Innovation Models | Innovation Process Models | Examples
Business innovation is of top priority for entrepreneurs and CEOs. But why does a business need an Innovation model? What’s the role of the innovation model?
As you know, Innovation is part of a successful business strategy. Most often, Innovators fail when they pursue the wrong model for the implementation of innovation. Lacking the required capabilities can also be the reason for failure.
An Innovation model provides a detailed framework to identify, advance, and implement ideas. Thus, focusing on adopting methods to create the needed value.
Roy Rothwell, a British Sociologist is a pioneer in industrial innovation. He made significant contributions to innovation management.
Rothwell put forward five generations of innovations from the 1950s onwards. His findings are based on various marketing factors. This includes- inflation, stagflation, economic recovery, unemployment, etc.
His findings are termed as a descriptive innovation model. It represents the different structuring of the company’s innovation process subject to market trends.
Hence, his Innovation Models are beneficial in creating an innovation management strategy for business.
Let’s understand Rothwell’s types of Innovation models…
Mục Lục
Types of Innovation Models
-
First-generation Innovation model (1G) – Technology Push
Technology push in the first Innovation model is the result of rapid economic growth from 1950. Nasa developed this as a management tool in the 1960s. They also termed it as ‘Phase-review-processes’.
The idea was to break down complex processes of space projects. It focused on systemizing the work and gaining control over activities.

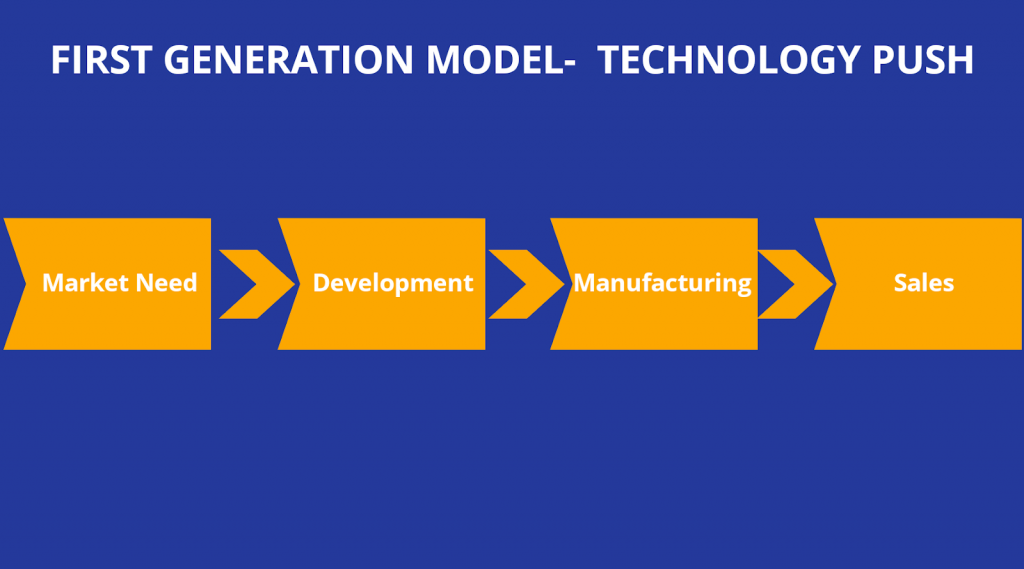
The Phase-review-processes implies consistent monitoring of each phase. Thus forming a linear sequential process. It focused on pushing technological innovation through extensive research & development.
It was applied at the stage of product research, its engineering, manufacturing & marketing to invent a successful product. As the entire focus was on the development of ideas- it ignored the marketing phase.
The complete emphasis on R&D had the disadvantage of not considering customer feedback and expectations. Thus, the innovations would often get ignored in the market.
-
Second-Generation Innovation Model (2G)– Market Pull
In the 1960s mid, the approach shifted from Technological push to Market pull. The focus began on responding to market needs. Factors ignored during the first generation are considered now in the second generation.
