and compete long-term.
The strategy building process can be broken down into five steps:
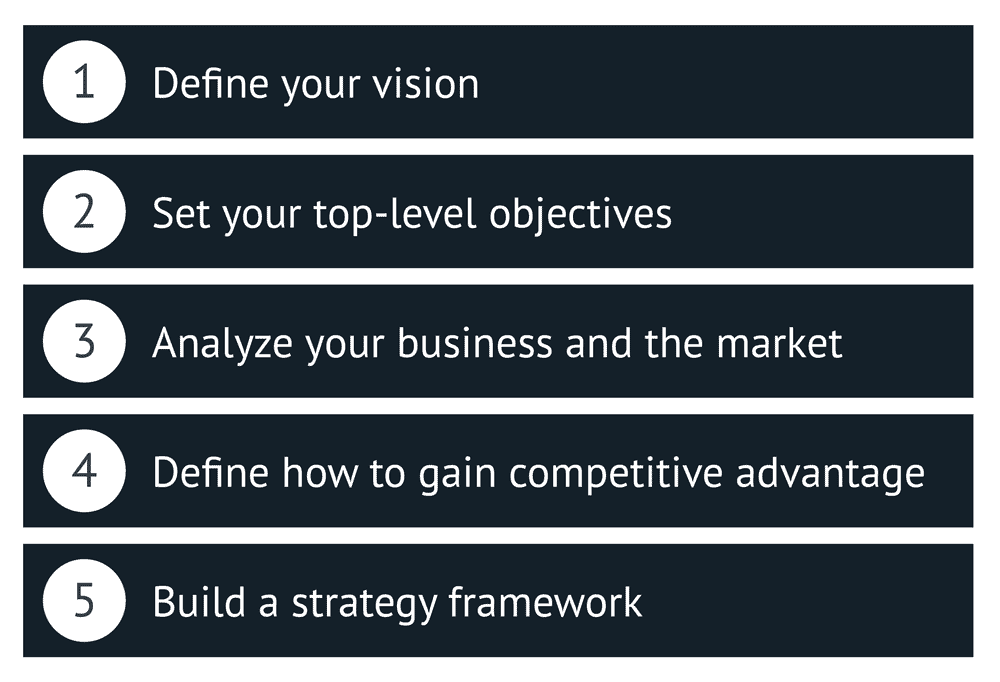
Step 1: Define your vision
Most online sources suggest that strategy formulation should begin by defining the objectives of an organization. But this reaches too far too fast, as it presumes that the offering, the market and the target customers have already been defined.
For a strategy to be successful, it must first consider the company’s core values and its desired future position in the market. This is also known as the company’s vision.
Examples of vision statements from some of the largest companies include:
“Apple strives to bring the best personal computing experience to students, educators, creative professionals, and consumers around the world through its innovative hardware, software, and internet offerings.”
Apple
“To be earth’s most customer-centric company; to build a place where people can come to find and discover anything they might want to buy online.”
Amazon
Based on a firm’s vision, the offer, its customers and the market can be defined.
This is an important step in the strategy building process because it ensures that the designed strategy reflects the actual needs of the relevant market.
Offer & Value Proposition
An effective business strategy builds directly on the company’s offering and value proposition.
The former lays out what goods and services are offered, while the value proposition explains why people should buy them in the first place.
Note that the value proposition answers why a firm exists and how it is different from its rivals. In other words, it explains how a firm plans to create demand and compete in the market.
To illustrate this with an example, take a look at Shopify. Their value proposition is to offer a single ecommerce platform that lets its customers sell across multiple channels.
 Shopify’s value proposition states why business owners should use their platform and how it is different from others.
Shopify’s value proposition states why business owners should use their platform and how it is different from others.
Customers
Another vital step in building an effective business strategy is to define the type of customer a company serves.
Customers are either categorized as consumers (B2C) or businesses (B2B).
Both groups have different criteria, reasons and motivations for purchasing goods and services. Knowing them allows a firm to accurately address their specific needs and wants in its strategy.
Target Market
Finally, strategy builders need to be clear about the market their offering and value proposition are targeting.
- If a firm sells to consumers (B2C), a market can be defined by demographic and socio-economic factors, such as gender, age, occupation, education, income, wealth and where someone lives.
