Types of Computer Networks – GeeksforGeeks
A computer network is a cluster of computers over a shared communication path that works for the purpose of sharing resources from one computer to another, provided by or located on the network nodes.
Some of the uses of computer networks are the following:
- Communicating using email, video, instant messaging, etc.
- Sharing devices such as printers, scanners, etc.
- Sharing files
- Sharing software and operating programs on remote systems
- Allowing network users to easily access and maintain information
Types of Computer Networks
- Personal Area Network (PAN)
- Local Area Network (LAN)
- Wide Area Network (WAN)
- Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
- Campus Area Network (CAN)
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
- Storage Area Network (SAN)
- System-Area Network (SAN)
- Passive Optical Local Area Network (POLAN)
- Enterprise Private Network (EPN)
- Virtual Private Network (VPN)
- Home Area Network (HAN)
These are explained as following below.
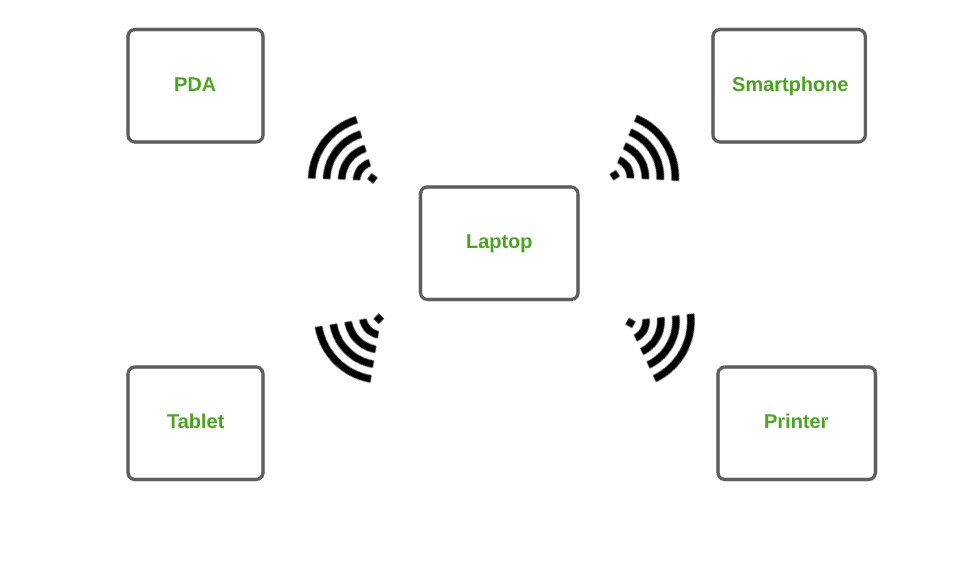
1. Personal Area Network (PAN) :
PAN is the most basic type of computer network. This network is restrained to a single person, that is, communication between the computer devices is centered only to an individual’s work space. PAN offers a network range of 10 meters from a person to the device providing communication.
Examples of PAN are USB, computer, phone, tablet, printer, PDA, etc.
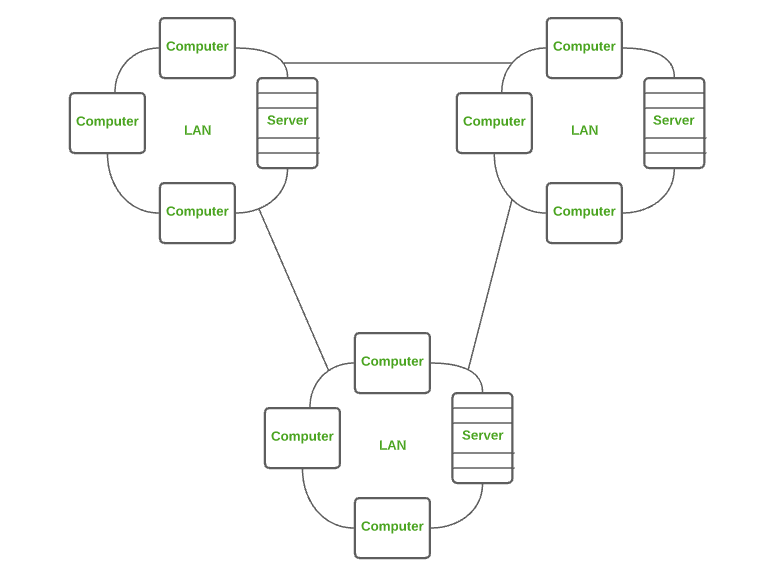
2. Local Area Network (LAN) :
LAN is the most frequently used network. A LAN is a computer network that connects computers together through a common communication path, contained within a limited area, that is, locally. A LAN encompasses two or more computers connected over a server. The two important technologies involved in this network are Ethernet and Wi-fi.
Examples of LAN are networking in a home, school, library, laboratory, college, office, etc.