It includes- the cost-benefit analysis of each project & systematic allocation of resources.

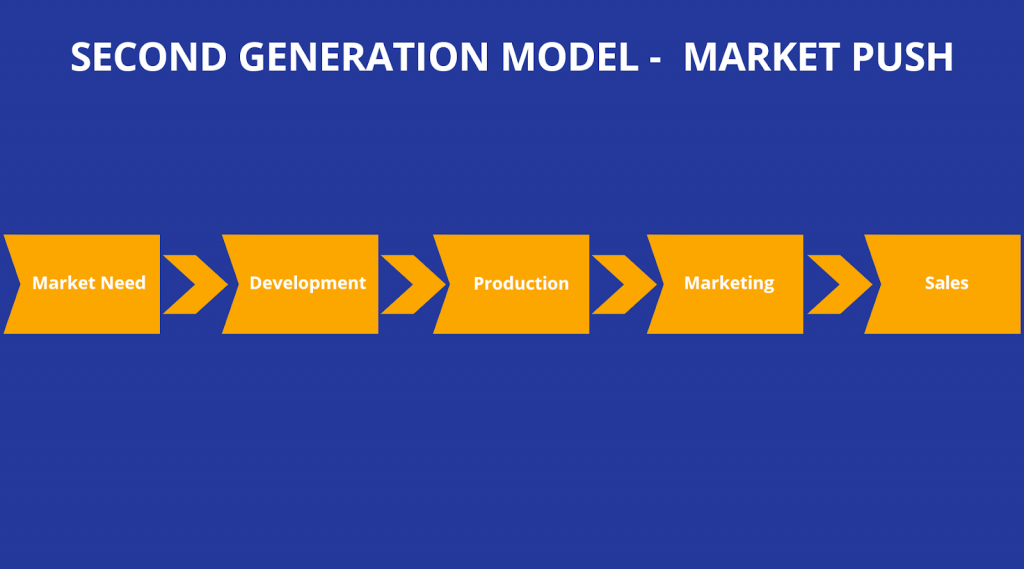
The process is similar or sequentially linear but emphasized market needs. Thus reducing the research time.
As the market needs are dynamic, the projects would last for a short for short period. Hence, resulting in numerous small projects.
-
Third-Generation Innovation Model (3G) – Coupling Method.
The third-generation model overcomes the limitations of the previous two linear models. It gained prominent acceptance during the inflation and stagflation phase of the economy.

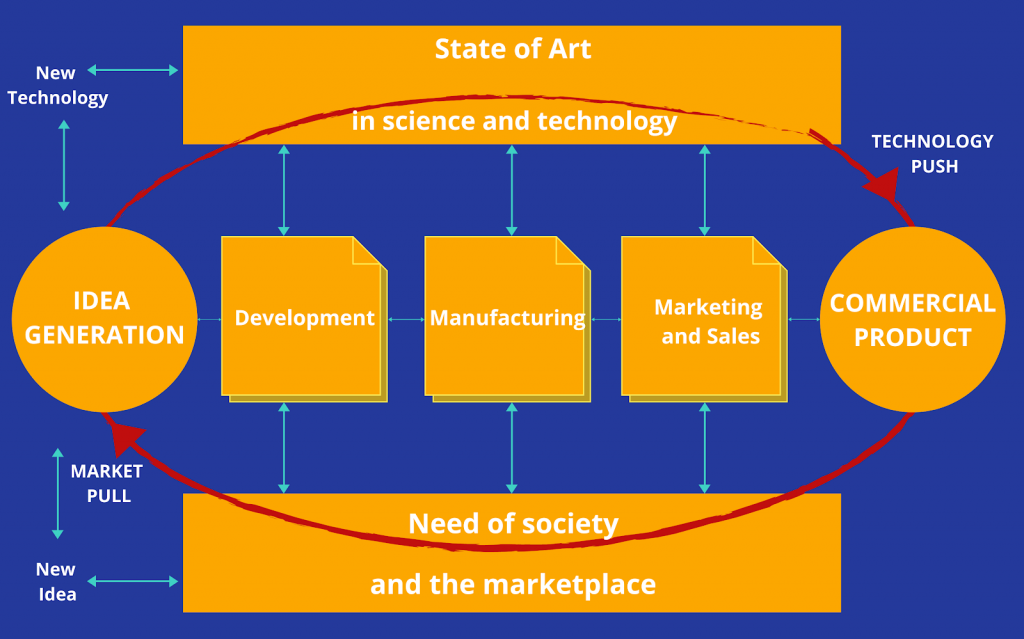
It tightly combined R&D and Marketing. The innovators coupled technological innovation with market needs. The model was based on the balanced coupling of Technology Pull and Market Push.
