Revenue Streams in Business Model Canvas
Social Share
Without a clear path for bringing money and resources into the enterprise, all businesses are doomed to fail. Every business model must clearly indicate which revenue streams will attract enough customers to keep the lights on. Businesses fail because, though the founders may have great ideas and motivation, their business models do not properly take into account how they will generate revenue.
What are Revenue Streams?
Revenue Streams outline how you earn money, what price is each of your customer segments truly willing to pay? Identify each possible revenue stream per customer segment.
Think hard about the possible pricing mechanisms per Revenue Stream. Surprisingly, pricing can often be a source of differentiation! Pricing mechanisms can include auctioning, bargaining, fixed-list prices, market- or volume-dependent prices, or yield management.
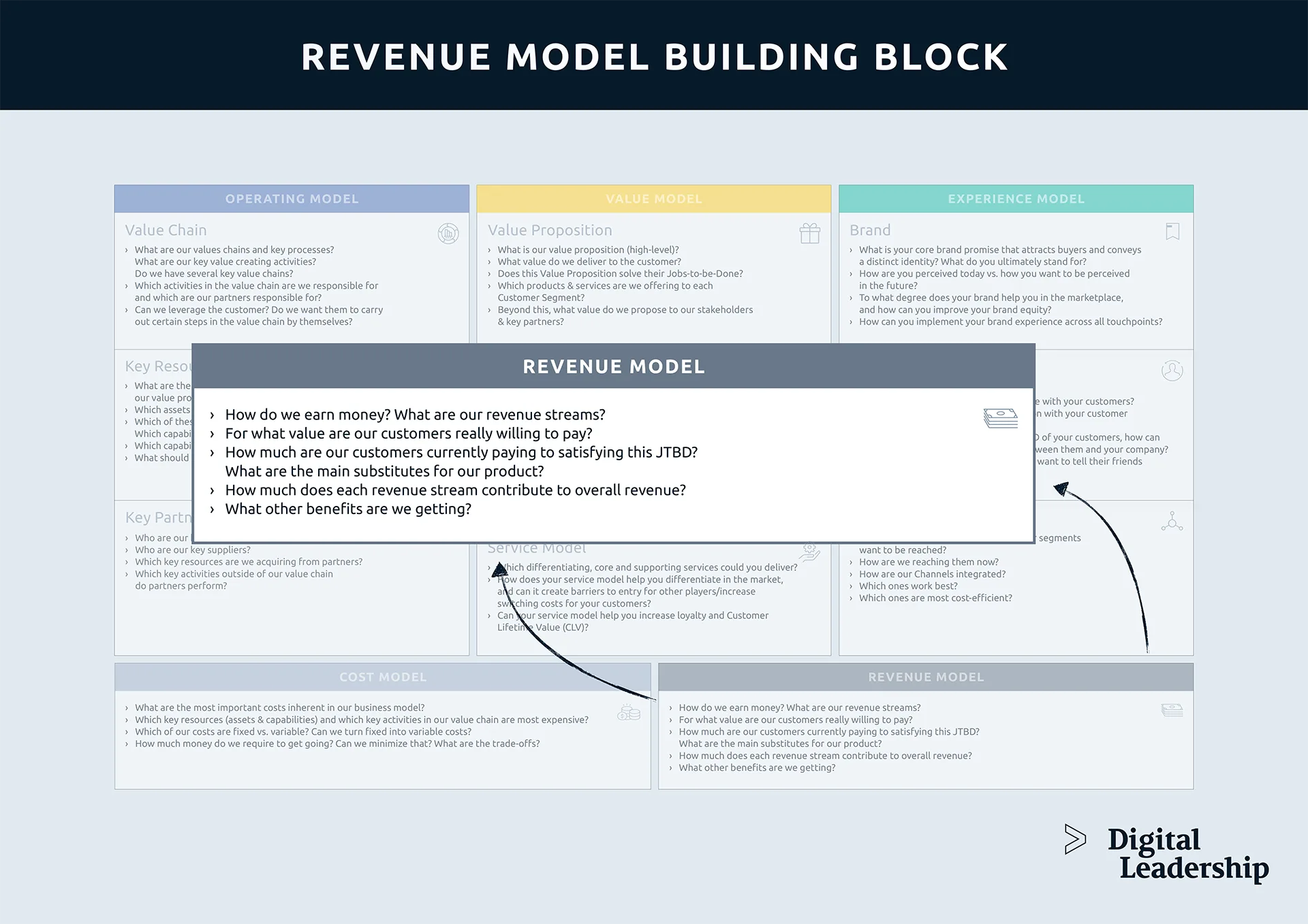 Revenue Model Building Block in BMC
Revenue Model Building Block in BMC
A Business Model can also involve transactional revenues resulting from one-time customer payments (e.g., a sale) or recurring payments (e.g., a subscription). In the context of the Revenue Model, think also about any other benefits you may be getting. Not all value is monetary!
