Everything you need to know about Trade Agreements – ResearchFDI
International trade is a critical part of a countries’ economy and prosperity, it allows for markets to expand, and countries to gain access to goods and services that would otherwise not be available.
Trade agreements help reduce the barriers and restrictions that come with international trade, which both encourages and makes international trade easier for the countries involved. Not only do they facilitate trade between the member countries, but trade agreements also fuel economic growth, encourage investment, help resolve behind-border barriers that impede the flow of goods and services, and aid in improving the rules that affect issues such as intellectual property, e-commerce and government procurement.
What is a trade agreement?
A trade agreement is a contract, agreement, or pact that occurs between two or more countries concerning their trade relationship. International trade is commonly regulated by barriers of several types, including tariffs, nontariff barriers, and prohibitions. Trade agreements are a way for countries to form an agreement on how they would cooperate to mutually benefit in their international trade and investments.
Trade agreements will occur when two or more countries agree on the terms of trade between them. These agreements can happen unilaterally (offered by one country to another), bilaterally (between two countries) or multilaterally (between multiple countries).
While there are multiple different types of trade agreements, the most common agreements are free trade and preferential trade agreements. These agreements are signed with the goal of eliminating trade barriers and facilitating trade between the signing countries.
Free Trade Agreements (FTA)
Free trade agreements are agreements that include trade in services and investment provisions as well as remove both tariff and non-tariff barriers to trade. These are interchangeably referred to as Regional Trade Agreements (RTAs) by the World Trade Organization, as a generic name for all reciprocal agreements such as customs unions, however they do not have to include members from the same region.
Preferential Trade Agreements (PTA)
These deals fall under the scope of FTAs but include a Generalized System of Preferences scheme. This allows signing countries to grant preferential tariffs on imports as well as allowing for other non-reciprocal agreements. These are also often referred to as partial scope agreements, as they include agreements that remove barriers to trade between members and offer preferential access to markets on a limited number of goods.
How many trade agreements are there?
With the advances in transportation and digital technologies that have occurred in recent decades, trade has expanded significantly. FTAs have significantly aided in expanding the global market through reducing various trade barriers.

(Graph 1: RTAs Currently in Force)
This also means that there has been a rapid increase in the number of FTAs (RTAs) in place. The World Trade Organization (WTO) reports that in 2022 there are 355 RTAs currently in force. There are also over 500 cumulative notifications of RTAs in force, meaning that WTO members have either notified participation in one or more RTAs in force or the accession of new parties to an agreement that already exists.
According to the WTO the EU-27 countries are some of the countries with the most FTAs in the world, with approximately 46 agreements in force each.
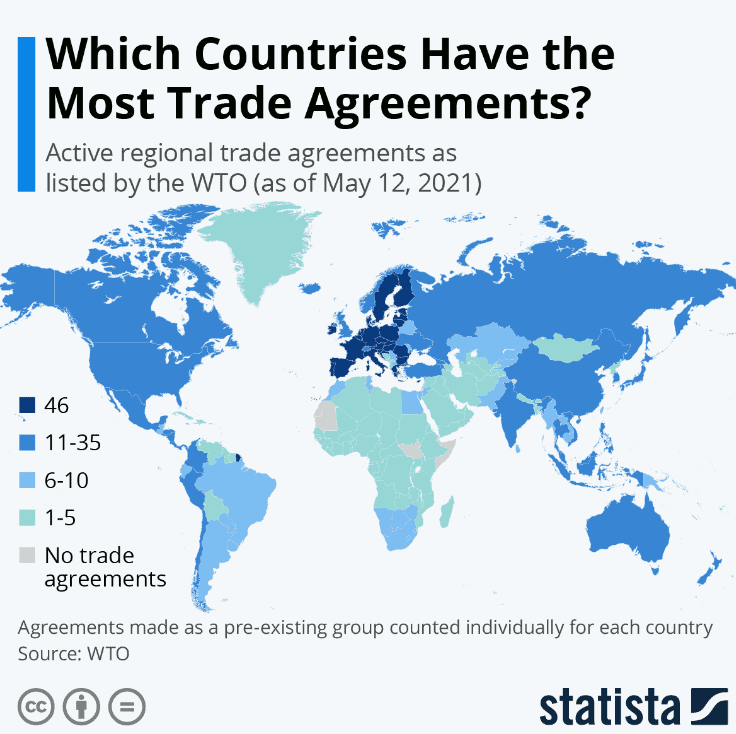
(Map 2: Which Countries have the most trade agreements?)
The EU countries are followed by the UK, who even after their exit from the EU, still has 35 FTAs currently in force. The US was reported as being part of 14 FTAs, the majority of which were bilateral agreements.
The largest trade agreements today
While there are hundreds of unilateral, bilateral and multilateral trade agreements worldwide, the largest enforced today are the following four multilateral FTAs;

(Map 2: The Four Largest Trade Agreements Today)
European Union (EU)
The European Union (EU) is an economic and political union between 27 European countries. Originally created in 1958 between six countries, the agreement has expanded over the decades and now includes Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Republic of Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain and Sweden. This is a multilateral FTA that enables goods, services, money and people to move freely among its members.
United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA)
The United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) is a multilateral FTA between Canada, Mexico, and the United States that entered into force on July 1, 2020. It replaced the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) implemented in 1994. This is a multilateral free trade agreement that was created with the intention of benefiting trade flows in North America while bolstering channels for investors, exporters, importers, non-governmental groups, and governments to seek to resolve problems and disputes.
Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP)
The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) is a is the newest multilateral FTA of these four. It entered into force on 1 January 2022 for ten original parties: Australia, New Zealand, Brunei Darussalam, Cambodia, China, Japan, Laos, Singapore, Thailand and Vietnam, later adding South Korea and Malaysia to the agreement. This multilateral free trade agreement will create the world’s largest trading bloc. It was created with the aim of establishing a modern, comprehensive, high-quality, and mutually beneficial economic partnership that will facilitate the expansion of regional trade and investment and contribute to global economic growth and development.
African Continental Free Trade Agrement (AfCFTA),
The African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) is a multilateral FTA that encompasses most of the continent of Africa. The agreement was established in 2018, and has 43 parties and another 11 signatories, making this agreement the largest free-trade area by number of member states, after the World Trade Organization, and the largest in population and geographic size.
In conclusion
The largest and most common trade agreements are often multilateral FTAs that include multiple signing parties. However, there are many different types of trade agreements, and hundreds of unique agreements are enforced today.
Trade agreements are a crucial aspect of international trade. They play an important role in gaining access to new markets, increasing GDP, and inviting new foreign investments. Without trade agreements, the global market we have today would not be possible, instead we would see a much more stagnant and non-competitive global market.















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