The core driving factor was reducing the operational costs during the contraction stage of the economy. So, the process formed a non-linear feedback loop. But the stages in the process made the model sequential.
-
Fourth-Generation Innovation Model (4G) – Integrated Model

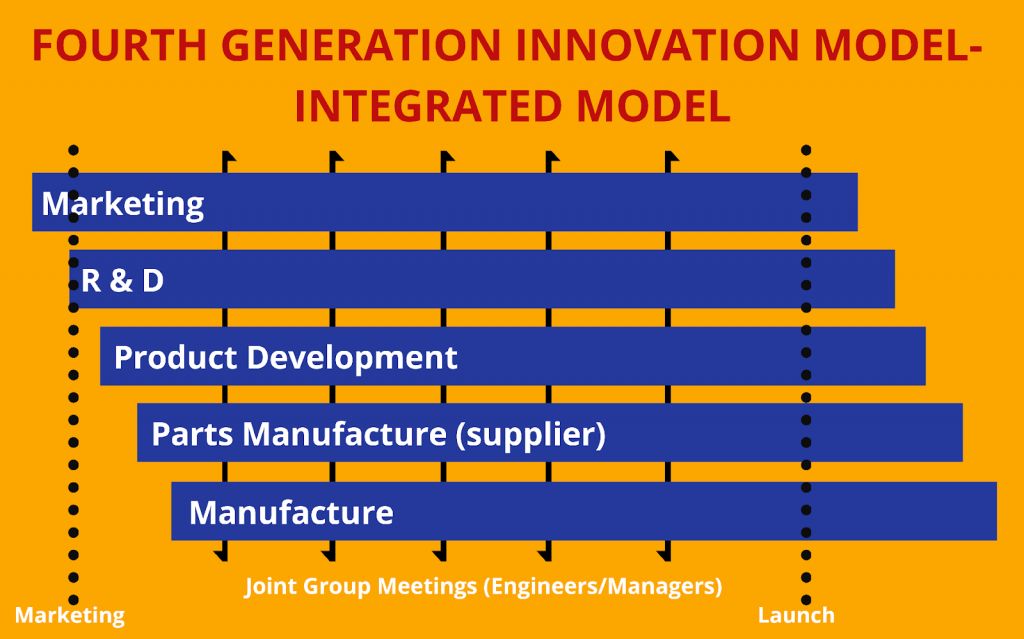
The fourth-generation model follows an integrated model for the business process. It moved away from the sequential process to follow the parallel process.
A parallel approach is followed in development, internal company communication, key suppliers at upwards, and customers downwards.
-
Fifth-Generation Innovation Model(5G) – Network Model
The network model focused on the effective distribution of network processes. It emphasized gaining flexibility and increasing the development speed.
The 5G model has integrated network systems to consolidate external and internal factors. Therefore, the model considers the external inputs of suppliers, customers, competitors, government, etc.

