Types of Batteries and Cells and Their Applications – Electrical Technology
Different Types Of Batteries and Cells & Their
Applications
Long back ago, the only way of making portable energy was either steam or fuel. After the invention of the battery, life has become easier than ever. Nowadays, everyone is looking for portable machines to ease their day to day tasks. In that case, batteries are capable of fulfilling the need of producing energy on the go.
No doubt batteries look pretty small and dull but they are surely capable of turning your small little cylinder into your own micro-power plant. The idea of generating portable power is nothing new and even prehistoric human used to produce that using woods and fuels. It is just that batteries are the instant way of power source. You can just hit a button and get the darkroom lighten up in a second or even less than that.
There are several kinds of batteries present in the market. All such batteries work on the same principle of converting chemical energy into electrical energy. Here in this article, we are going to discuss everything you need to know about the different types of batteries, their working and usage.
Before starting with the working and types of the battery, just have a look over the history of the batteries. Where they came from? And By whom they are discovered.

History of Batteries
In 1800, Volta discovered that certain fluid can generate continuous electric power when used as a conductor. This discovery lead to the first voltaic cell called battery. Volta’s invention of battery started a new era of battery experimentation. And, number of scientist tried various experiments to make batteries. But few of them was able to reach to a conclusion. Volta and Daniel were two scientist made cells known as Voltaic and Daniel respectively.
Voltaic Cell: A voltaic cell uses chemical reaction to produce electrical energy. One anode and cathode are made opposite to each other. At anode, oxidation occurs and reduction occurs at cathode. A salt bridge is created in between to complete the circuit. The parts where oxidation and reduction occur are called half cells. An external circuit is used to conduct the flow of electrons.
The voltaic cell invented by Volta was not that much portable and had too many disadvantages as well. After that, Daniel’s cell designed by “John Fredric Daniel” become popular.
Daniel Cell: After the invention of voltaic cell, Daniel cell was popular in earlier centuries as source of electricity. In this cell type, a container divided into two compartments. The gap was made by a membrane permeable to ions. In one of the components, Zinc electrolyte was dipped in a Zinc sulfate solution. In the other compartment, a copper electrode in a copper sulfate solution was dipped. The cell was capable of delivering current until it runs out of Zinc or Copper sulfate.
John Dancer carried forward this experiment and designed the first battery with porous design.
In 1859, the lead acid battery designed by Gaston Plante became popular due to the rechargeable feature of the battery. The simple design of the battery allowed recharging by reversing the flow of current back to the battery. This battery is still used in many places like car batteries, motor vehicles etc.
Further, Leclanche battery was invented by Carl Gessner as dry design which didn’t have any liquid electrolyte.
Let’s have a look at Leclanche cell.

This invention made the use of battery very easy and convenient as the spilling and orientation problem was totally eradicated. Again nickel-cadmium battery was invented which was commonly known as alkaline battery. In 1970’s century most of the lithium batteries were invented to be used in portable devices.
General Chemistry of Battery:
A battery have three layers the cathode, anode and a separator. The negative layer of the battery is called as anode and the positive layer is called as cathode. When a load is attached with the battery the current starts flowing through the anode to cathode. Similarly, when we connect the battery charger the current starts flowing into the opposite direction i.e. cathode to anode.
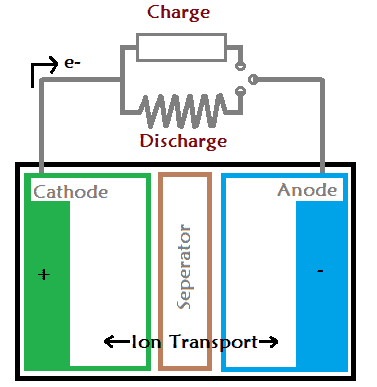
Every battery work on a chemical reaction called oxidation-reduction reaction. The reaction take place in between the cathode and the anode via the separator (electrolyte).
In result, one electrode gets negatively charged due to oxidation reaction. And, that negatively charged electrode is called as cathode. The second electrode gets positively charged due to reduction reaction, which is further called as anode. When two different kind of metals are immersed in the same electrolyte solution, one of the electrode will gain electron and other will lose electron.
In result, one of the metals will lose electron and the other metal will gain electron. This difference in electron concentration of two metals cause an electrical potential difference between the metals. This potential difference can be used as source of voltage in any electrical device.
The ions flows through the separator only, it blocks all the movement from anode to cathode. Hence, the only way to get the current out is from the terminals of the battery.
Let’s see how the batteries are categorized…
Different Types of Batteries
Batteries are commonly used in household devices as well as for industrial applications. Each battery is designed to fulfill a specified purpose and can be used according to the requirement. There are mainly two categories of battery called primary and secondary cells. However, batteries are classified into four broad categories namely primary cell, secondary cell, fuel cell and reserve cell. Below are the everything you need to know about the different types of batteries and their working.
-
Primary Cell
-
Secondary Cell
-
Reserve Cell
-
Fuel Cell
Primary Cell (Non-rechargeable Batteries)
Non-rechargeable batteries also known as primary batteries or primary cell. Primary batteries are those which cannot be used again once their stored energy is being used fully. These batteries cannot restore energy by any external source. This is the reason primary cells are also called disposable batteries.