Importance of Revenue Streams
It’s a matter of good business to reflect upon how your company generates cash and other revenues, and the full leveraging of revenue streams is only possible when you take a full accounting of your entire business model.
Each customer segment that you develop provides one or more revenue streams, each of which needs to be considered. It’s a lot of work, analyzing each revenue stream to make sure that you’re being properly compensated for the value you provide. But without revenue, clearly, a business cannot succeed.
At Digital Leadership, we see companies struggle to turn great ideas in ongoing revenue generation. This is truly one of the most difficult facts that all business analysts face. An entrepreneur might have good ideas, customer demand may be robust, but these great services and products will cease to be available if a solid revenue stream cannot be developed.
The Main Categories of Revenue Streams
We divide the key concepts here in two main types of revenue streams: transaction revenue and recurring revenue. Strong businesses have many ways of generating income, and the business that relies on merely one revenue stream risks oblivion with that revenue stream dries up.
Mục Lục
Transaction-Based Revenue Streams
Transaction-based revenue focuses on one-time customer payments for goods or services. Typically, this is how most people recognize business relationships.
Transaction-based revenue streams have some distinct advantages. First, sales revenue is clean: it’s easy to track and record. Money comes in when a customer pays, money goes out when the business replaces inventory and provides an employee a wage. (That simplifies the concept of a business’s overhead costs, but you should understand the point.)
Second, sales revenue streams are relatively easy to adjust. For example, if you identify that customers pay a certain amount for a certain product or service, you can adjust the price to maximize profits. If you’re thinking about inventory, you can manipulate your stock so that you maximize the amount of investment you have generating revenue.
Third, customers appreciate the directness of the experience. The interaction between the customer and the business is reduced to a personal connection. When companies employ a customer-centric model, this connection can be a powerful way to create a long-term relationship with customers who can provide a predictable income.
These revenue streams have drawbacks, however. The first is that each transaction requires an employee to “do” something: make the sale, complete a service, shift product. There is a lot of opportunities for the transaction to break down, resulting in a loss of revenue.
Because there is so much competition for transaction-based revenue streams, businesses face price deterioration as they try to attract customers. This is a big drawback given the already slim profit margins companies can face.
Recurring Revenue Streams
Recurring revenue streams are ongoing charges customers pay for continuing services and after-sale services. These revenue streams could include subscription fees, service contracts, rent revenue, interest revenue, brokerage fees, advertising charges, and any other ongoing revenue source that is paid as part of a medium- or long-term agreement.
A recurring revenue stream is advantageous because the revenue is collected through a low-friction process that requires little investment to maintain. Additionally, with contracts in place, revenue predictions are easier. Because recurring revenue streams generate money at a steady rate, they also make investments easier to map out as a business looks to expand.
On the other hand, when we use recurring charges to generate revenue, we run the risk of damaging the relationship we have with our customers. Other businesses, who may be perceived as being more hands-on if we’re not careful, can swoop in and lure away customers.
Recurring revenues comprise some of the most predictable income a business would have opportunity to cultivate.
Types of Revenue Streams
Revenue is a key performance indicator for nearly every business model. Understanding the different revenue streams and the way a business earns money is important as the business prepares for or considers the implementation of innovation.
Successful businesses rarely have a single revenue stream. Employing multiple revenue streams hedges your bets in case part of your operation fails or the business environment changes.
