Strategies for Reading Comprehension :: Read Naturally, Inc.
Mục Lục
Comprehension: The Goal of Reading
Comprehension, or extracting meaning from what you read, is the ultimate goal of reading. Experienced readers take this for granted and may not appreciate the reading comprehension skills required. The process of comprehension is both interactive and strategic. Rather than passively reading text, readers must analyze it, internalize it and make it their own.
In order to read with comprehension, developing readers must be able to read with some proficiency and then receive explicit instruction in reading comprehension strategies (Tierney, 1982).
 Strategies for reading comprehension in Read Naturally programs
Strategies for reading comprehension in Read Naturally programs
 General Strategies for Reading Comprehension
General Strategies for Reading Comprehension
The process of comprehending text begins before children can read, when someone reads a picture book to them. They listen to the words, see the pictures in the book, and may start to associate the words on the page with the words they are hearing and the ideas they represent.
In order to learn comprehension strategies, students need modeling, practice, and feedback. The key comprehension strategies are described below.
Using Prior Knowledge/Previewing
When students preview text, they tap into what they already know that will help them to understand the text they are about to read. This provides a framework for any new information they read.
Predicting
When students make predictions about the text they are about to read, it sets up expectations based on their prior knowledge about similar topics. As they read, they may mentally revise their prediction as they gain more information.
Identifying the Main Idea and Summarization
Identifying the main idea and summarizing requires that students determine what is important and then put it in their own words. Implicit in this process is trying to understand the author’s purpose in writing the text.
Questioning
Asking and answering questions about text is another strategy that helps students focus on the meaning of text. Teachers can help by modeling both the process of asking good questions and strategies for finding the answers in the text.
Making Inferences
In order to make inferences about something that is not explicitly stated in the text, students must learn to draw on prior knowledge and recognize clues in the text itself.
Visualizing
Studies have shown that students who visualize while reading have better recall than those who do not (Pressley, 1977). Readers can take advantage of illustrations that are embedded in the text or create their own mental images or drawings when reading text without illustrations.
Strategies for Reading Comprehension: Narrative Text
Narrative text tells a story, either a true story or a fictional story. There are a number of strategies that will help students understand narrative text.
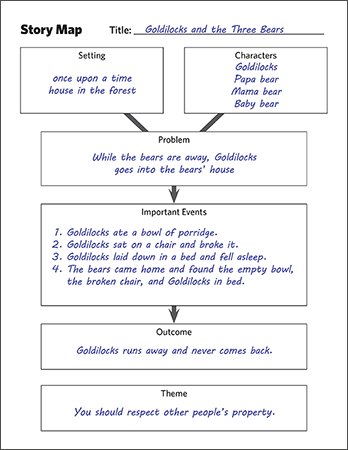 Story Maps
Story Maps
Teachers can have students diagram the story grammar of the text to raise their awareness of the elements the author uses to construct the story. Story grammar includes:
- Setting: When and where the story takes place (which can change over the course of the story).
- Characters: The people or animals in the story, including the protagonist (main character), whose motivations and actions drive the story.
- Plot: The story line, which typically includes one or more problems or conflicts that the protagonist must address and ultimately resolve.
- Theme: The overriding lesson or main idea that the author wants readers to glean from the story. It could be explicitly stated as in Aesop’s Fables or inferred by the reader (more common).
 Printable story map (blank)
Printable story map (blank)
Retelling
Asking students to retell a story in their own words forces them to analyze the content to determine what is important. Teachers can encourage students to go beyond literally recounting the story to drawing their own conclusions about it.
Prediction
Teachers can ask readers to make a prediction about a story based on the title and any other clues that are available, such as illustrations. Teachers can later ask students to find text that supports or contradicts their predictions.
Answering Comprehension Questions
Asking students different types of questions requires that they find the answers in different ways, for example, by finding literal answers in the text itself or by drawing on prior knowledge and then inferring answers based on clues in the text.
Strategies for Reading Comprehension: Expository Text
Expository text explains facts and concepts in order to inform, persuade, or explain.
The Structure of Expository Text
Expository text is typically structured with visual cues such as headings and subheadings that provide clear cues as to the structure of the information. The first sentence in a paragraph is also typically a topic sentence that clearly states what the paragraph is about.
