Types of Computer Network
Computer Network Types:
A computer “Network Types” is a collection of computers that are linked together so that one computer can communicate with another and share resources, data, and applications.
The size of a computer network can be classified. There are four primary types of computer networks:




- LAN(Local Area Network)
- PAN(Personal Area Network)
- MAN(Metropolitan Area Network)
- WAN(Wide Area Network)
LAN (Local Area Network):
- A local area network (LAN) is a collection of computers connected in a small area, such as a building or an office.
- A local area network (LAN) connects two or more computers using a communication means such as twisted pair or coaxial cable.
- It is less expensive since it is made up of low-cost components such as hubs, network adapters, and ethernet cables.


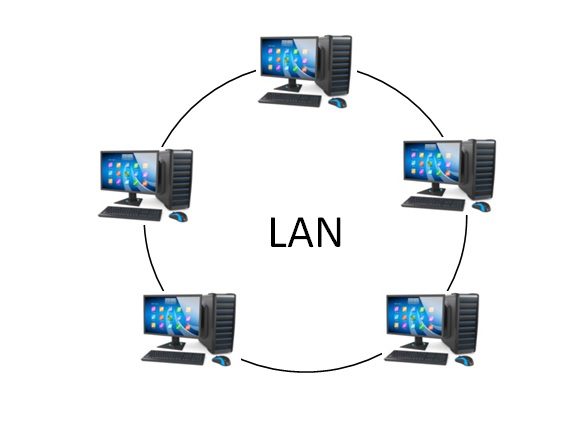

- In a Local Area Network, data is exchanged at an exceedingly fast rate.
- A higher level of security is provided by a Local Area Network.
PAN (Personal Area Network):
- A Personal Area Network (PAN) is a network that is set up within a single person and normally has a range of 10 metres.
- The term “Personal Area Network” refers to a network that is used to connect personal computing devices.
- The Personal Area Network was first proposed by Thomas Zimmerman, a research scientist.
- The Personal Area Network (PAN) covers a 30 foot radius.
- Laptops, mobile phones, media players, and play stations are examples of personal computing devices that are utilised to form a personal area network.