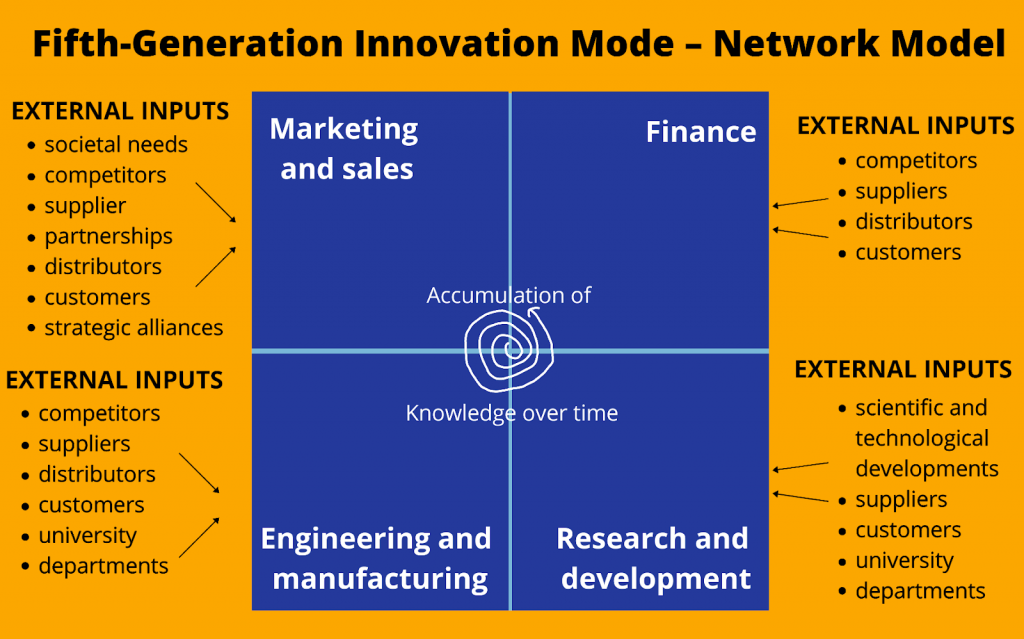
Thus gaining market competitiveness in times of rapid technological changes and shorter product cycles.
The Integrated and network model intensifies the fact that technological innovation is cross-functional & multi-factor but not sequential.
-
Sixth-Generation Innovation model (6G) – Open Innovation Model

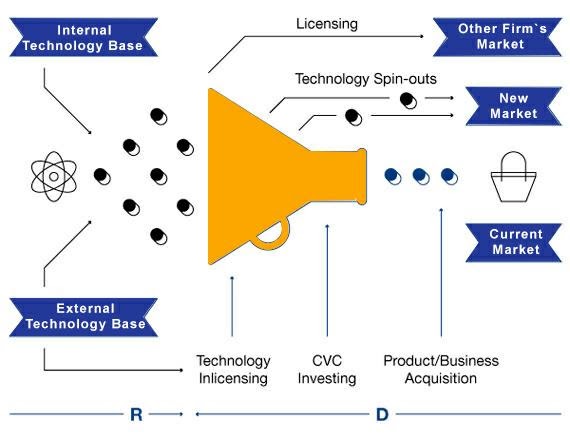
As Chesbrough defines, “Open innovation is the use of purposeful inflows and outflows of knowledge to accelerate innovation internally while also expanding the markets for the external use of innovation.”
It looks out for technological advancements by combining internal and external ideas. The funnel representation shows- Initiating with a large pool of ideas to narrow down later at the best choice of the idea.
And further implementing the best innovation in the market. So, check out this blog to get a detailed understanding of Open Innovation.
