Gain a Better Understanding of the COSO Enterprise Risk Management…
As discussed in our previous blog, Enterprise Risk Management: What Is It and How Can It Help Your Organization, we looked at the definition of Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) and the three guiding frameworks for a better understanding of the topic.
ERM is an ongoing process of planning, organizing, and leading an organization’s actions to support its goals without setbacks from avoidable obstacles. Understanding these ERM frameworks and how they are implemented can assist organizations in making informed, risk-based strategic decisions.
Turning our attention to the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) ERM Framework, below is a deep dive into the components and principles that make up the foundation of the framework. With an understanding of the COSO ERM Framework, you can better gauge how this risk management framework can maximize value in your organization.
Mục Lục
The Components of the COSO ERM Framework
The 2017 COSO ERM Framework is built upon the idea of interrelated components and principles. The ERM components and principles are meant to be the ‘DNA’ of the organization, providing the foundation that allows organizations to maximize value by mitigating risk. The ERM components should have a direct relationship with an organization’s mission and core values. Below are the five ERM components:
- Governance & Culture: Sets the organization’s tone from the top down, establishing oversight responsibilities and setting the desired culture.
- Strategy and Objective Setting: Based on the risk appetite, performance indicators are created and dictate day-to-day activities.
- Performance: The identification and assessment of risks that may impact performance and selecting mitigating techniques for the identified risks to evaluate if the current strategy is working.
- Review & Revision: Review of performance in relation to targets to determine how well the ERM is working and if any changes are necessary.
- Information, Communication, & Reporting: Constant review and communication of ERM impacts using both internal and external information.
The Strategy and Objective Setting, Performance, and Review and Revision components represent avenues to implement processes within the organization, while the Governance and Culture and Information, Communication, and Reporting components represent support pillars that guide the success of ERM framework.
The Principles of the COSO ERM Framework
A COSO ERM Framework consists of 20 principles that span across the five components. Each principle is meant to represent the range of inputs needed for each respective component to properly drive the decision-making process from staff to upper management. The following identifies the 20 principles and their relationship to each of the components.
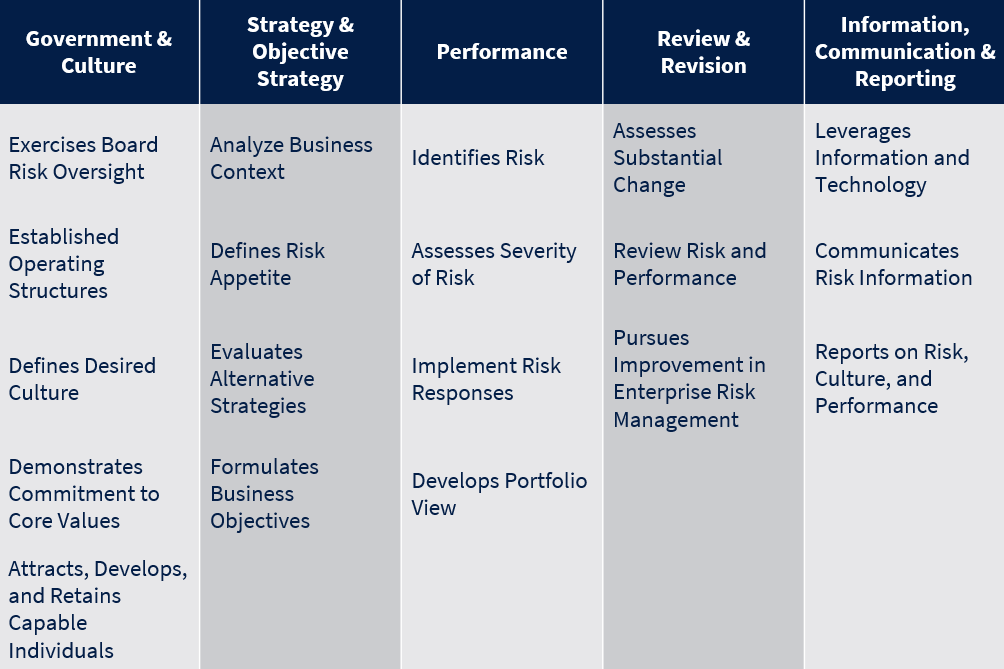
Governance & Culture (Principles 1-5): Organizational culture is at the core of a successful COSO ERM program. The Governance & Culture principles provide guidance for an organization to select a representative, or independent board, that will drive the overall culture of the organization. The Board’s leadership and direction reinforces efficient behavior and develops incentives to retain capable human capital.