- If, however, the offering targets other businesses (B2B), markets are typically defined by using factors such as the industry, business or sales model of the targeted customer groups.
I recommend reading this article from Annmarie Hanlon if you want to learn more about the specifics of segmenting a market.
Step 2: Set your top-level objectives
After defining the vision, the next step in formulating a business strategy is to set an organisation’s top-level objectives.
These objectives are usually focused on increasing a firm’s sales and profits, as they ensure its existence and improve the shareholder value if publicly traded.
That’s why a strategy essentially aims to answer the question of how a business can compete in the market to grow its revenue, while also improving its financial position.
Note that the formulation of high-level objectives does not include any goals to achieve a company’s mission or to reflect its core values.
This is because the sole purpose of a generic business strategy is to increase the company’s economic value for its owners or shareholders.
The core values and mission are later taken into account when designing the lower-level strategies, such as the marketing or operational strategy.
Step 3: Analyse your business and the market
Once the vision and objectives are defined, strategy builders need to become aware of their business’s strengths and weaknesses and the opportunities and challenges in the marketplace.
This can be done using a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats):
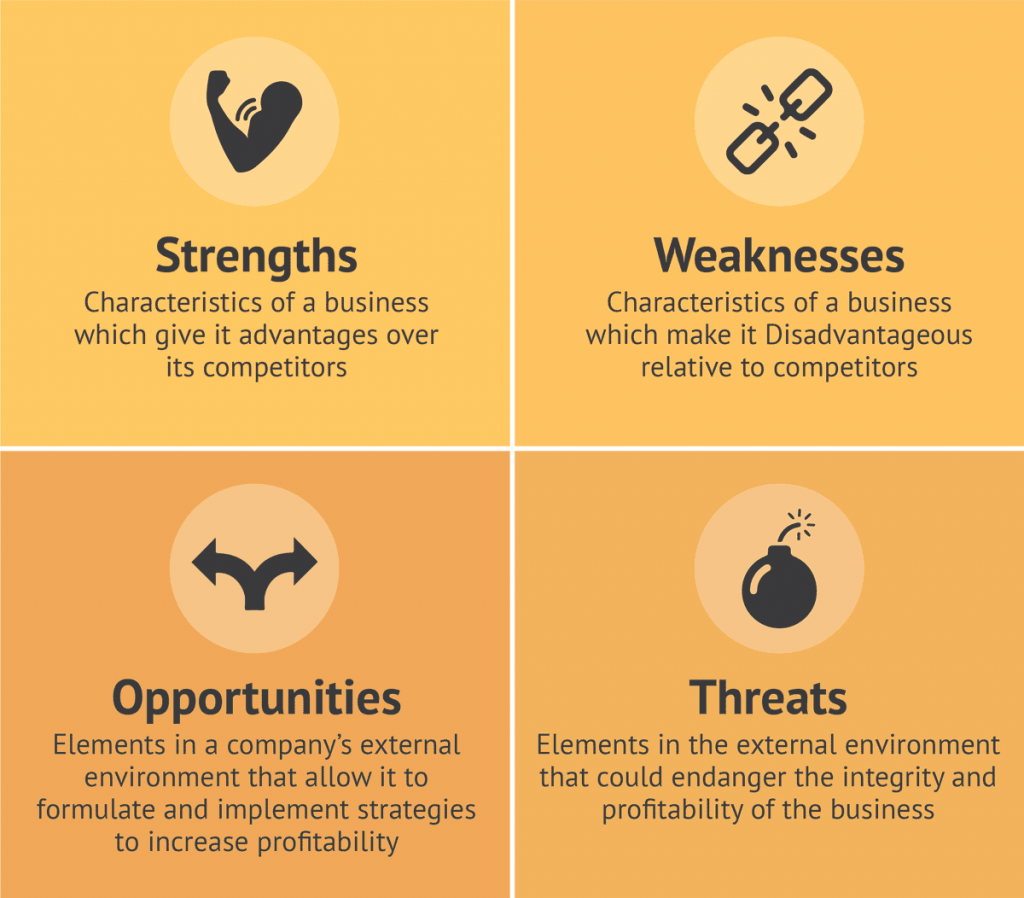
The information obtained in the course of a SWOT analysis serves as a basis for the strategy formulation that considers the company’s internal characteristics and the external situation of the market segment.