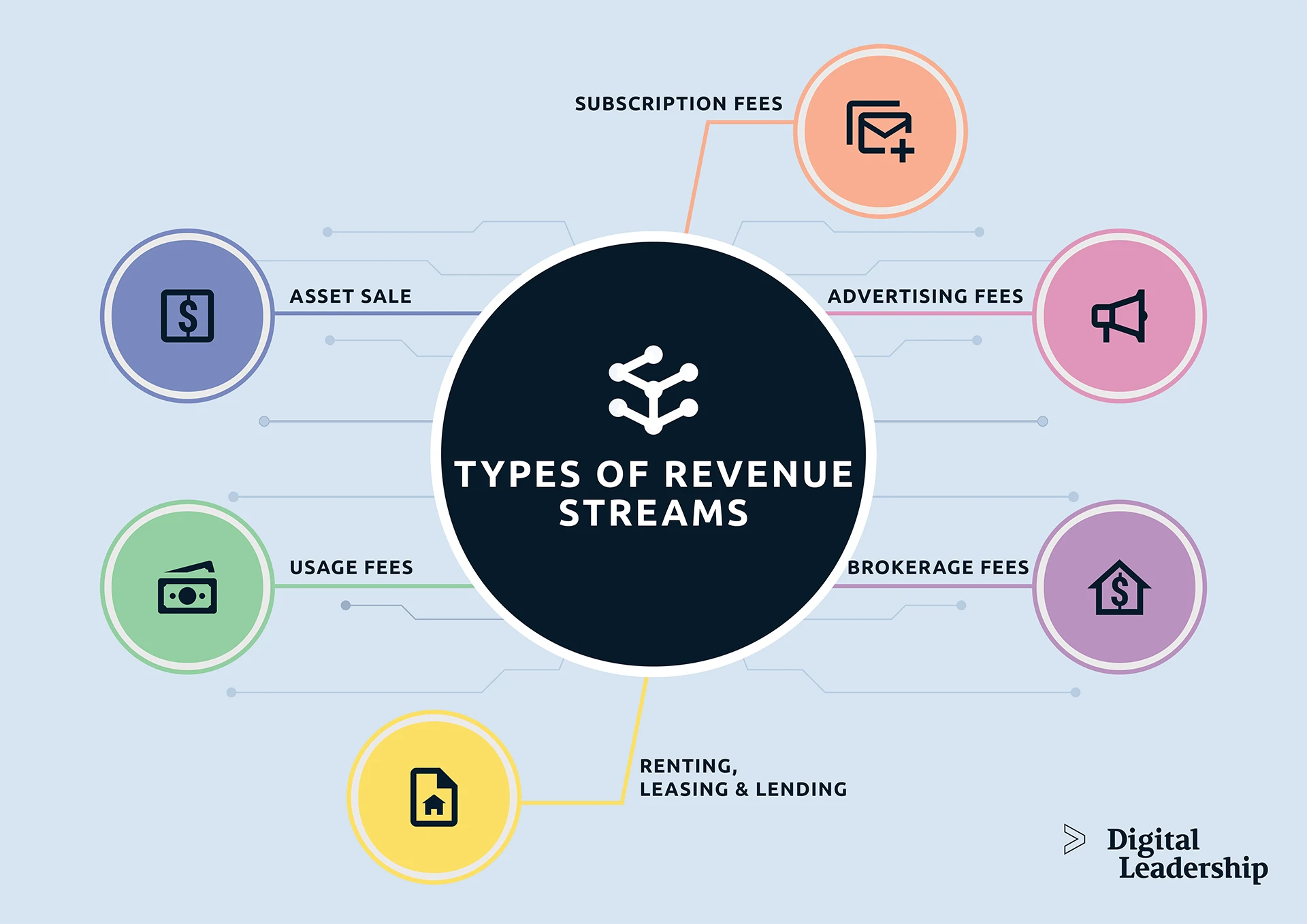 Types of Revenue Streams
Types of Revenue Streams
We identify six different revenue streams you might be able to leverage in your business. Again, having the chance to draw revenue from multiple revenue models will always provide your strongest chance of success. Revenue models and other important concepts behind business transformation strategy are further discussed in our new book, How to Create Innovation, which you can download through the Digital Leadership website.
1- Asset Sale Revenue Stream
Customers pay for a good or service. Selling assets is a one-time transaction, and therefore fairly limited.
This is a simple form of creating revenue, though it’s short-term, and depending on the market, can be difficult to predict.
2- Usage Fees Revenue Stream
Customers pay for access to a service. Usage fees leverage existing infrastructure to continue generating revenue.
These fees can be valuable income streams when the business model includes services that need to be regularly repeated. Hotels operate through this revenue model, as do package delivery companies and coworking space companies.
3- Renting, Leasing & Lending Revenue Stream
Customers pay for the temporary right to use an asset for a fixed time period. Renting, leasing and lending assets lets companies generate revenue while the customer incurs only limited charges. This revenue stream is similar to the previous example of usage fees, but rather than service revenue, renting and lending assets use material to generate income.