A major factor reducing the lifetime of primary batteries is that they become polarized during use. To extend the battery life by reducing the effect of polarization, chemical depolarization is used i.e. oxidizing the hydrogen to water by adding an oxidizing agent to the cell. Like as, in zinc-carbon cell and Leclanche cell Manganese dioxide is used, and in Bunsen cell and Grove cell nitric acid is used.
Related Post: How to test a battery with Test meter?
Applications of Primary Cells:
-
They can be used in clock and toys
-
It can be used in small household devices
-
It can be used in personal computers
-
It can be used in portable emergency lights and inverters
The non-rechargeable batteries are many types. They are given below
-
Zinc-Carbon Battery (aka. ‘Heavy Duty’)
-
Alkaline
-
Lithium Cells
-
Silver Oxide Cells
-
Zinc Air Cells
Related Post: Types Of Capacitors | Fixed, Variable, Polar & Non-Polar
-
Zinc-Carbon Battery
Zinc-carbon batteries are first commercial dry batteries which provide very low power and are also known as dry cell. A carbon rod is placed in the battery, which collects the current from the manganese dioxide electrode. It can give a 1.5Volts of DC supply. These types of batteries are used in Flashlight, radios, remote controls, and wall clocks.
-
Alkaline
Alkaline is also a dry cell battery, it consists of zinc anode and manganese dioxide cathode. The alkaline battery is packed with steel can and the outermost inner region is filled with manganese dioxide. Zinc and the potassium hydroxide electrolyte is filled in the center most region of the battery. Alkaline batteries have higher density then the other batteries. Generally, it is used in Audio players, radios and the torch lights.

-
Lithium Cells
Lithium cell batteries are comes in coin or button type design form. It provider higher voltage (3V) value than the zinc, alkaline and manganese batteries. Lithium cells are smaller in size and lighter in weight. The internal resistance of lithium cells are high and they are not rechargeable. The most popular coin cell used in number of electronics application is CR2032 which provides 3V output. Lithium cells have longer life span (around 10 years).
-
Silver Oxide Cells:
Silver oxide batteries are low power batteries with high capacity. They are similar in appearance to mercury cells and provides a higher emf of 1.5 volt. The cathode of the battery is made up of silver oxide. The electrolyte present inside the battery is made of potassium or sodium hydroxide. As silver is expensive, this battery has very limited applications.
The excellent features of silver oxide cells are:
-
The unique sealing of the battery structure makes the battery highly leak-proof.
-
Constant voltage output given by the battery makes it useful to get stable discharge
-
The use of antioxidants contributes to the high energy density of the battery.
Applications of silver oxide cells:
- IOT based devices
-
Electric watches
-
Precision instruments
-
Medical devices
-
Zinc Air Cells
A zinc air battery reaches full operating voltages within 5 mins right after un-sealing. These are primary batteries with rechargeable designs. The oxygen content in the air acts as the active mass of the battery. The cathode is a porous body made up of carbon with air access. The output voltage capability of the cell is 1.65 volts. While discharge, a mass of zinc particle forms a porous anode saturated with an electrolyte. The oxygen present in the air reacts with the hydroxyl ion and form zincate. This Zincate forms zinc oxide and water returns to the electrolyte.
Secondary Cell (Rechargeable Batteries)
Rechargeable batteries are also known as secondary cell. It can be use again and again by plugging them into charge and get multiple uses before the battery needs to be replaced. The initial cost of rechargeable batteries is commonly more than disposable batteries, but the total cost of ownership and environmental impact of these batteries are lower because they can be recharged inexpensively many times before they need to replace it.

