Open Source NMS – Best Free Tools for Network Monitoring & Management
Network Monitoring Software covers a surprisingly wide gambit of software and functionality.
Here is our list of the five best free open source network monitoring software and tools:
- Zabbix – EDITOR’S CHOICE A free system monitoring package that includes network, server, application, services, and cloud platform monitoring capabilities. This system uses SNMP and ICMP to discover all devices and continuously monitor their availability and performance. Runs on Linux.
- Observium This free network monitor saves time by squeezing many system graphs of live data into each view and has detail view overlays to allow greater scrutiny. Installs on Linux.
- Cacti An SNMP-based free network performance monitor that also displays live traffic data in graphs. Runs on Linux.
- Nagios Core A comprehensive free open source monitoring package that includes network device and traffic monitoring. This system can be expanded by hundreds of free plug-ins. Runs on Linus or on Windows over a VM.
- Icinga 2 This is a fork of Nagios Core and it can take all of the Nagios plug-ins. Offers network performance monitoring and traffic analysis. Runs on Linux.
Some software is focused purely on observation and tracking of monitoring network traffic, while others are more geared on response and awareness, with features that let you set alarms or even trigger scripts based on specific events, and still other pieces of software allow you to focus on the trends of traffic and network performance for sake of longer term adjustments and heuristics for hardware devices.
Whatever your needs may be there’s likely a free, open-source option that can perfectly fit the bill.
Every network should have at least one of these tools available; whether you’re performing some in-depth troubleshooting and need a program with powerful data aggregation and graphing abilities to help pinpoint a problem device or application, or if you’re tracking the traffic of several physical devices over several different network environments over time to watch for trends in your bandwidth needs or other statistics.
Mục Lục
What should you look for in free network monitoring tools?
We reviewed the market for free network monitoring software and analyzed the options based on the following criteria:
- Device discovery routines that continuously search for new equipment
- An automatic network inventory creation system
- Graphical representations of live traffic data
- Performance monitoring with alerts when problems arise
- Traffic monitoring to detect bottlenecks
- An easy-to-use, self-installing package
- A package that is forever free and works well without the necessity for paid extras
With these selection criteria in mind, we have found a selection of very good free network monitoring systems. We made sure to find options for Windows and Linux.
Here’s the Best Open-Source Network Monitoring Software:
1. Zabbix
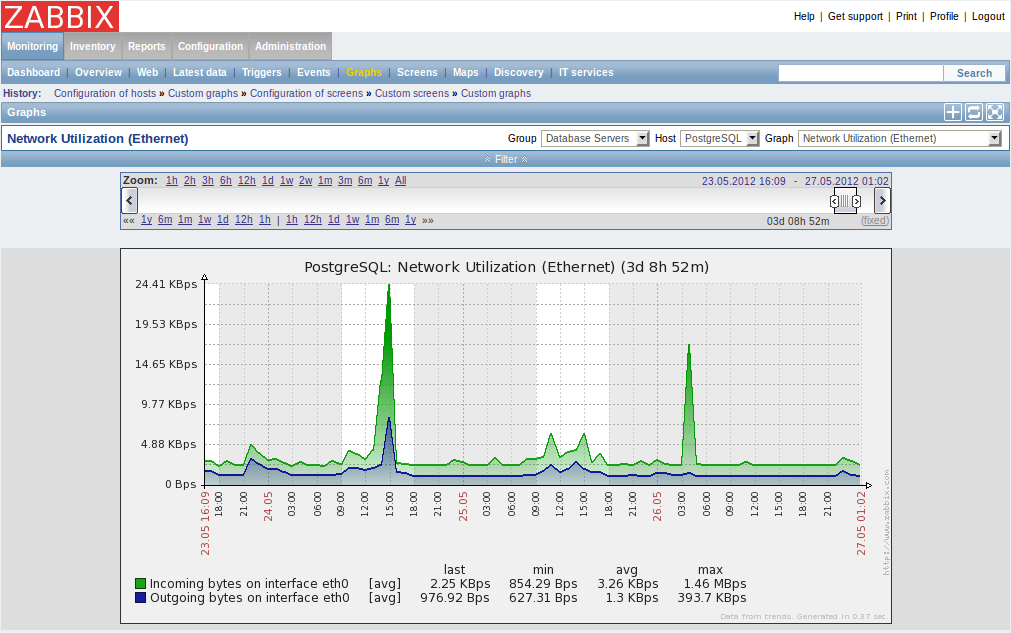
The interesting thing about Zabbix is that there is no enterprise-level paid version, it’s all completely open-source and completely free. They do offer some consulting and monitoring contracts, but the software itself is wide open! It’s one of the most powerful open-source options in this realm and can handle most all of the standard NMS needs, plus some.