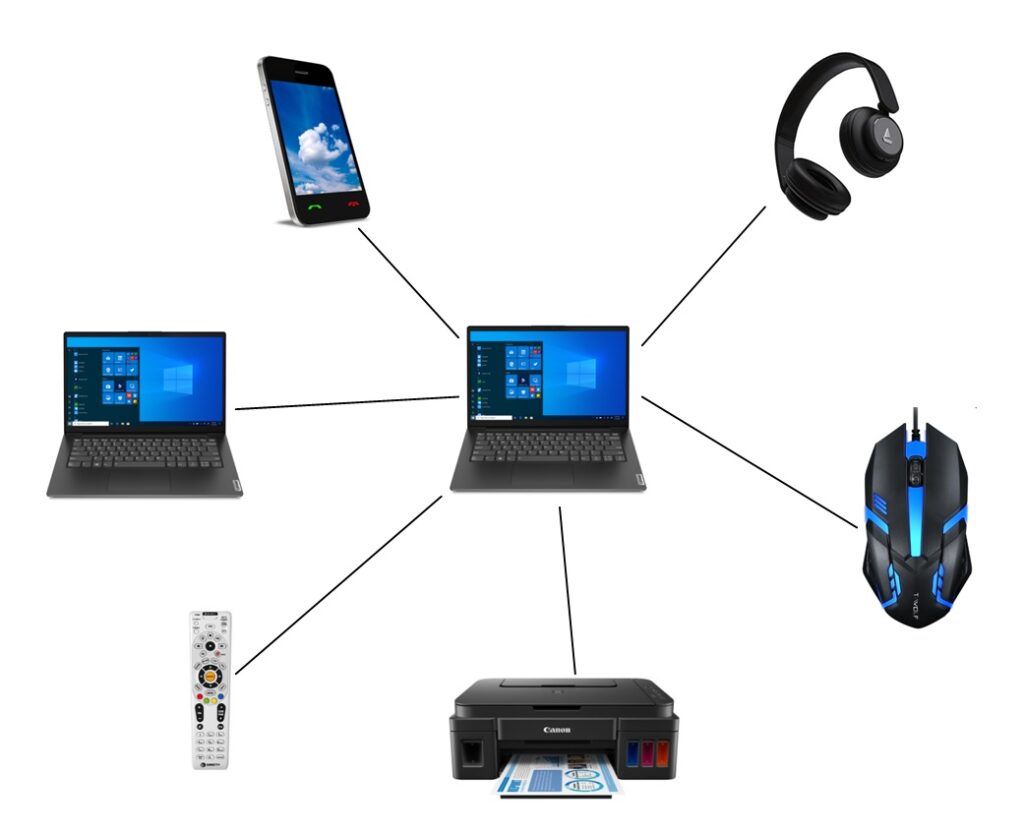

Personal Area Network Types are divided into two categories:
- Wireless Personal Area Network
- Wired Personal Area Network.
Wireless Personal Area Network :
Wireless Personal Area Network is a wireless personal area network that is created utilising wireless technologies such as WiFi and Bluetooth. It’s a network with a short range.
Wired Personal Area Network:
A USB is used to construct a wired personal area network.
Personal Area Network (PAN) Examples:
Following are the some examples of PAN.
Body Area Network:
A network that travels with a person is known as a body area network. A mobile network, for example, follows a person. Assume a person establishes a network connection and then establishes a connection with another device in order to transfer data.
Offline Network:
An offline network, often known as a home network, can be constructed within the home. The purpose of a home network is to connect devices such as printers, computers, and televisions that are not connected to the internet.
Small Home Office:
It connects a variety of devices to the internet and to a corporate network via a virtual private network (VPN).
MAN (Metropolitan Area Network):
- A metropolitan area network (MAN) is a network that connects multiple LANs to form a larger network that covers a greater geographic area.
- MAN is used by government organisations to engage with citizens and private businesses.
- MAN connects many LANs using a telephone exchange line.
- RS-232, Frame Relay, ATM, ISDN, OC-3, ADSL, and other protocols are commonly used in MAN.
- Its range is greater than that of a Local Area Network (LAN).




Metropolitan Area Network Applications:
- The Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) is used to communicate amongst banks in a city.
- It can be used to make a reservation for a flight.
- It can be used in a city-based college.
- It can also be used for military communication.
WAN (Wide Area Network):
- A wide area network (WAN) is a network that spans a vast geographic area, such as many states or countries.
- A Wide Area Network (WAN) is a much larger network than a local area network (LAN).
- A Wide Area Network (WAN) is a network that connects multiple locations over a vast geographical area via a telephone line, fiber optic cable, or satellite connectivity.
- The internet is one of the world’s largest WANs.
- In the fields of business, government, and education, a wide area network is commonly employed.