These insights allow decision-makers to ensure that a firm’s strengths exploit the opportunities in the market, while also addressing potential weaknesses and threats that can limit the organization’s long-term success.
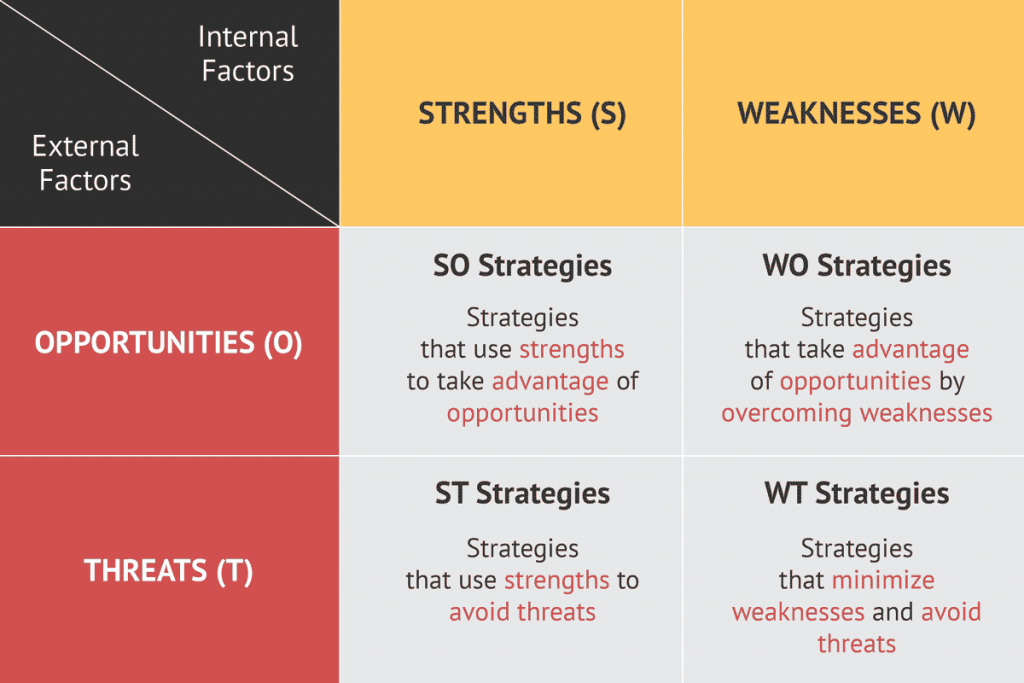 Different strategies can emerge from a SWOT analysis
Different strategies can emerge from a SWOT analysis
Step 4: Define how to gain competitive advantage
The fourth step in the strategy formulation answers the question of how the set objectives are achieved.
Firms that sell in competitive industries need to define how they want to compete in the market, create demand and increase their sales and margins.
Types of business strategies
Harvard Business School professor Michael E. Porter identified three types of generic strategies that businesses can choose from when defining their competitive advantage:
- Cost Leadership,
- Differentiation, or
- Focus.
However, firms can also fail to pursue one of these generic strategies effectively. Porter refers to this as being “stuck in the middle”.
In this case, a company does not offer a product or service unique enough to entice customers to buy. At the same time, the price of the offering is too high to compete effectively in the market.
Failure to gain a competitive advantage will result in a poor sales performance, which threatens the future company’s existence.