This type of recurring revenue is the basis for car rental companies.
4- Subscription Fees Revenue Stream
Customers incur a subscription fee for ongoing access to a service. This is a recurring revenue stream, though you need to constantly refresh what you’re offering through your subscription.
In this revenue model, customers want persistent access to a service they value. Examples here include gym memberships and streaming services that are becoming more and more popular within the media industry.
5- Brokerage Fees Revenue Stream
Consumers invest in the work of a mediator. A brokerage fee acknowledges the value of the access or expertise someone provides.
Brokers serve as a go-between in many revenue models, working on behalf of a customer and taking a percentage of the transaction as their fee. These revenue streams for the basis for business for real estate agents and credit card merchants. Service providers who charge commissions are usually following this business model.
6- Advertising Fees Revenue Stream
Clients pay for marketing products and services. Marketing agencies create advertisements and messaging that is broadcast through media and other channels that reach potential customers.
Most of us are familiar with advertising. We are exposed to marketing messages across television, radio, the Internet, and even people’s clothing (and maybe our own!)
Revenue Model Framework
Your capabilities are the processes, systems of knowledge, and specific skills that a firm possesses based on which it operates, earns revenue, and competes with other firms.
In Digital Leadership’s eXtended Business Model Canvas, Revenue streams and the Revenue Model play a significant role in business innovation. More information about this canvas, and many other business model canvas suggestions and work-throughs, are available on the Digital Leadership website, and in the book How to Create Innovation.
 The UNITE eXtended Business Model Canvas
The UNITE eXtended Business Model Canvas
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Building on the work of Alexander Osterwalder, the Lean Canvas and the thinking of Patrick Stahler
UNITE Business Model Canvas
1 file(s) 11.70 MB
Final Thoughts: Questions for Reflection
In closing, understanding your various revenue streams, and developing multiple revenue streams, is vital in securing your company’s future. If there are types of revenue streams your company hasn’t considered, we urge you to consult with innovation experts so you can advance your current business model.
Some of the questions we’d explore are listed below. If you can’t answer all of them, there’s a chance you don’t completely understand how your company generates revenue.
We’d love to explore it with you.
- How do we earn money?
- What are our revenue streams?
- For what value are our customers really willing to pay?
- How much are our customers currently paying to satisfying this JTBD?
- What are the main substitutes for our product?
- How much does each revenue stream contribute to overall revenue?
- What other benefits are we getting?
Connecting The Dots: The UNITE Business Model Framework
How to Create Innovation includes a number of canvases that focus on value creation and finding the right business model to meet your customer segment and customer needs. The framework is built to inspire drastic changes that help you find a competitive advantage. Our hope is that your company grows through business model innovation, and so we again encourage you to look deeper into our website and the book.
Here is a summary of the key ingredients of the framework:
 The UNITE Business Model Framework
The UNITE Business Model Framework
Designed By: Digital Leadership AG
UNITE Business Model Canvas
1 file(s) 11.70 MB
Business Models
The centerpiece is the Business Model Canvas, which covers the six main areas of a Business Model (the Operating, Value, Service, Experience, Cost, and Revenue Models).
The eXtended Business Model Canvas adds the immediate business context, including Business Drivers, customers, and the team, as well as the Unfair Advantage.
Detailed Models
A Business Model can be broken out into its numerous aspects. Depending on what challenges you face, you can zoom in on your area of interest using an appropriate tool or canvas:
- Your Business Intention and objectives as well as your Massive Transformative Purpose summarize your drivers and give direction to what you do.
- The Value Proposition Canvas details the central components of your offering (the product or service).
- To dig into your Customer Segments, work with data-driven Personas.
- The JTBD Customer Job Statement and Job Map frame the JTBD of your customers.
- The Business Model Environment puts your Business Model in a market context composed of emerging trends and disruptive forces.
- The Innovation Culture Canvas helps you understand and consciously shape a culture that supports innovation.
- The Innovation team structure enables you to draft a team structure for your innovation initiative.
- Using learning and growth metrics, you can measure progress at the initial stages of development. These metrics help you focus on what really matters instead of creating a detailed business plan that will not really help you. Later on, you can expand the financial aspect of the Revenue and Cost Models with a full business case.
- The Operating Model Canvas helps you think through the Operating Model.
Social Share















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