Expository text also often uses one of five common text structures as an organizing principle:
- Cause and effect
- Problem and solution
- Compare and contrast
- Description
- Time order (sequence of events, actions, or steps)
Teaching these structures can help students recognize relationships between ideas and the overall intent of the text.
Main Idea/Summarization
A summary briefly captures the main idea of the text and the key details that support the main idea. Students must understand the text in order to write a good summary that is more than a repetition of the text itself.
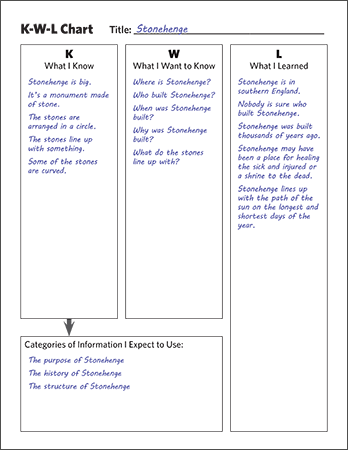 K-W-L
K-W-L
There are three steps in the K-W-L process (Ogle, 1986):
- What I Know: Before students read the text, ask them as a group to identify what they already know about the topic. Students write this list in the “K” column of their K-W-L forms.
- What I Want to Know: Ask students to write questions about what they want to learn from reading the text in the “W” column of their K-W-L forms. For example, students may wonder if some of the “facts” offered in the “K” column are true.
- What I Learned: As they read the text, students should look for answers to the questions listed in the “W” column and write their answers in the “L” column along with anything else they learn.
After all of the students have read the text, the teacher leads a discussion of the questions and answers.
 Printable K-W-L chart (blank)
Printable K-W-L chart (blank)
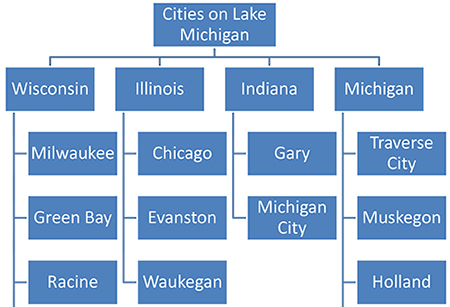
Graphic Organizers
Graphic organizers provide visual representations of the concepts in expository text. Representing ideas and relationships graphically can help students understand and remember them. Examples of graphic organizers are:
Tree diagrams that represent categories and hierarchies
Tables that compare and contrast data
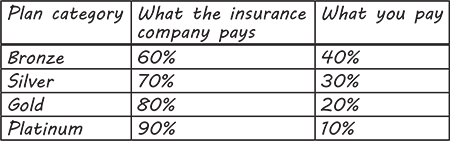
Time-driven diagrams that represent the order of events
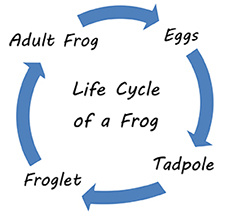
Flowcharts that represent the steps of a process
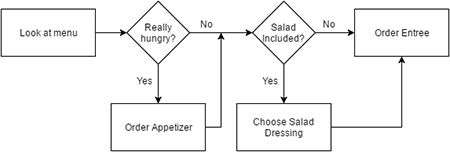
Teaching students how to develop and construct graphic organizers will require some modeling, guidance, and feedback. Teachers should demonstrate the process with examples first before students practice doing it on their own with teacher guidance and eventually work independently.
Strategies for Reading Comprehension in Read Naturally Programs
Several Read Naturally programs include strategies that support comprehension:
Bibliography
Honig, B., L. Diamond, and L. Gutlohn. (2013). Teaching reading sourcebook, 2nd ed. Novato, CA: Arena Press.
Ogle, D. M. (1986). K-W-L: A teaching model that develops active reading of expository text. The Reading Teacher 38(6), pp. 564–570.
Pressley, M. (1977). Imagery and children’s learning: Putting the picture in developmental perspective. Review of Educational Research 47, pp. 586–622.
Tierney, R. J. (1982). Essential considerations for developing basic reading comprehension skills. School Psychology Review 11(3), pp. 299–305.















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