Key Features:
- Native graphing
- Wide variety of cross-platform support
- Highly customizable
One prime advantage is that it has a particularly slick and intuitive interface, while also being exceptionally easy to install with compatibility across numerous systems and environments. On the flip side, some of its ability to aggregate and report information, and especially then exporting that information, could definitely be a bit stronger in their offering.
Available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5, 6 and 7, CentOS, Debian, Oracle Linux and Ubuntu 12.04 and 14.04
Pros:
- Open-source transparent tool
- Uses both SNMP and ICMP for a broader monitoring range
- Can detect new devices and configuration changes immediately
- Offers useful templates for quick insights
- Robust notification system supports SMS, email, custom script, and webhook
Cons:
- Would like to see better-alerting features, specifically related to reducing false positives
EDITOR’S CHOICE
Zabbix is our top pick for a free, open source network monitoring tool because it has a very appealing interface, which makes it easy to use. The service includes a network discovery process that identifies all devices and maps your network. The monitor makes frequent checks on all devices for statuses, using the SNMP protocol.
Official Site: http://www.zabbix.com/download.php
OS: Linux
2. Observium
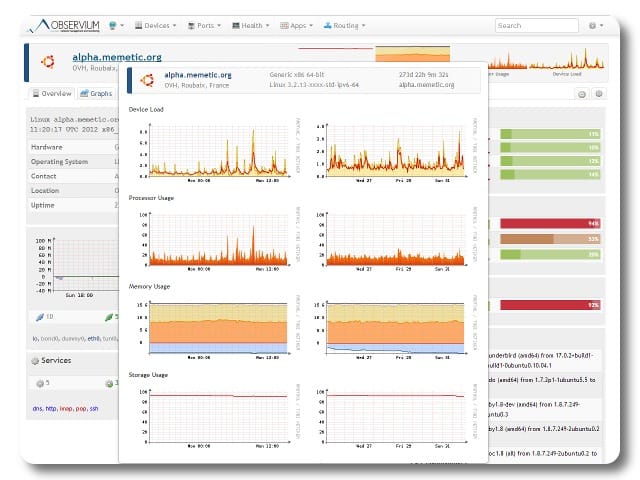
Observium is another offering with a really slick interface style to it. The charts and graphs are all readily available and organized in a beautifully intuitive fashion. This program pushes more into the realm of physical monitoring of devices and can even show where, geographically, systems are located and how they’re communicating and passing traffic!
Key Features:
- Customizable graphing widgets
- Detailed reporting and audits
- Support for a professional version
It uses a variety of methods for monitoring and does an excellent job of providing automatic discovery while still allowing manual additions. There are few NMS software packages that will do so much of the legwork for you and do it accurately!
Observium even has a cohesive web interface, meaning you have a lot less to worry about when it comes to accessing controls and viewing network status and statistics from anywhere you are. The software itself is, however, Linux-based aside from the web-based front-end. Observium does have a professional edition.
Available for Linx/Unix including Debian, RHEL, Ubuntu, CentOS 6 and 7.