Applications of Secondary Cells:
-
It can be used in fitness bands, smart watches.
-
It can be used in military and submarines
-
Cameras and artificial pacemakers
The rechargeable or secondary batteries are mainly of three types:
-
Lead Acid
-
Lithium Ion (Li-ion)
-
Nickel Metal Hydride (Ni-MH)
-
Nickel Cadmium (Ni-Cd)
Related Post: Battery Life Calculator
-
Lead Acid
Lead acid is a very common type of rechargeable battery. They are generally used to store energy from solar energy because their quality differ them from others. These batteries provides high current, and used in vehicle. When the battery stops working, it can be used for recycling. About 93% of all battery lead is reused for recycle to make new Lead-Acid batteries.
-
Lithium Ion (Li-ion)
Lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable batteries, also known as Li-ion battery. These batteries are commonly used in electronics as they have great power density. These batteries can store 150 watt-hours per kg. During discharge lithium ions move from the negative electrode to the positive electrode and vice versa. Overheating can cause battery damage or fire.
-
Nickel Metal Hydride (Ni-MH)
Nickel Metal Hydride batteries are rechargeable batteries. The metal of the battery is inter-metallic. These types of batteries have good life and high current capability. It can store 100 watt-hour per kg. They are more thermally stable than the lithium ion batteries. The self-discharge is higher than the other batteries.
Nickel Cadmium (Ni-Cd)
In Nicker-Cadmium rechargeable battery, Nickel Oxide Hydroxide and Metallic Cadmium are used as electrode. It is also known as NiCd battery or NiCad Battery. Ni-Cd batteries are good to maintain the voltage and hold electric charge when not in use. A major drawback of Ni-Cd battery which may cause lowing the future capacity of battery is that if a partially charge battery is recharged, it may fall a victim of “Dreaded Memory Effect” (i.e. changes in the negative or cadmium plate e.g charging involves converting CD(OH) to Cd metal.) and voltage depression.
Nickel Cadmium are good to deliver the rated capacity at full discharge rate and has good life cycle at low temperature rate operations.
Difference Between Primary and Secondary Cells:
Specifications:
Primary cells have high internal resistance, higher capacity and are smaller in designs. While secondary cells have low internal resistance, have reversible chemical reactions and are complex in design.
Design:
Primary cells are usually dry cells. That means, they don’t have fluid and are full of paste that allow the movement of ions inside the battery. This is the reason primary cells are spill-resistant. However, secondary cells are either made up of liquid or molten salt.
To give you a better comparison between the primary and secondary cells, their advantages and disadvantages, we have summed up the differences in the below given table:
Primary Cells
Secondary Cells
Suitable for portable applications due to light weight and smaller design
Not suitable for portable devices
Good charge retention
Inferior charge retention
Not suitable for high cost applications
Highly recommended for backup and high cost applications
Limited to specific applications
Highly versatile and therefore has large spectrum of applications
Low initial cost
Higher initial cost
After going through the above table, I hope you will now be able to figure out the pros and cons of the primary and secondary batteries.
Reserve cell
The reserve batteries or cell are also known as stand-by battery. The electrolyte remains inactive in solid state until the melting point is reached. As soon as the melting point is reached, ionic conduction begins and battery is activated.
Reserve cells are further classified into three categories:
-
Water Activated Batteries
-
Heat Activated Batteries
-
Electrolyte Activated Batteries
-
Gas Activated Batteries
Applications of Reserve Batteries:
-
It is used in devices used for sensing time and pressure
-
They are largely used in weapon systems
-
They are also used in car batteries and other vehicles
Related Post: What is the difference between a battery and a capacitor?
Fuel cell
In this class of batteries, active materials are fed from outside source. Fuel cells are capable of producing electrical energy as long as active materials are fed to the electrodes. The proton exchange membrane uses hydrogen and oxygen gas as fuel. The reaction takes place inside the cell and as the product of the reaction water, electricity and heat are produced. The four basic elements of the fuel cells are namely anode, cathode, electrolyte and catalyst.
Advantages of technology used behind the fuel cell:
-
The process of converting chemical potential energy directly into electrical energy avoids the “thermal bottleneck”.
-
Due to no moving parts in the cell, it is convenient and highly reliable
-
Due to the production of hydrogen in environment friendly manner, this is comparatively less harmful for environments as compared to others.
Applications of fuel cell
-
This is mainly used in transport like cars, buses and other motor vehicles.
-
This is very often used as backup to produce electricity in case of power failure.
Related Post: How to Wire Solar Panel to 12V battery and 12V,DC Load?
Advantage of Battery over other Power Sources
-
