How to switch back networking to /etc/network/interfaces on Ubuntu 20.04 Focal Fossa Linux
This article will explain how to switch back networking from NetPlan/CloudInit on Ubuntu 20.04 Focal Fossa Linux to yet now already obsolete networking managed via /etc/network/interfaces.
In this tutorial you will learn:
- How to revert to eth0..n network naming convention
- How to install
ifupdown - How to remove CloudInit
- How to enable networking daemon
WARNING
Switching back from NetPlan/CloudInit to the now obsolete networking daemon is not supported nor recommended as you might end up with a broken system.
How to switch back networking to /etc/network/interfaces on Ubuntu 20.04 Focal Fossa Linux
Software Requirements and Conventions Used
Software Requirements and Linux Command Line Conventions
Category
Requirements, Conventions or Software Version Used
System
Installed Ubuntu 20.04 or upgraded Ubuntu 20.04 Focal Fossa
Software
N/A
Other
Privileged access to your Linux system as root or via the sudo command.
Conventions
# – requires given linux commands to be executed with root privileges either directly as a root user or by use of sudo command
$ – requires given linux commands to be executed as a regular non-privileged user
How to switch back networking to /etc/network/interfaces on Ubuntu 20.04 step by step instructions
- First step is to install tools to configure network interfaces
$ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install ifupdown net-tools
- Next, change from current
enp0s3to old network interfaces naming conventioneth0. To do so with administrative privileges edit the/etc/default/grubfile anf change the following line:FROM: GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="" TO: GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="net.ifnames=0 biosdevname=0"

Edit Grub boot to change to old network interfaces naming convention eg.
eth0Once ready update Grub with:
$ sudo update-grub
- Reboot your system:
$ sudo reboot
- As root or any administrative user edit the
/etc/network/interfacesfile and seteth0network interface to obtain the IP address from DHCP:source /etc/network/interfaces.d/* # The loopback network interface auto lo iface lo inet loopback # The primary network interface allow-hotplug eth0 iface eth0 inet dhcpCheck this article if you need to set your network interface to a static IP address.
- Restart
eth0interface:$ sudo ifdown --force eth0 $ sudo ifup eth0
NOTE
Network restart via/etc/init.d/networkingis not functional. To restart your network use theifdownandifupcommands as shown above. - At this stage you should have your
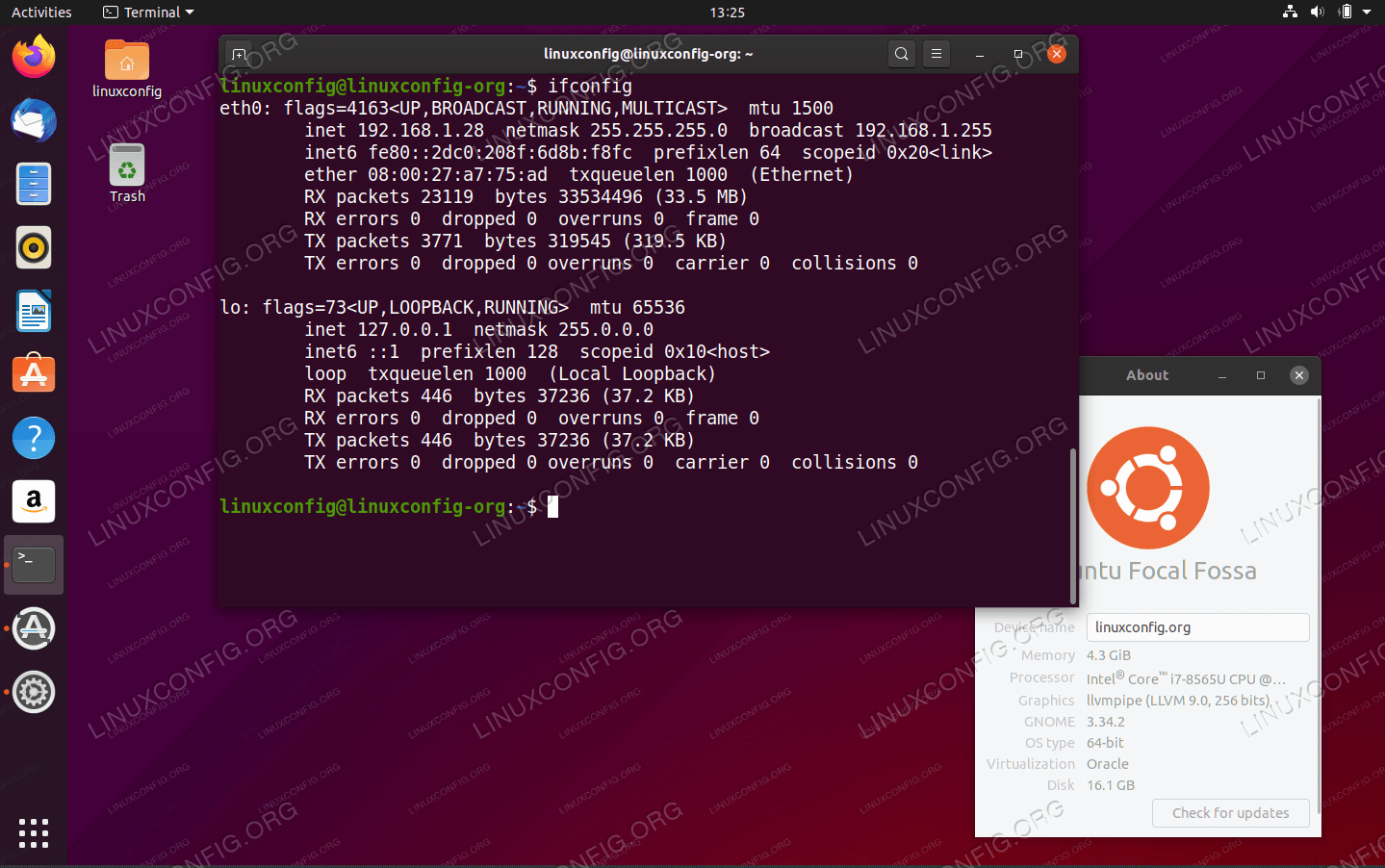
eth0configured. Useifconfigcommand to check the networking interface configuration:ifconfig eth0: flags=4163 mtu 1500 inet 192.168.1.28 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.1.255 inet6 fe80::2dc0:208f:6d8b:f8fc prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20 ether 08:00:27:a7:75:ad txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet) RX packets 22820 bytes 33504917 (33.5 MB) RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 3446 bytes 282861 (282.8 KB) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0 lo: flags=73 mtu 65536 inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0 inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10 loop txqueuelen 1000 (Local Loopback) RX packets 409 bytes 34213 (34.2 KB) RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 409 bytes 34213 (34.2 KB) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0 -
First disable and stop Configure DNS resolution to eg.
8.8.8.8nameserver:$ sudo unlink /etc/resolv.conf $ sudo echo nameserver 8.8.8.8 >> /etc/resolv.conf
- Let’s perform soul cleanup. Remove cloud init package:
$ sudo dpkg -P cloud-init $ sudo rm -fr /etc/cloud/
Disable and stop systemd-resolved service:
$ sudo systemctl disable --now systemd-resolved















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