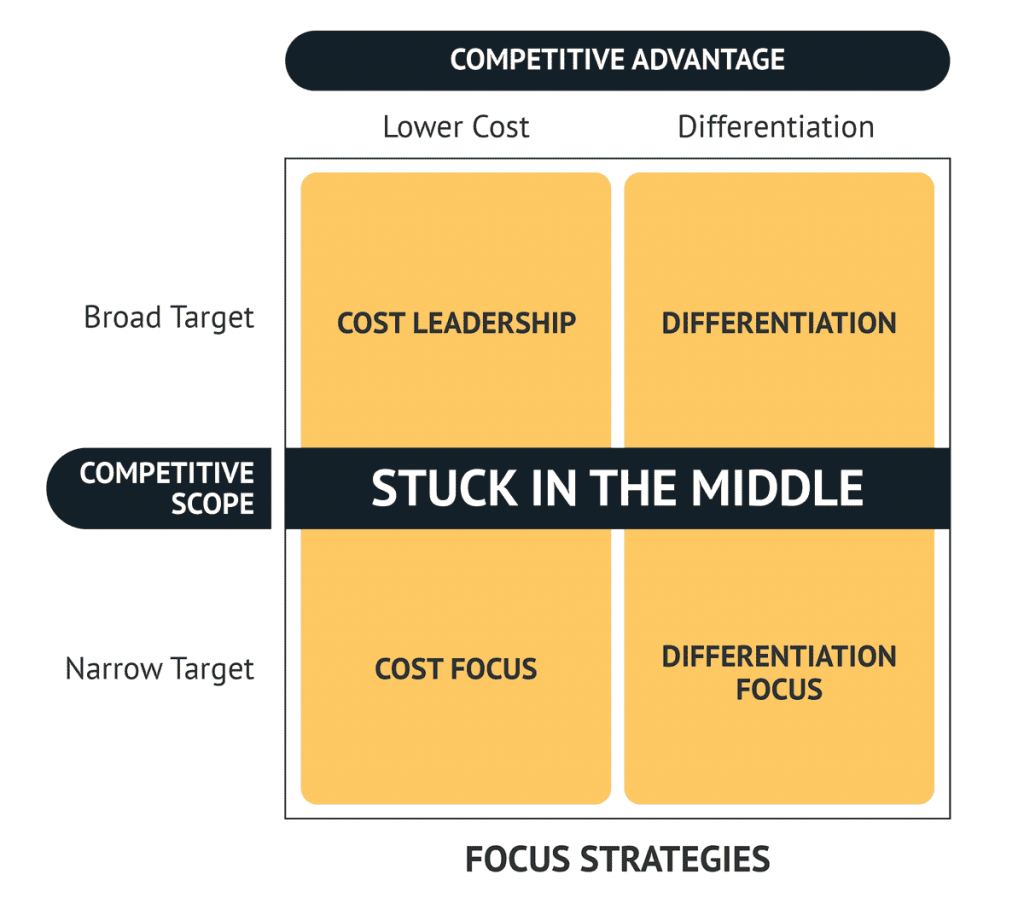 Porter’s Generic Competitive Strategies Framework
Porter’s Generic Competitive Strategies Framework
Let’s take a closer look at the different ways a company can gain a competitive advantage:
Cost Leadership
Cost leadership refers to a company’s ability to produce a product at the lowest cost in its industry.
This cost advantage can be achieved by using economies of scale, proprietary technologies or the ability to create and maintain cost benefits along the supply chain.
The cost leadership strategy requires a firm to effectively lower its cost structures while charging prices for its products that are in line with the industry average.
Example: Low fare airline Ryanair is a typical example of a firm that applies a cost leadership strategy. They successfully compete in the airline industry by driving down costs and utilize economies of scale. For that reason, Ryanair only operates one type of aircraft (Boeing 737-200) in its entire fleet.
Differentiation
In a differentiation strategy, a firm seeks to create a unique offer that is valued by its target customers. Buyers must perceive the offer as far more valuable compared to other alternatives in the industry. In return, a company is able to demand higher prices for its products.
Example: Starbucks is a great example of a firm that has successfully implemented a differentiation strategy. While it sells coffee as a widely available commodity, its well-designed stores, and the unrivalled number of flavour variations are the reason why customers are willing to pay a premium.
Focus
The generic strategy of focus aims at only a small number of target market segments. Porter’s matrix defines the competitive scope in these cases as narrow, as a firm only aims at a small portion of the wider market segment.
In that case, a company can either have a cost focus or a differentiation focus:
When a firm seeks to gain a cost advantage, it follows a cost-focused strategy. The firm’s offer is a low-cost alternative to the leading product in the market that still appeals to a specific group of buyers.
On the other hand, the differentiation focus seeks to cater to a specific need in a customer segment. This differentiation focus is the classic niche marketing strategy many small and local businesses follow to compete against the larger chains in their market.
Example: Small online shops that specialize in offering vegan and vegetarian products are a good example of firms that follow a generic focus strategy. Their narrow target scope allows them to become the preferred choice of environmental and health-conscious customer segments.
Step 5: Build a strategy framework
Based on the execution of the previous steps, a generic business strategy can be formulated.
However, functions such as marketing or finance will not contribute effectively to this generic strategy unless it is translated into more specific lower-level strategies.