Pros:
- Sleek and easy-to-navigate interface
- Supports hardware and traffic monitoring in one solution
- Supports native geolocation tracking – great for tracking global assets
Cons:
- Not available for Windows operating systems
Download Link: http://www.observium.org/docs/
3. Cacti
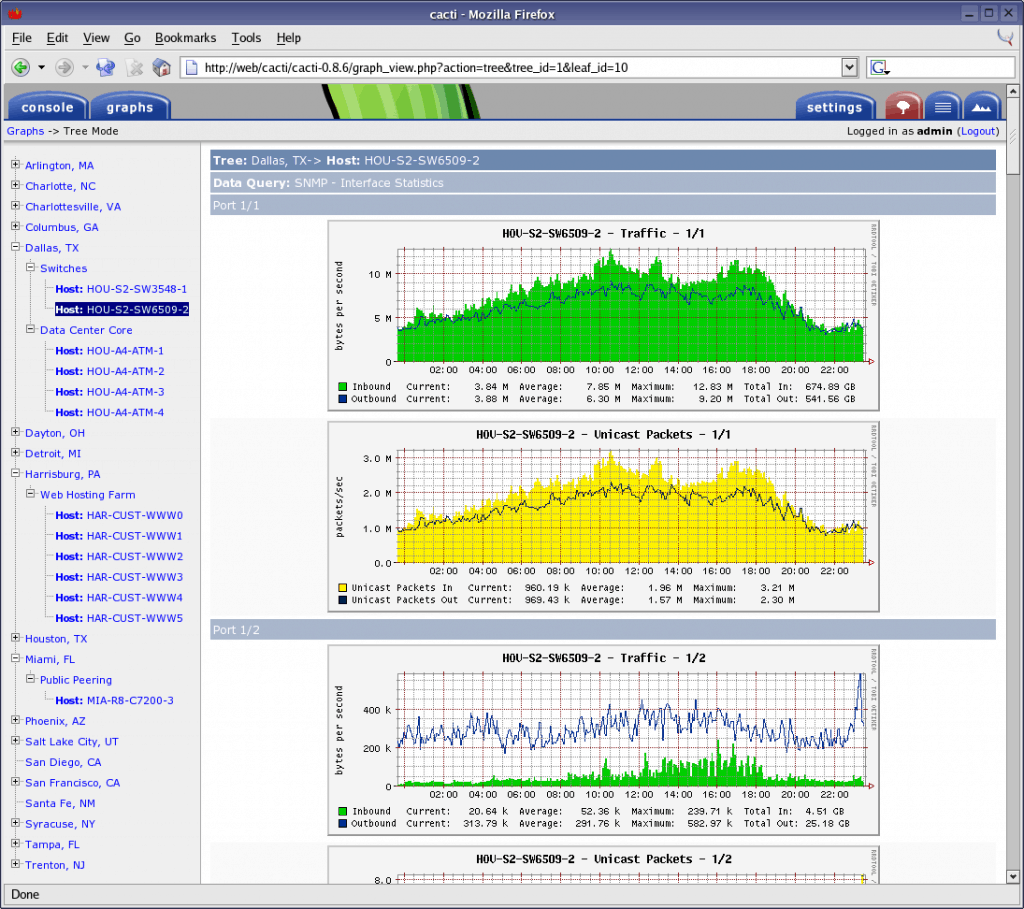
Cacti is a little more particular in its purpose, and slightly more restricted – it does require a MySQL back end database and SNMP has to be installed and configured on agent devices for full functionality, in addition to Cacti itself requiring a PHP/Apache backbone.
Key Features:
- Wide range of integrations
- Highly customizable
- Powerful data aggregation, filtering, and processing
Despite this, it’s an extremely powerful but simple tool – it takes data, aggregates it, and presents it in just about any way or combination you can possibly want or imagine. If there’s any need to see several sets of data side by side, to manipulate them, to draw in data from several other metrics that normally wouldn’t even be relevant, Cacti can do it all.