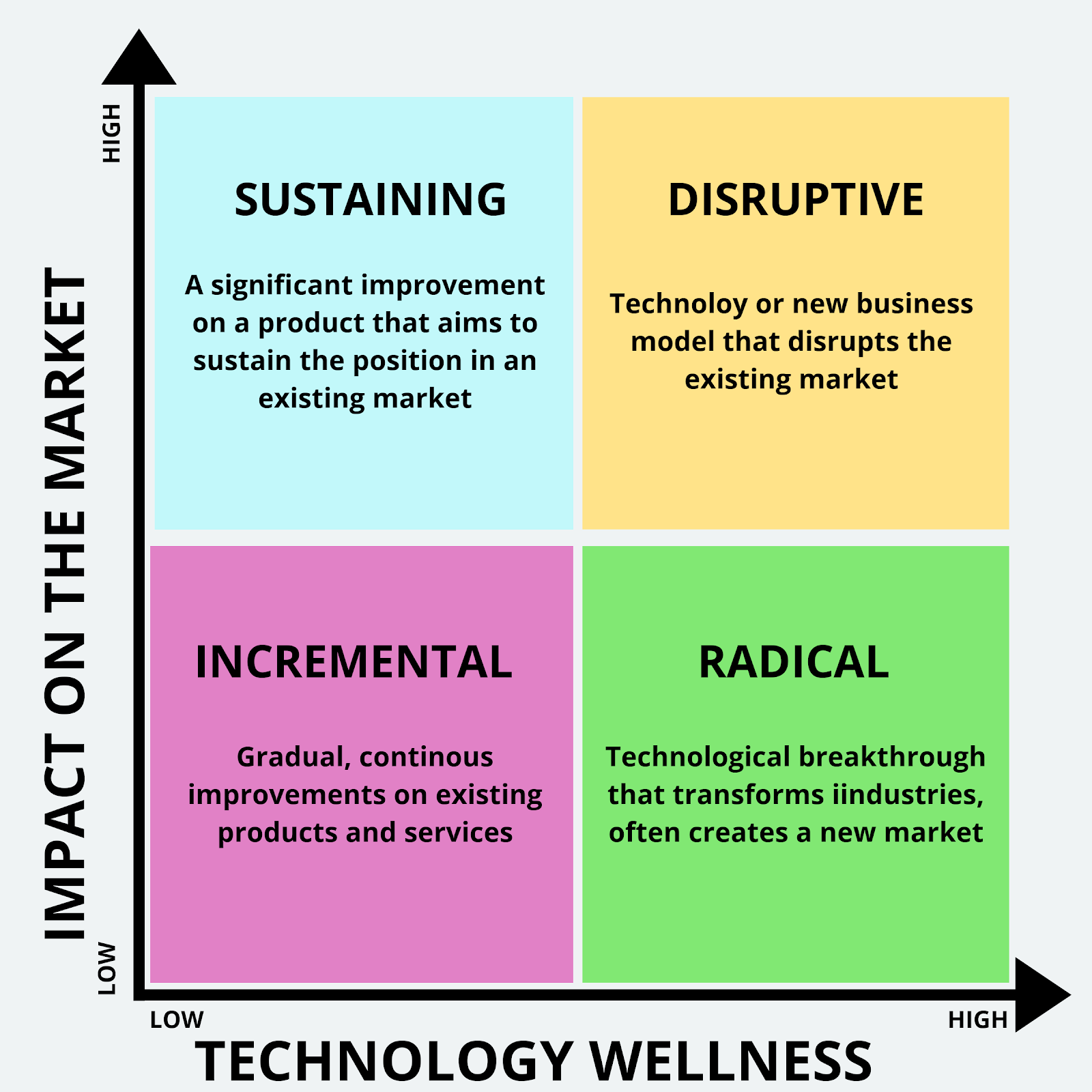
The 4 Main Types of Innovation:
There are various types of Innovation. Most often the characteristics of each innovation type make them overlap. The following types are the most common and basic forms of innovation.
So here goes the 4 main types of innovation or innovation matrix…

-
Incremental Innovation
As the word says, Incremental innovation is increasing the current value of the product. It makes the product a better version than the previous one.
So, it can be about improving efficiency while retaining the core features. It focuses on improving the experience of the current customer market.
-
Disruptive Innovation
Disruptive innovation is a market disruptor. They blow away the existing market or industries. This innovative power makes a non-customer into their customer.