Strategy & Objective Setting (Principles 6-9): Understanding the overall risk landscape that an organization operates within is crucial to overall strategy and objectives. The Strategy & Objective Setting principles provide context for an organization’s business environment, which helps identify and define a risk profile that will be followed in pursuit of the organization’s goals. Based on its risk profile, the organization should establish business objectives that align with both its goals and risk profile. An organization should always look to evaluate alternate strategies and potential impact on risk profiles.
Performance (Principles 10-14): Identifying and understanding the impact of specific risks that may impact the organization are vital to mitigating risks that can hamper its ability to achieve goals. The Performance principles allow an organization to specifically identify and prioritize risks that may affect its operations/business. Based on its risk profile, an organization can take a more conservative or aggressive approach to mitigating or accepting identified risks.
Review & Revision (Principles 15-17): Once an organization applies a COSO ERM program, it should consistently review its performance against the established framework. Business environments change and the evaluation of the potential impacts of those changes should be addressed within the ERM program to ensure success of the established framework. The overall risk portfolio, compared against both the success and failure of the business, should be monitored and updated to ensure the ERM framework stays relevant to the needs of the organization.
Information, Communication, & Reporting (Principles 18-20): A COSO ERM Framework is only as effective as the systems in place to monitor, communicate, and report on the status of the risk profile across the organization. This reporting ability allows the organization to make the best data driven decisions that will help achieve long-term goals. Leveraging the improvement of IT system capabilities, paired with a targeted review process, will allow organizations to be agile in the decision-making process, as an effective ERM program relies upon a fluid approach to adapt with a shifting business environment.
These components and principles allow management and employees to focus on separate aspects of ERM simultaneously. Each component addresses different organizational needs, and management can distribute the responsibility of achieving those different objectives across the organization. Management is responsible for defining and establishing programs and procedures that align with ERM components and principles. However, all employees, regardless of hierarchy, play a role in meeting the organization’s objectives.
Combining the Principles and Components of a COSO ERM Framework
As stated by COSO, to understand the relationship between the defined components and principles, an organization’s components can be thought of as what an organization sets out to achieve, while its principles are what is required from the organization to achieve its goals. The combination of an organization’s components and principles allows employees to understand the interconnectedness of the COSO ERM Framework. It is important for the entire organization, particularly those who are responsible to drive forward each principle, to understand how their specific role is a crucial piece that allows a COSO ERM framework to operate properly.
Effective and successful COSO ERM programs may not move linearly where there is a chain reaction of cause and effect. COSO ERM programs are a multidirectional, on-going process where objectives and components can affect each other. It is important for an organization to understand the relationships between COSO ERM components and principles because this correlation can impact the effectiveness of the overall COSO ERM program.
When designing and implementing a COSO ERM program, it is critical that the organization establishes a clear picture of its mission, vision, and core values (overarching values). Without this fundamental understanding, it can be difficult to ensure that the organization’s strategies and objectives align. Misaligned values can lead to improper strategies and objectives, and misaligned strategies and objectives can impact a framework’s ability to operate properly. Once the organization aligns its overarching values to its strategies and objectives, an effective COSO ERM Framework can help monitor and re-evaluate the organization’s performance, balancing risk to maximize performance.
Implementing an ERM to Maximize Value
At the end of the day, organizations operate to provide value to their internal and external stakeholders. At its core, an ERM framework exists to provide the organization, regardless of industry or size, an efficient way to identify, measure, and adapt business practices to provide the most value to its stakeholders.
A one-size-fits-all ERM framework is not ideal when implementing an ERM program, and it is the responsibility of management to understand the components and principles of the ERM framework to implement the practices that make the most sense for the organization and its risk tolerance. Providing value to stakeholders correlates with management’s ability to make the right decisions that mitigate risks that may have a negative impact on the organization reaching its goals. With an established ERM program, the organization can be positioned to navigate the challenges that pose a threat to its operations.
In our next blog, we will take a deep dive into the International Organizations for Standardization (SIO) 31000 Framework. If you have any questions, please reach out to our team who would love to speak with you about your organization’s risk management needs.
















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