Specific Energy Capacity: The energy storage capacity of battery is very less as compared to fossil fuel. However, batteries have the capacity of delivering energy more effectively as compared to thermal engine.
-
Power bandwidth: Batteries are capable of handling small and large loads more effectively due to high power bandwidth.
-
Responsiveness: Batteries are able to deliver power over short-notice. This means that warm up is not required as in case of combustion engines.
-
Environment: The batteries are easy t use and stay reasonably cool. Most of the batteries don’t make noise as in case of other fuel-based engines.
-
Installation: Nowadays, the sealed batteries can be operated in almost any position. They are good shock and vibration tolerance.
Related Post: How to Wire Solar Panel to 220V inverter, 12V battery, and 12V,DC Load?
Drawbacks of Batteries
-
Charge Time: Once the batteries are primary batteries are discharged, it takes hours to get recharged again for use. This is not in case of using fuels which takes a few minutes.
-
Operation cost: Price and weight of large batteries make it impractical for the reliable usage and large vehicles.
-
Energy storage capacity: AS compared to fossil fuels, the energy storage capacity of batteries is low.
Related Post: How To Wire Two 24V Solar Panels in Parallel with Two 12V Batteries in Series
Choosing the Right Battery According to your Application?
It is quite important to choose the right battery for your application to avoid the damage of your device or application. Below are some of the considerations that should be kept in mind while choosing the right battery for your application.
Primary or secondary: This is the one of the most important factors in choosing the right battery type for your device. You can use the primary battery for occasional use and in disposable devices like toys etc. However, if you are using the device for long stretches of time then secondary or rechargeable batteries are more suitable.
Temperature range: Choosing a right battery with right temperature help you reduce the risk of thermal runaway. Lithium ion batteries can be charged within a narrow temperature range of 20 degree to 45 degree Celsius. Exploding of batteries may happens as a result of overcharging, high temperature charging or short circuit that eventually harm the device or application.
Durability: The durability of the battery largely depends on two factors namely charge life and total life. In addition, the physical factors of battery also contribute to the long life of battery.
Energy Density: The total amount of energy stored in the battery per unit volume is called as the energy density. It defines the stability of the battery that how long it run will till the next recharge
Safety: The battery you are choosing should be according to the operating temperature of it. Sometimes, the battery temperature exceeds and might damage components of the device. Also, if the device temperature exceeds the performance may get reduced.
The other factors include:
-
cell chemistry
-
transportation
-
physical shape and size
-
cost
-
reliability
Electrical vehicle (EV) battery
Electrical vehicle batteries are designed to provide power over a sustained period of time. The factors that makes them different from the other batteries is ignition and lightning. The electrical vehicle batteries are increasing their share in market due to reliability and environment friendly nature.
The most common batteries in modern car are lithium ion and lithium polymer battery. The cells are installed in forms of modules. In other words, one form of battery is installed to make a pack. Let us take an example of BMW electric car, in which a total of 96 cells are installed. The number of cells put into a frame that protect the batteries from external heat and vibration. A combination of cells is called as module.
A number of such modules, a cooling pack and battery management system is combined together to form a pack.
The two main types of Lithium ion batteries used in the electrical vehicles are:
-
Meta oxides
-
Phosphate
In automotive applications like vehicles, lithium-ion batteries are safer in terms of chemical hazard and convenience.
Construction of EV Batteries
Currently, the electric cars are running on lithium batteries. The normal voltage of a lithium cell is 3.7 volt, but an EV (electrical vehicle) requires 300V. For achieving this voltage and current value lithium cells are combined into series and parallel. The combination of such lithium cells is known as module. The modules comes with a BMS (Battery management system) for their protection. Below is the picture of Nissan Leaf, showing the lithium cell modules created to achieve the required voltage.

Important Instruction to use Electrical Vehicle Batteries
-
Don’t let the battery to reach below the cut-off voltage, which is also called as over discharging.
-
The maximum efficiency can be achieved only when the current ratings are lower.
-
The EV batteries comes in KWH (Kilo watt Hour) rating, which defines that how long the battery vehicle will run.
-
There is always a self-discharge rate of the batteries.
-
BMS (Battery Management System) helps you to find the amount of charge remaining in to the battery.
Related Posts:
URL Copied















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


