Learn Spring Boot Tutorial – javatpoint
Mục Lục
Spring Boot Tutorial

Spring Boot Tutorial provides basic and advanced concepts of Spring Framework. Our Spring Boot Tutorial is designed for beginners and professionals both.
Spring Boot is a Spring module that provides the RAD (Rapid Application Development) feature to the Spring framework.
Our Spring Boot Tutorial includes all topics of Spring Boot such, as features, project, maven project, starter project wizard, Spring Initializr, CLI, applications, annotations, dependency management, properties, starters, Actuator, JPA, JDBC, etc.
What is Spring Boot
Spring Boot is a project that is built on the top of the Spring Framework. It provides an easier and faster way to set up, configure, and run both simple and web-based applications.
It is a Spring module that provides the RAD (Rapid Application Development) feature to the Spring Framework. It is used to create a stand-alone Spring-based application that you can just run because it needs minimal Spring configuration.
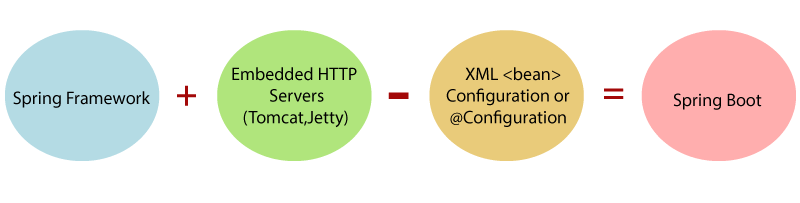
In short, Spring Boot is the combination of Spring Framework and Embedded Servers.
In Spring Boot, there is no requirement for XML configuration (deployment descriptor). It uses convention over configuration software design paradigm that means it decreases the effort of the developer.
We can use Spring STS IDE or Spring Initializr to develop Spring Boot Java applications.
Why should we use Spring Boot Framework?
We should use Spring Boot Framework because:
- The dependency injection approach is used in Spring Boot.
- It contains powerful database transaction management capabilities.
- It simplifies integration with other Java frameworks like JPA/Hibernate ORM, Struts, etc.
- It reduces the cost and development time of the application.
Along with the Spring Boot Framework, many other Spring sister projects help to build applications addressing modern business needs. There are the following Spring sister projects are as follows:
- Spring Data: It simplifies data access from the relational and NoSQL databases.
- Spring Batch: It provides powerful batch processing.
- Spring Security: It is a security framework that provides robust security to applications.
- Spring Social: It supports integration with social networking like LinkedIn.
- Spring Integration: It is an implementation of Enterprise Integration Patterns. It facilitates integration with other enterprise applications using lightweight messaging and declarative adapters.
Advantages of Spring Boot
- It creates stand-alone Spring applications that can be started using Java -jar.
- It tests web applications easily with the help of different Embedded HTTP servers such as Tomcat, Jetty, etc. We don’t need to deploy WAR files.
- It provides opinionated ‘starter‘ POMs to simplify our Maven configuration.
- It provides production-ready features such as metrics, health checks, and externalized configuration.
- There is no requirement for XML configuration.
- It offers a CLI tool for developing and testing the Spring Boot application.
- It offers the number of plug-ins.
- It also minimizes writing multiple boilerplate codes (the code that has to be included in many places with little or no alteration), XML configuration, and annotations.
- It increases productivity and reduces development time.
Limitations of Spring Boot
Spring Boot can use dependencies that are not going to be used in the application. These dependencies increase the size of the application.
Goals of Spring Boot
The main goal of Spring Boot is to reduce development, unit test, and integration test time.
- Provides Opinionated Development approach
- Avoids defining more Annotation Configuration
- Avoids writing lots of import statements
- Avoids XML Configuration.
By providing or avoiding the above points, Spring Boot Framework reduces Development time, Developer Effort, and increases productivity.
Prerequisite of Spring Boot
To create a Spring Boot application, following are the prerequisites. In this tutorial, we will use Spring Tool Suite (STS) IDE.
- Java 1.8
- Maven 3.0+
- Spring Framework 5.0.0.BUILD-SNAPSHOT
- An IDE (Spring Tool Suite) is recommended.
Spring Boot Features
- Web Development
- SpringApplication
- Application events and listeners
- Admin features
- Externalized Configuration
- Properties Files
- YAML Support
- Type-safe Configuration
- Logging
- Security
Web Development
It is a well-suited Spring module for web application development. We can easily create a self-contained HTTP application that uses embedded servers like Tomcat, Jetty, or Undertow. We can use the spring-boot-starter-web module to start and run the application quickly.
SpringApplication
The SpringApplication is a class that provides a convenient way to bootstrap a Spring application. It can be started from the main method. We can call the application just by calling a static run() method.
Application Events and Listeners
Spring Boot uses events to handle the variety of tasks. It allows us to create factories file that is used to add listeners. We can refer it to using the ApplicationListener key.
Always create factories file in META-INF folder like META-INF/spring.factories.
Admin Support
Spring Boot provides the facility to enable admin-related features for the application. It is used to access and manage applications remotely. We can enable it in the Spring Boot application by using spring.application.admin.enabled property.
Externalized Configuration
Spring Boot allows us to externalize our configuration so that we can work with the same application in different environments. The application uses YAML files to externalize configuration.
Properties Files
Spring Boot provides a rich set of Application Properties. So, we can use that in the properties file of our project. The properties file is used to set properties like server-port =8082 and many others. It helps to organize application properties.
YAML Support
It provides a convenient way of specifying the hierarchical configuration. It is a superset of JSON. The SpringApplication class automatically supports YAML. It is an alternative of properties file.
Type-safe Configuration
The strong type-safe configuration is provided to govern and validate the configuration of the application. Application configuration is always a crucial task which should be type-safe. We can also use annotation provided by this library.
Logging
Spring Boot uses Common logging for all internal logging. Logging dependencies are managed by default. We should not change logging dependencies if no customization is needed.
Security
Spring Boot applications are spring bases web applications. So, it is secure by default with basic authentication on all HTTP endpoints. A rich set of Endpoints is available to develop a secure Spring Boot application.
Prerequisite
Before learning Spring Boot, you must have the basic knowledge of Spring Framework.
Audience
Our Spring Boot Tutorial is designed to help beginners and professionals.
Problem
We assure you that you will not find any problem with the Spring Boot Tutorial. But if there is any mistake, please post the problem in the contact form.
Next Topic
Spring Boot Version
next →















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