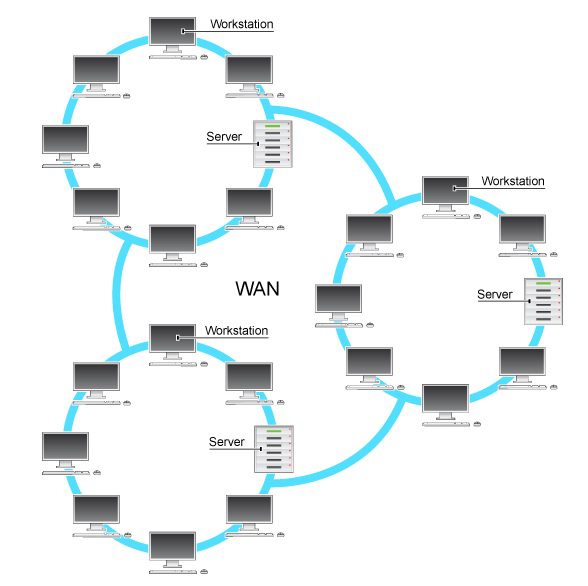

Wide-Area Network (WAN) Examples:
- Mobile Broadband: In an area or country, a 4G network is commonly used.
- Last mile: A telecom provider connects customers’ homes with fibre to deliver internet services to clients in hundreds of cities.
- Private Network: A bank creates a private network that links the 44 offices together. The telecom company’s telephone leased line is used to create this network.
Benefits of a Wide Area Network:
The following are some of the benefits of a wide area network:
- Geographical coverage: A Wide Area Network covers a broad area. If our office has a branch in a distant city, we can use WAN to communicate with them. We can link to another branch over the internet, which provides a leased line.
- Centralized data:Data is centralised in the case of a wide-area network (WAN). As a result, we won’t have to spend money on email, files, or backup servers.
- Get updated files: To obtain updated files, go to: On the live server, software companies work. As a result, the programmers receive the updated files in a matter of seconds.
- Exchange messages: Messages are sent quickly across a WAN network. You can contact with pals via web applications such as Facebook, Whatsapp, and Skype.
- Software and resource sharing: In a WAN network, we can share software as well as other resources such as a hard drive and RAM.
- Business on a global scale: We may do business on a worldwide scale via the internet.
- High bandwidth: If we use leased lines for our business, we will have a lot of bandwidth. The increased data transmission rate boosts our company’s production as a result of the increased bandwidth.
Wide Area Network Disadvantages:
The following are some of the Wide Area Network’s drawbacks:
- Security issue: A WAN network has more security difficulties than a LAN or MAN network since all of the technologies are merged, resulting in a security challenge.
- Needs Firewall & antivirus software: Firewall and antivirus software are required because data is transported via the internet, which can be altered or hacked by hackers, necessitating the installation of a firewall. Because some people can implant viruses into our systems, antivirus software is required to protect us.
- Expensive Setup Costs: The cost of setting up a WAN network is high because it requires the purchase of routers and switches.
- Troubleshooting issues: Because it spans such a broad area, resolving the issue is tough.
Inter network:
- Two or more computer network LANs, WANs, or computer network segments are connected using devices and set by a local addressing system to form an internetwork. The term “internetworking” refers to this technique.
- The term “internetworking” refers to the interconnection of public, private, commercial, industrial, or government computer networks.
- The internet protocol is used in internetworking.
- Open System Interconnection is the internetworking reference model (OSI).
Inter Network Types:
Inter Network Types are as below.
- Extranet: An extranet is a communication network that uses internet protocols such as Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol to communicate. It is used to share information. Users with login credentials are the only ones who can access the extranet. The lowest level of internetworking is an extranet. It can be classified as a MAN, a WAN, or another type of computer network. An extranet cannot have a single LAN, but it must have at least one external network connection.
- Intranet: An intranet is a private network that uses internet protocols such as Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol to communicate. An intranet is a website that belongs to a company and is only accessible by the company’s employees or members. The intranet’s primary goal is to allow employees of the company to share information and resources. The ability to operate in groups and hold teleconferences is provided by an intranet.
Intranet Network benefits :
- Communication: It allows for inexpensive and simple communication. An organization’s employee can communicate with another employee via email or chat.
- Time-saving: Because intranet information is communicated in real time, it saves time.
- Collaboration: One of the most significant advantages of the intranet is collaboration. The information is disseminated among the organization’s personnel and only the authorised user has access to it.
- Platform independence: The computer can be connected to another device with a different architecture, making it a neutral architecture.
- Cost-effective: People can see data and documents using a browser, and duplicate copies are distributed via the intranet. As a result, the cost is reduced.
Read Also
OSI layer Model
Point to point Netwok topology















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


