(Update 2021) What Are SFP Ports Used For? – Router Switch Blog

If you know Cisco SFP Modules, you must know the SFP Ports. If you didn’t know what are SFP modules or SFP ports, you can read this article, which can tell you what are SFP ports on a Gigabit Switch used for?
Cisco SFP Modules, the industry-standard Cisco Small Form-Factor Pluggable Gigabit Interface Converter, links your switches and routers to the network.
SFP sockets are found in Ethernet switches, routers, firewalls and network interface cards. It interfaces a network device motherboard (for a switch, router, media converter or similar device) to a fiber optic or copper networking cable.
In many cases, SFP ports are also known as mini-Gigabit interface converter (GBIC) modules, as they have replaced the older GBIC transceivers.
SFP Port Advantage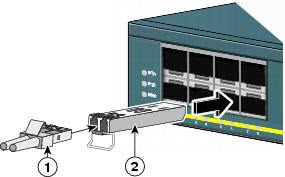
It is flexible for the SFP port link to the network. The SFP port is the I/O device which is able to be hot-plugged. We are able to insert the Gigabit Ethernet port or slot into the SFP port and then connect the SFP port with the network. The SFP port is applied in many products and is able to exchange with the port of the 1000BASE-SX, 1000BASE-LX/LH, 1000BASE-ZX or the 1000BASE- BX10-D/U.
Why Need SFP Module?
Compared with GBIC module, SFP Modules volume ratio reduced by half, and the number of ports can be configured more than 2 times on the same panel. That can be inserted mini head fiber module slot. The Other basic features are consistent with GBIC.SFP Modules for Gigabit Ethernet Applications: Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) links your switches and routers to the network.
The hot-swappable input / output device plugs into a Gigabit Ethernet port or slot. Optical and copper models can be used on a wide variety of products and intermixed in combinations of 1000BASE-T, 1000BASE-SX, 1000BASE-LX / LH, 1000BASE-EX, 1000BASE-ZX, or 1000BASE-BX10-D / U on a port-by-port basis.
SFP Ports on a Gigabit Switch
SFP ports enable Gigabit switches to connect to a wide variety of fiber and Ethernet cables in order to extend switching functionality throughout the network.
The SFP devices allow the switch to connect to fiber cables of different types — including single-mode and multimode–and speeds (1 Gbps, 10 Gbps), or even Ethernet copper cables, such as CAT5e and CAT6.
Almost all enterprise-class switches include two or more SFP ports, allowing them to become part of a ring or star-based network topology spread among different buildings, floors or areas, and connected via fiber optic cabling.
The Hot SFP Modules
The latest SFP modules, such as GLC-BX-D and GLC-BX-U, support digital optical monitoring, which lets end users monitor the performance of SFPs in real time, tracking such metrics as temperature, optical output power, optical input power, transceiver supply voltage and laser bias current.
SFPs can support speeds of up to 1 Gbps, with transmission ranges of 10 kilometers (1000BASE-BX10-D), 40 km (GLC-BX40-D) or 80 km (GLC-BX80-D), depending on the model selected.
Newer SFP+ modules support increased speeds of up to 10 Gbps; however, not all rival SFP+ modules are automatically compatible.
Cisco SFP Modules for Gigabit Ethernet Applications
Cisco Optical Gigabit Ethernet SFP

Cisco 1000BASE-T Copper SFP

Cisco 2-Channel 1000BASE-BX Optical SFP

Features and Benefits
-
Hot swappable to maximize uptime and simplify serviceability
-
Flexibility of media and interface choice on a port-by-port basis, so you can “pay as you populate”
-
Robust design for enhanced reliability
-
Supports digital optical monitoring (DOM) capability
1000BASE-T SFP for Copper Networks: The 1000BASE-T SFP operates on standard Category 5 unshielded twisted-pair copper cabling of link lengths up to 100 m (328 ft). Cisco 1000BASE-T SFP modules support 10/100/1000 auto negotiation and Auto MDI/MDIX.
1000BASE-SX SFP for Multimode Fiber Only: The 1000BASE-SX SFP, compatible with the IEEE 802.3z 1000BASE-SX standard, operates on legacy 50 μm multimode fiber links up to 550 m and on 62.5 μm Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI)-grade multimode fibers up to 220 m. It can support up to 1km over laser-optimized 50 μm multimode fiber cable.
1000BASE-LX/LH SFP for Both Multimode and Single-Mode Fibers: The 1000BASE-LX/LH SFP, compatible with the IEEE 802.3z 1000BASE-LX standard, operates on standard single-mode fiber-optic link spans of up to 10 km and up to 550 m on any multimode fibers. When used over legacy multimode fiber type, the transmitter should be coupled through a mode conditioning patch cable.
1000BASE-EX SFP for Long-Reach Single-Mode Fibers: The 1000BASE-EX SFP operates on standard single-mode fiber-optic link spans of up to 40 km in length. A 5-dB inline optical attenuator should be inserted between the fiber-optic cable and the receiving port on the SFP at each end of the link for back-to-back connectivity.
1000BASE-ZX SFP for Long-Reach Single-Mode Fibers: The 1000BASE-ZX SFP operates on standard single-mode fiber-optic link spans of up to approximately 70 km in length. The SFP provides an optical link budget of 21 dB, but the precise link span length depends on multiple factors such as fiber quality, number of splices, and connectors.
When shorter distances of single-mode fiber (SMF) are used, it might be necessary to insert an inline optical attenuator in the link to avoid overloading the receiver. A 10-dB inline optical attenuator should be inserted between the fiber-optic cable plant and the receiving port on the SFP at each end of the link whenever the fiber-optic cable span loss is less than 8 dB.
1000BASE-BX10-D and 1000BASE-BX10-U SFP for Single-Fiber Bidirectional Applications
The 1000BASE-BX-D and 1000BASE-BX-U SFPs, compatible with the IEEE 802.3ah 1000BASE-BX10-D and 1000BASE-BX10-U standards, operate on a single strand of standard SMF.
A 1000BASE-BX10-D device is always connected to a 1000BASE-BX10-U device with a single strand of standard SMF with an operating transmission range up to 10 km.
The communication over a single strand of fiber is achieved by separating the transmission wavelength of the two devices as depicted in Figure 2: 1000BASE-BX10-D transmits a 1490-nm channel and receives a 1310-nm signal, whereas 1000BASE-BX10-U transmits at a 1310-nm wavelength and receives a 1490-nm signal. As shown, the presence of a wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) splitter integrated into the SFP to split the 1310-nm and 1490-nm light paths.
Platforms Support
Table 1. The Cisco 1-Gbps SFPs are supported across a variety of Cisco networking equipment.
Info: Cisco SFP Modules for Gigabit Ethernet Applications Data Sheet
More Related…
What are the Cisco 100G CPAK, QSFP-100G, CFP2, CXP and CFP Modules?
The Types Comparison of SFP and QSFP
Features and Benefits of Cisco 25G, QSFP and QSFP28 Modules
Certain Supported GBICs/SFPs Optical Transceiver Modules on Catalyst 3850 Switch
Cisco Optics Modules Pages: https://blog.router-switch.com/category/reviews/cisco-optics-modules/















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