It set forth the failure of traditional business models which require a new variation for survival.
-
Sustaining Innovation
Sustaining innovation is more or less like Incremental innovation. It grows its existing market while focusing on current customers. They take small steps of innovation to grow their business.
-
Radical Innovation
Radical innovation is similar to Disruptive innovation. This takes an extensive length of time to make disruptive changes. Thus making it a rare innovation type.
It brings transformations that were previously unknown to the world. Innovations for example computers, mobile phones, and the internet. So, these innovations have completely changed the way of communication in the entire world.
Innovation Strategy
An innovation model can adopt any of the Innovation strategies. Innovation strategies determine the intensity of the innovation process. Here are some of the innovation strategies:
-
Proactive Innovation Strategy
Proactive innovation is an outcome of rapid technological development and shorter economic cycles. It focuses on creating a new market niche and customer. They are their competitors.
Therefore, they step into the market intending to create disruption. For eg: Apple.
-
Active Innovation Strategy
Active Innovation is a defensive strategy against competitors. It’s mainly upgrading current technology to respond to rapid market changes.
The innovators drive for medium to low risk. So, the companies invest a good deal in research and development. For Eg: Microsoft
-
Reactive Innovation Strategy
Reactive Innovation is a wait-and-see approach. They need not proactively seek to evolve the product. They wait to get evidence of the product’s success from the market.
So, they duplicate proven market innovation. Instead, they are operationally focused to adapt to business pressure. Thus, paving their way to survive in the market.
-
Passive Innovation Strategy
Passive innovators are ‘chillers’ of the market. They wait for a demand to arise. So, they don’t act until the customers demand changes in current products.
Their core approach is to produce as per customer’s reviews and expectations. Whereas a Proactive innovator searches for hidden expectations and responds to the market.
Process of Innovation Model
The Innovation Model process is the method of bringing an idea or invention into reality as a product. The innovation model should make the process economical and a great value driver.
In this we will go through the steps in the Innovation Model process:
-
Idea Generation
The first step is choosing a concept to develop. At the organizational level, it involves taking into account the customer’s and employees’ opinions. Before considering an idea, answering the reasons to develop the idea will give clarity in vision.
Therefore, along with internal advice, opinions of customers, partners, and suppliers will give direction to your Innovation process.
-
Screening
One can get a bunch of ideas. Will you implement them all? No, That’s impossible!!! Thus, screening of ideas will help to make the right choice of ideas.
So, measuring the benefits and potential risks of ideas while screening will determine the Business idea viability.
-
Experimentation
As the right idea is selected. But will it be accepted by customers? Will they approve the pricing? Is it suitable for customers?
All these questions will be answered when you do a pilot test in your target market. If the idea is too complex or too early for the current market, the implementation should be dropped.
Even if the target market accepts your product, one should not haste to release the product immediately. Instead waiting for the right time to launch the project will increase the chances of winning in the market.
-
Commercialization
If you reach here, that means you have survived all the previous battles. Here your focus is to increase product awareness. Product awareness should be accompanied by a persuasive approach.
Most often, customers are not even aware that they needed this innovation. Thus, demonstrating its benefits and being specific about its usage will attract customers.
-
Implementation
Here the focus is to build the reality of the idea. It includes production, operation, logistics, marketing, selling, and taking consumer feedback.
Hence, building relations with investors, suppliers, customers, government, etc. to implement the innovation.
Innovation in Business Models
Business Model Innovation is a strategy in itself. As we know, the Business Model is the framework about how a company creates and delivers the needed value to customers.
Thus, Innovation in Business Model refers to upgrading the business model of the organization. It can depict changes in revenue streams, up-gradation of value proposition, changes in cost structure, etc.
Business Model Innovation aims to drive competitive advantage, value creation, and profitability.
But which type of Business Model Innovation will drive the results? To answer this, BCG has developed the following four approaches to ease your decision process:
-
The Reinventor Approach
The reinventor approach is followed during the slow growth of the business. It’s the best choice to go for when the market response is uncertain.