3. Wide Area Network (WAN) :
WAN is a type of computer network that connects computers over a large geographical distance through a shared communication path. It is not restrained to a single location but extends over many locations. WAN can also be defined as a group of local area networks that communicate with each other.
The most common example of WAN is the Internet.
4. Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) :
WLAN is a type of computer network that acts as a local area network but makes use of wireless network technology like Wi-Fi. This network doesn’t allow devices to communicate over physical cables like in LAN but allows devices to communicate wirelessly.
The most common example of WLAN is Wi-Fi.

5. Campus Area Network (CAN) :
CAN is bigger than a LAN but smaller than a MAN. This is a type of computer network which is usually used in places like a school or college. This network covers a limited geographical area that is, it spreads across several buildings within the campus.
Examples of CAN are networks that cover schools, colleges, buildings, etc.

6. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) :
A MAN is larger than a LAN but smaller than a WAN. This is the type of computer network that connects computers over a geographical distance through a shared communication path over a city, town or metropolitan area.
Examples of MAN are networking in towns, cities, a single large city, large area within multiple buildings, etc.

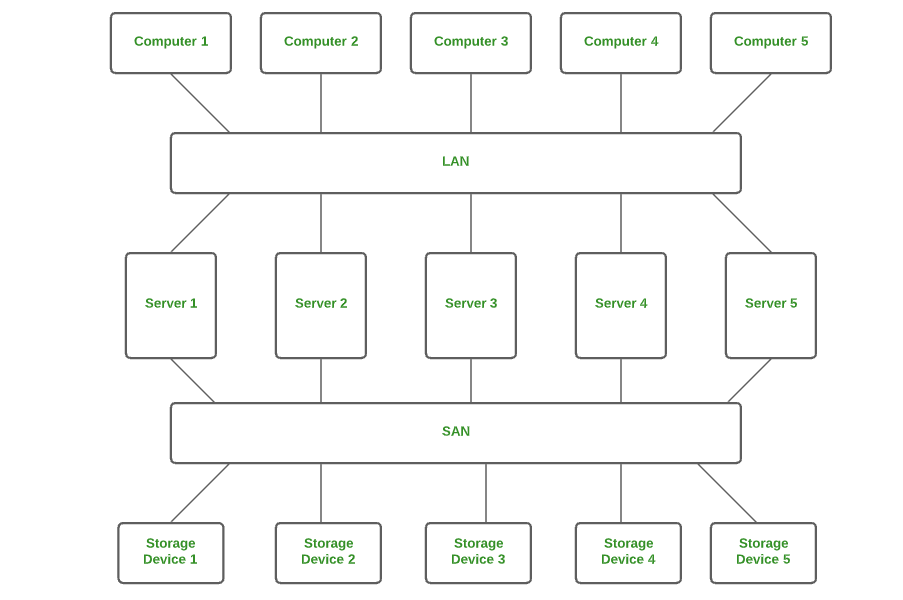
7. Storage Area Network (SAN) :
SAN is a type of computer network that is high speed and connects groups of storage devices to several servers. This network does not depend on LAN or WAN.. Instead, a SAN moves the storage resources from the network to its own high-powered network. A SAN provides access to block-level data storage.
Examples of SAN are a network of disks accessed by a network of servers.
8. System Area Network (SAN) :
A SAN is a type of computer network that connects a cluster of high-performance computers. It is a connection-oriented and high bandwidth network. A SAN is a type of LAN that handles high amounts of information in large requests. This network is useful for processing applications that require high network performance.
Microsoft SQL Server 2005 uses SAN through virtual interface adapter.

9. Passive Optical Local Area Network (POLAN) :
A POLAN is a type of computer network which is an alternative to a LAN. POLAN uses optical splitters to split an optical signal from a single strand of single mode optical fibre to multiple signals to distribute users and devices. In short, POLAN is a point to multipoint LAN architecture.

10. Enterprise Private Network (EPN) :
EPN is a type of computer network mostly used by businesses that want a secure connection over various locations to share computer resources.

11. Virtual Private Network (VPN) :
A VPN is a type of computer network that extends a private network across the internet and lets the user send and receive data as if they were connected to a private network even though they are not. Through a virtual point-to-point connection users can access a private network remotely. VPN protects you from malicious sources by operating as a medium that gives you a protected network connection.

12. Home Area Network (HAN) :
Many of the houses might have more than a computer. To interconnect those computers and with other peripheral devices, a network should be established similar to the local area network (LAN) within that home. Such a type of network that allows a user to interconnect multiple computers and other digital devices within the home is referred to as Home Area Network (HAN). HAN encourages sharing of resources, files, and programs within the network. It supports both wired and wireless communication.
My Personal Notes
arrow_drop_up
















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