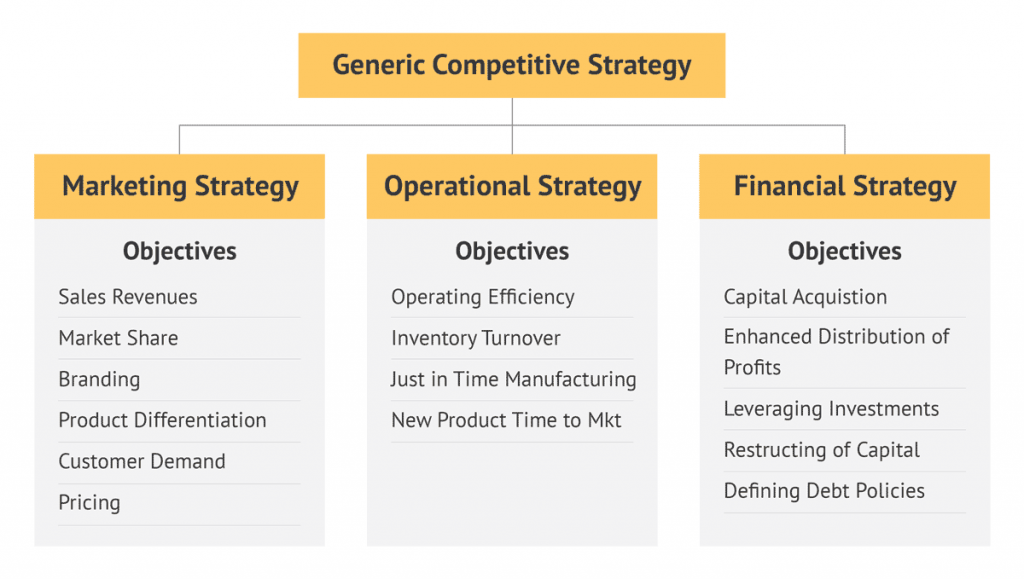
The formation of these lower-level strategies that sit underneath a generic business strategy is called a strategy framework.
It ensures the success of the generic business plan, as it captures the vision and needs of the single departments and aligns them with the higher-level objectives.
Product, branding, marketing or operational strategies are only a few examples that contribute to the success of a firm’s overall generic business strategy.
![]() PRO INSIGHT
PRO INSIGHT
Note that strategic frameworks can quickly become quite complex in practice. That’s why managers need to ensure that they regularly review the alignment between low- and high-level strategies.
How to measure strategy success
Business strategies are successful when they are directly responsible for growth and improved competitive or financial performance.
The success of a strategic plan can be evaluated by monitoring a range of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs).
However, it is important that …
- … these KPIs measure the level of achievement of the objectives defined in step two of the strategy formulation process.
- … the KPIs are defined before the strategy implementation takes place to ensure accurate measurement.
Normally, some or all of the following KPIs are measured when implementing a new business strategy:
Growth
- Sales revenue
- Number of customers
- Repeat customer sales
- Customer retention rate
- Conversion Rate
- Average Order Value (AOV)
- Business Volume
Competitive Position
- Market share
- Market position
- Sales win rate
- Brand awareness & press mentions
- Margin position vs. industry average
- Sales growth vs. industry average
Financial Performance
- Gross Profit
- Net Profit
- Operating Profit
- EBIT and EBITDA
- Return on Assets
- Free Cash Flow
- Operating Cash Flow
In practice, companies may measure strategy success in a more granular way. This is because individual departments define their own lower-level strategies.