It’s a tool that focuses primarily, if not almost exclusively, on trend tracking and graphical representations of data sets. Available for Windows, Linux/Unix variations (Gentoo, Debian, Fedora and SUSE)
Pros:
- Highly customizable monitor with a focus on data visualization
- Large dedicated community of over 20,000 members
- Simple interface
- Ideal for researchers looking for more flexibility in their data collection
Cons:
- Has a steeper learning curve than competing product
Download Link: http://www.cacti.net/download_cacti.php
4. Nagios
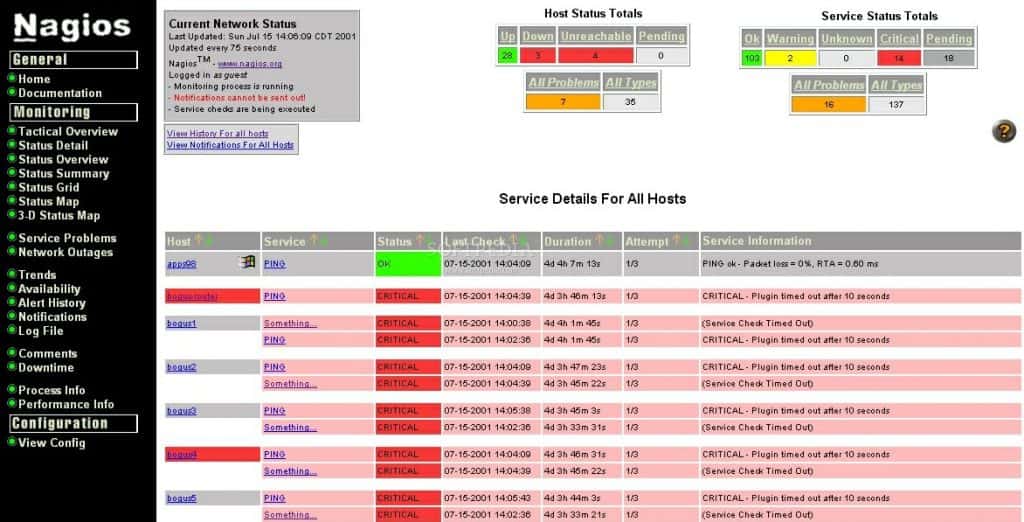
Nagios is one of those programs that is an absolute rose but definitely has its thorns. It’s an older software, meaning it’s tried and true – it’s extremely fast and incredibly reliable, but the learning curve for newcomers can easily be prohibitive.
Key Features:
- Multitenant support
- Lightweight installation
- Integrates with other Nagios products
It is similar to some other offerings in that it is immensely flexible – Nagios can track, monitor, and follow trends of almost any data that can be gathered from a network environment, and it’s that same flexibility and wide-open capabilities that are both its strength and it’s main drawback.
A powerful piece of monitoring software that is not for the faint of heart. If nagios doesn’t fit the bill, check out the best nagios alternatives for other options. Available For RHEL, CentOS and Nagios for Windows using VMWare or Virtual PC virtual machines.
Pros:
- Simple, yet informative interface
- Flexible alerting options support SMS and email
- Robust API backend makes it a great option for developers who want to integrate their own custom applications
Cons:
- Open-source version lacks quality support found in paid products
- Installation can be technical and complex
Download link: https://www.nagios.org/downloads/
5. Icinga
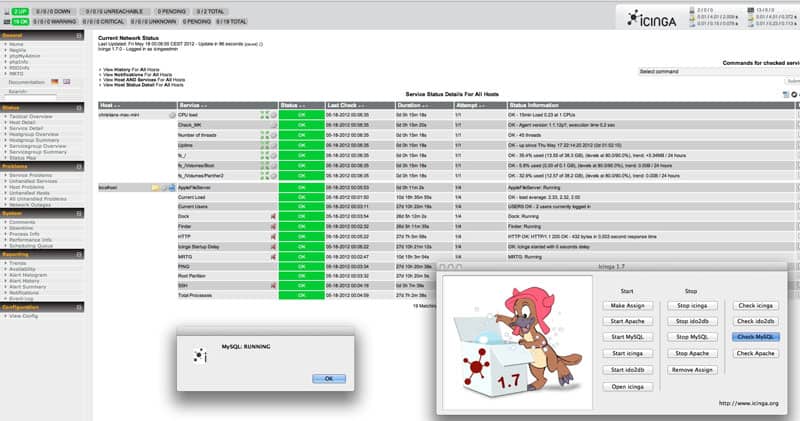
Icinga is a program that gives some of the others, Zabbix especially, a run for its money but falters when it comes to intuitive setup and configuration. Icinga requires a good wealth of knowledge to know how to get it setup just right, but once you do it’s among the Best open-source NMS on the market.
