Splunk Architecture & Splunk Architecture Components
Mục Lục
What is Splunk?
Splunk is a well-developed and advanced software tool designed for organizations to perform indexing and searching log files stored in a system. It analyzes machine-generated data in real-time. It also searches, monitors, and examines machine-generated data via a web-style interface. Apart from examining machine-generated data it also captures, indexes, and correlates the real-time data in a searchable container from where they are produced in the form of graphs, reports, alerts, dashboards, and visualizations for diagnosis and provides various solutions to the business problems.
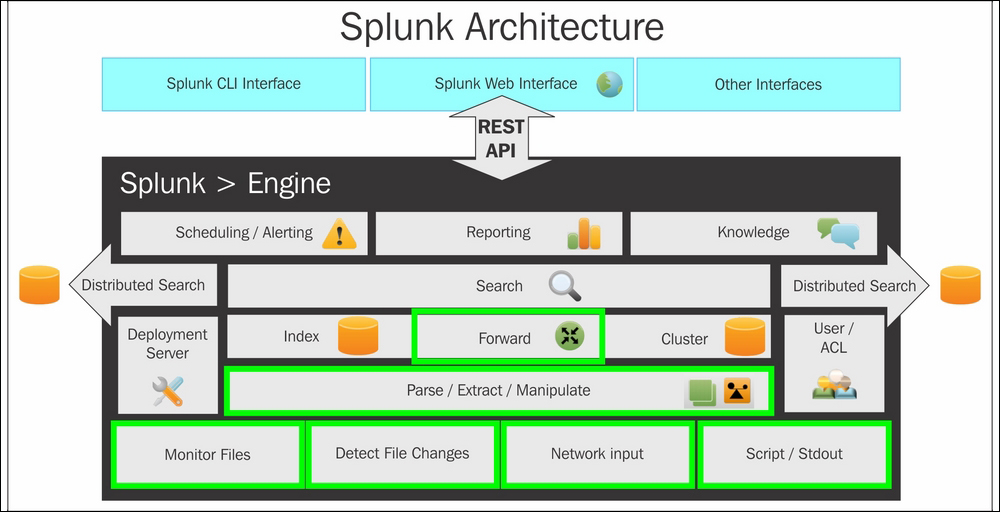
Splunk Architecture
Let’s look into the architecture of Splunk and how it works to retrieve the desired data output out of complex data.
The pictorial representation of the Splunk architecture is as follows:
First of all, let’s understand the terms used in this pictorial representation architecture of Splunk:
- Universal Forwarder (UF): Splunk Universal Forwarder is considered a lightweight component that helps in pushing data to the heavy Splunk forwarder. Here, the task of the component is to forward the log data from the server. The universal forwarder can also be installed on the client-side or application side.
- Load Balancer (LB): The main task of the load balancers is to distribute the workloads over the network or the application traffic over a cluster of servers.
- Heavy Forwarder (HF): Splunk Heavy Forwarder is acknowledged as a heavy component. It mainly filters the data that is collecting only error logs.
- Indexer: The indexer stores and indexes the filtered data. It also improves Splunk’s performance and automatically implements indexing.
- Search Head (SH): It helps in distributing the searches to the other indexers, and is also used to achieve intelligence and perform reporting.
- Deployment Server (DS): In the deployment server sharing of data is performed between the components. The deployment of the configurations like the update of the UF configuration file plays a main role in the deployment server in Splunk.
- License Master (LM): A license slave is controlled by a License Master. It is based on quality and usage.
Do you want to become a certified Splunk Professional? Join in the “Splunk Certification Training” Course. This training will help you to achieve excellence in this domain & help you to get a high-paying job in the Cyber Security field.
Splunk Workflow
Versions of Splunk
Versions of Splunk consist of 3 parts that are:-
- Splunk Enterprise: Splunk enterprise components are the paid version with unlimited access to the IT businesses. Its architecture supports single and multi-site clustering for disaster recovery. Splunk Enterprise also gathers and analyzes the data from websites, applications, etc.
- Splunk Cloud: Splunk Cloud is the hosted platform provided as a service with subscription pricing. The features included in this package are similar to the Splunk enterprise version. In the architecture, clustering is managed by Splunk.
- Splunk Light: Splunk light is the free version with up to 500MB indexing per day. In this version, the features and functionalities are limited as compared to other versions. The architecture supports only a single instance.
Stages In Data Pipeline
It consists of 3 data stages in Splunk Architecture, that is:-
- Data Input Stage: Here in this stage, Splunk software absorbs the raw data stream from the source and breaks it into 64K blocks. The blocks are added to metadata keys that include hostname, source, character encoding, source type, and index of the data.
- Data Storage Stage: Data storage stage consists of 2 different phases:-
- Parsing – Since the Splunk software extracts the relevant data after examining, analyzing, and transforming the data, so this stage is also known as event processing. In this stage, the data stream is broken into individual events. Also, there are some sun phases in the storage phase like:
- The stream of data is broken into individual lines.