The company should adopt this approach to reinvent its business model. Thus, ensuring alignment of activities to satisfy customer and market needs.
-
The Adapter Approach
The approach is adopted when a business fails to face market challenges. Adapters should focus their model on persistent experimentation. In addition, this will help to find a successful path while surviving in the market.
-
The Maverick Approach
As the name says, it follows an independent-minded approach. They select their successful core business to apply the innovation. Mavericks aim to disrupt the market. So, they seek to bring revolution in the industry and drive business growth.
Search Active-Investors Across The World At One Place and Get Funding For Your Startup Today.
Learn More
-
The Adventurer Approach
The approach insistently operates to expand its business territory & capture adjacent markets. The adventurer’s exploration is aspiring for breakthrough growth. So, they have to be careful in their game of exploring new markets.
Here are some of the wonderful examples of Business Model Innovation:
- Zara’s
secret sauce is they produce where the sale is made. They follow the tight supply chain right from designing to the final production of clothes. Thus, the lead times are shorter in length and sold-out merchandise gets filled up easily.
- IKEA
follows
a
n uncomplicated business model. It is owned by a charitable non-profit organization. Thus enjoying the benefits of reduced taxes & hostile takeover. This is their magic potion to produce inexpensive furniture.
- Airbnb
operates with zero inventory. The idea is to connect the world of sellers with the world of buyers. So, their focus is on providing a good user interface and improving usability with new upgrades.
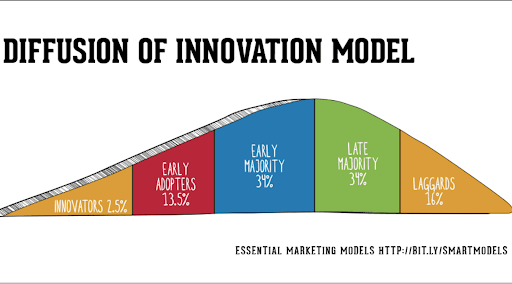
Understanding Diffusion of Innovation Models
Diffusion refers to a pattern that innovation or product takes to expand in the market. The pattern understands how the customers engage with the product right from awareness to final adoption.
Everett M. Roger coined different terms for each group of adopters. The following categorizations are based on the characteristics of each group:

-
Innovators:
This group explores new ideas, new practices, or new technologies. They are open to taking risks with emerging new technologies. Hence, they have high financial liquidity & broad networking with other innovators.
-
Early adopters:
Early adopters are the opinion leaders. They make discrete discreet choices. They are judicial in their activity of engaging with products.
Their evaluation helps in making improvements to the products. Therefore, their reviews act as a guide in making required changes to improve the output.
-
Early Majority:
They adapt to market innovation after a brief period. They come into the picture after innovators and early adopters. So, the early majority engage and observe the reviews of the product before adopting the innovation.
-
Late Majority:
They are less active adopters in the process. They have a sense of skepticism in their mind. Also, they adopt innovation only if they get a strong positive feeling to purchase the product.
So, they do thorough research and look for shreds of evidence before making the choice.
-
Laggards:
These are the lazybones. They adapt to innovation extremely late. They will read the other’s opinion about it before adopting it.
A Marketer needs to understand the behavior of these various adopters. So, examining their behavior will allow you to influence their actions. Thus benefiting in creating strategies to generate an impact to acquire customers.
Conclusion:
To survive the competitive business world, simply building a product is not sufficient. Adopting the culture of developing lucrative Innovation models will make your business a market leader.
Though it comes with a big risk, the benefits are worthwhile. The company should focus on a consolidated approach to market needs, technology, and cost-benefit analysis while implementing innovation.
Therefore, following a systematic approach and using proven methods generates sustainable innovation models.
Overcome The Challenges In Financial Consolidation, With The Help of Our team of experts
Click Here















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