A more realistic KPI overview is shown in the following chart:
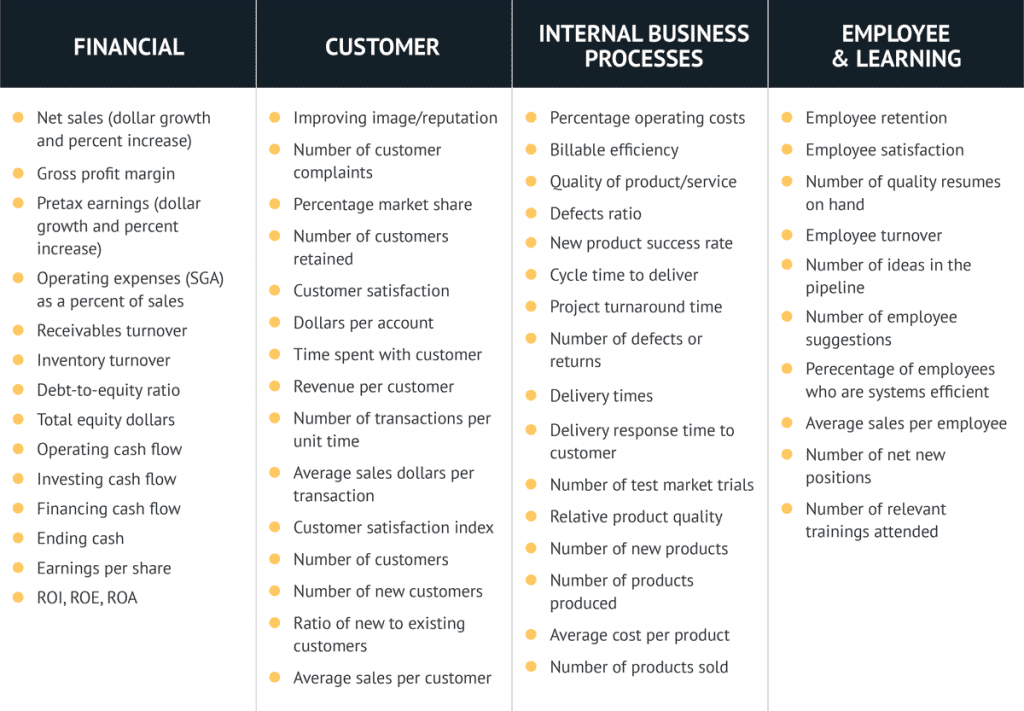
Business Strategy Examples
To illustrate the earlier discussed principles, I have compiled two examples of companies that have successfully implemented their generic business strategy: Amazon and Reckitt Benckiser.
Example 1: Amazon
Amazon is known for its great customer service and fast shipping options.
And while its vision is to be earth’s most customer-centric company, Amazon makes this a reality by continually innovating in existing and new markets. The result? Further growth and greater shareholder value.
In his first shareholder letter from 1997, Jeff Bezos himself outlined the four principles that guide the company: customer obsession rather than competitor focus, passion for invention, commitment to operational excellence and long-term thinking.
Amazon’s generic business strategy is to gain a competitive advantage by driving down costs (cost leadership), paired with its ability to innovate in competitive markets.
The focus is always the same: serving the needs of end-customers.
This allows Amazon to overtake its competition that often struggles to catch up with the tech giant within several years (ST-Strategy).
Its lower-level strategies (operational, marketing, etc.) all follow the generic strategy of focusing on choice, price and economies of scale to create value for customers.
This strategic framework has allowed Amazon to become one of the most successful tech companies in the 21st century.
Example 2: Reckitt Benckiser
Although the company’s name is not known by many consumers, Reckitt’s brand portfolio consists of major household brands, such as Finish, Dettol, Nurofen, Vanish, or Durex.
Faced with slowing sales and increased competition back in 2012, the company had to change its business strategy to return to a path of solid growth.
Under the new strategy, RB:
- Focused on R&D for new product lines that allowed it to achieve its high-level objectives to increase sales and margins;
- Increased its budgets in markets that grew above-average to stimulate further growth;
- Overhauled its brand and marketing strategies and increased budgets in those areas;
- Set and closely monitored multiple key performance indicators with the aim to increase its net revenue growth by +200bps vs. market average each year until 2017.
While Reckitt could not achieve all of its set targets, the modifications of its business strategy helped the company to grow its sales and profits above the market average.
As a result, RB grew £33bn in value for its shareholders between 2012 and 2017.
Still have questions about business strategy?
If you need help to come up with a strategy for your ecommerce business, then get in touch. I offer tailored advice that will help you get clarity about your vision, objectives and how to build a more effective business.
—
Enjoyed this article? Here are more things you might like:
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis – A complete guide to Michael E. Porter’s 5 Forces Analysis to help you assess your competitive landscape.
The Importance of the Product Life Cycle – A complete break down of the individual stages of the product life cycle to plan your next marketing moves.
Ecommerce Glossary – Stop the guessing. My glossary explains every ecommerce term in under 30 seconds.















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