- Adding individual events with metadata from the source-wide keys.
- Identifying and parsing timestamp
- Transforms the event data and metadata as per regex rules.
- Indexing – Here the software writes the parsed events to the index queue. The main advantage of this phase is that the data can be accessed easily during the search.
- Data Searching Stage: In the search stage, the user accesses, uses, and views the event data. As part of the search, the software stores user-defined knowledge data/objects like reports, dashboards, alerts, field extractions, etc.
Real-Time Splunk Administration & Architecture Training with 75 days of real-time lab access
Splunk Components
Let’s discuss the components of Splunk in the Splunk Architecture:
- Splunk Forwarder: Splunk Forwarder is an agent deployed on IT systems, collecting logs and sending them to the indexer. Also, it is used to gather real-time data and help users to analyze real-time data. It is scalable as well as consumes less processing power compared to other monitoring tools. There are 2 categories in Splunk forwarders that is a) Universal Forwarder b) Heavy Forwarder
- Splunk Indexer: Splunk indexer is a component used for indexing and storing data coming from the heavy forwarder. After transforming the data into events and storing it into a disk for performing search operations efficiently, Splunk indexes the data and creates some files separating them into directories called buckets. those files consist of:
- A compressed form of raw data
- Indexes point to raw data that is TSIDX files or index files.
- Some metadata files
Incoming data is processed to enable fast search and analysis. This process is also known as event processing. Data replication is another advantage to Splunk Indexer.
- Splunk Head: A search head is for interaction with Splunk. Users perform various operations on the user interface provided to them. By entering search words you can search and query the data stored in the indexer and get the expected results. Splunk instance functions both as search head as well as search peer. Search heads performing searching and not indexing are commonly known as dedicated search heads. Whereas, indexing and responding are done by search peer to search requests from other search heads.
Different Types of Splunk Forwarders
There are 2 different types of Splunk forwarders in Splunk Architecture:
- Splunk Universal Forwarder – It is used to forward the raw data collected at the source. The component performs minimum processing on incoming data streams before forwarding them to an indexer, a lot of unnecessary data is also forwarded which causes performance overheads.
- Splunk Heavy Forwarder – Splunk heavy forwarder is used for reducing the problems, as one level of data processing takes place on the source itself before forwarding data to the indexer. It routes the data to the Indexer saving bandwidth and storage. Hence, the main role of the heavy forwarders is to parse the data at the source.
Read our next blog The complete guide of the Importance Role of the Cyber Kill Chain in Cyber Security
Why Should you learn Splunk for your career growth?
With the advancement of technology there comes a lot of responsibility for security maintenance. So, job opportunities for maintaining the security of the organization are growing day by day. With all the job opportunities down the line in cybersecurity, there is an important career in Splunk made by many individuals. The demand for Splunk is increasing in the market for companies in Information Technology. The companies like TCS, IBM, Accenture, Capgemini, HP, Sony, etc have a lot of opportunities.
The daily work of Splunk Engineers is mainly balanced, neither stressed nor relaxed, but is competitive and collaborative. The industry sectors like finance and insurance, information technology, retail, trade, etc are now giving tremendous opportunities to build your career in cybersecurity.
Here is a graph showing how the demand for Splunk jobs has grown since 2012:
The job profiles for Splunk career are:
- Systems Engineer
- Splunk Administrator
- Splunk Architect
- Splunk Application Developers
- Splunk Programming Analyst
- Security Engineer
- Technical Service Manager
- Security Analyst
- DevOps Engineer, etc.
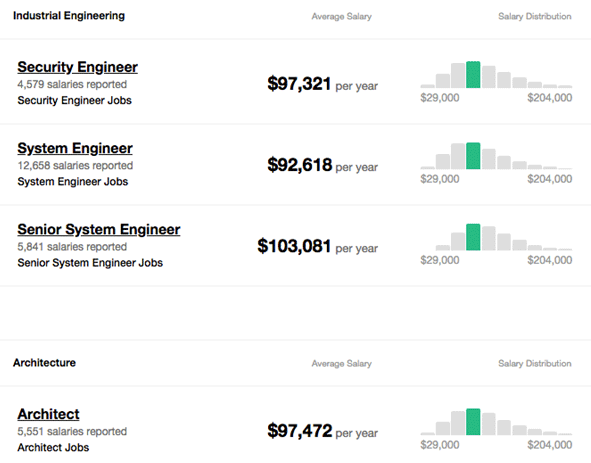 Splunk Professional Salary
Splunk Professional Salary
The bottom line is the growth of unstructured data and the requirement for skilled Splunk professionals is increasing in different sectors. Hence, opting for a career in Splunk is the wisest decision an individual can take.
SIEM XPERT provides the respective courses: Splunk training in Indore, Splunk training in Jabalpur, Splunk training in Kanpur, Splunk training in Kochi, Splunk training in Kolkata, Splunk training in mumbai, Splunk training in Noida, Splunk training in Trivandrum, Splunk training in Visakhapatnam















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