Key Features:
- Simple interface
- Support for a wide range of platforms
- Offers additional modules for extended functionality
Of particular note is the unusual modularity of Icinga – the core software can be installed with just a few small commands, which is the easy part, and from there almost any other functionality, both standard NMS and beyond, can be added one by one.
The downside is that each one has to be installed and configured individually, and that coupled with documentation that isn’t so great for quick setup, makes this another powerful tool that’s challenging to put to use right away.
Available for Debian, Ubuntu, RHEL/CentOS, openSUSE, SLES, Gentoo, FreeBSD, ArchLinux and Icinga for Windows will require Vagrant and VirtualBox or Parallels Desktop, along with Ruby for Windows installed.
Pros:
- Can be configured via GUI or DSL, making it a good choice for admins who enjoy CLI tools
- Supports built-in visual reporting
- Modules allow for different functionality, keeping the base installation sleek and lightweight
- Can run on Linux as well as Windows operating systems
Cons:
- Designed for more technical users, other options have better out-of-box features
Download link: https://www.icinga.org/download/
Conclusion
Whatever program you choose you can take full advantage of the Open-Source nature of each, meaning that an attractive price-tag of ‘Free!’ lets you try out all the different software options to see what works best for you and your monitoring needs.
And you can rest easy knowing that the source code is fully available and heavily audited and monitored by the community, which helps reduce security concerns and prevent issues normally present from developer shortsightedness.
Grab one of the above Free Open Source Network Monitor tools for Linux or Windows and give a whirl and see which one works Best for you and your needs.
Open Source Network Monitoring Software FAQs
What is the difference between Open-Source Network Monitoring and Commercial Network Monitoring?
Open-Source Network Monitoring and Commercial Network Monitoring differ in terms of cost, features, and support. Open-Source Network Monitoring is free, but may require more time and technical expertise to install and configure, while commercial network monitoring may be more expensive, but typically provides more comprehensive features and support.
How do I get support for an Open-Source Network Monitoring tool?
Support for Open-Source Network Monitoring tools is typically available through online forums, community support, and online documentation. Some open-source network monitoring tools also offer paid support services for users who need more comprehensive assistance.
How do I integrate an Open-Source Network Monitoring tool with my existing network infrastructure?
Integration of an Open-Source Network Monitoring tool with your existing network infrastructure will depend on the specific tool and network infrastructure you are using. Most open-source network monitoring tools offer online documentation, community support, and step-by-step instructions for integration.
Why use Open-Source Network Monitoring?
Open-Source Network Monitoring can offer several benefits, including lower cost, customization options, and community support. Additionally, many open-source network monitoring tools are built on open-source technologies, providing compatibility with other open-source tools.
What are the most popular Open-Source Network Monitoring tools?
Some of the most popular Open-Source Network Monitoring tools include Nagios, Zabbix, Icinga, and Cacti.
What features should I look for in an Open-Source Network Monitoring tool?
When selecting an Open-Source Network Monitoring tool, features to consider include compatibility with your network infrastructure, scalability, alerting capabilities, performance reporting, and ease of use.
Related Articles:
Top 4 Open Source sFlow Collector and Analyzers
13 Free Open Source NetFlow Analyzers for Windows and Linux/Unix















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


