Business Model Canvas – Comprehensive Guide with Examples
The Business Model Canvas (BMC) is useful for people looking to create a model or adapt the structure of their organization or development idea. It enables you to create value out of new ideas. Simply having a good idea for a new product or service is not enough if you can’t answer some key questions about how to take it forward.
The Business Model Canvas offers a concise tool for thinking through the business and keeping the key points highly visible to you, your team and your other stakeholders. It is a graphical, one-page framework that allows you to design, describe and/or challenge your business model.
Leading global companies such as MasterCard, General Electric, Adobe, and Nestlé, use the Canvas to manage strategy or create new growth engines, while start-up businesses, schools, development organizations, and other enterprises use it in their search for the right business model.
Why Use Business Modeling Canvas?
It is often very difficult to think through every single influence on your ideas and plans: how can you explain what you do, why you do it and how you do it in a simple and structured way? When you are planning or looking back at an initiative it is useful to look at how you are doing things now and how you could do them better in the future.
To get the most value from the strategic nature of the inputs and outputs, you may want to consult with many other people, both within and outside your organization. When you come to use the Canvas, you’re likely to make several revisions until you are happy with it. Business Model Canvas creates a complete overview of your strategy which includes:
- The products you should offer
- The people you should focus on
- The paths you should take
- The resources you should use to make your idea as successful as possible
Taking the time to sketch out your model and explore it in detail enables you to identify both its advantages and drawbacks so that you can make an informed decision about whether or not to commit resources to take it forward.
The Structure of Business Model Canvas
The Business Model Canvas is a single-page overview that lays out both what you do (or want to do) and how you go about doing it, enabling structured conversations around management and strategy. This visual format is useful for both existing and new organizations and businesses.
Look at the Business Model Canvas template below; you will see nine key elements. Let’s take a few moments to understand each of these elements in the sections below:
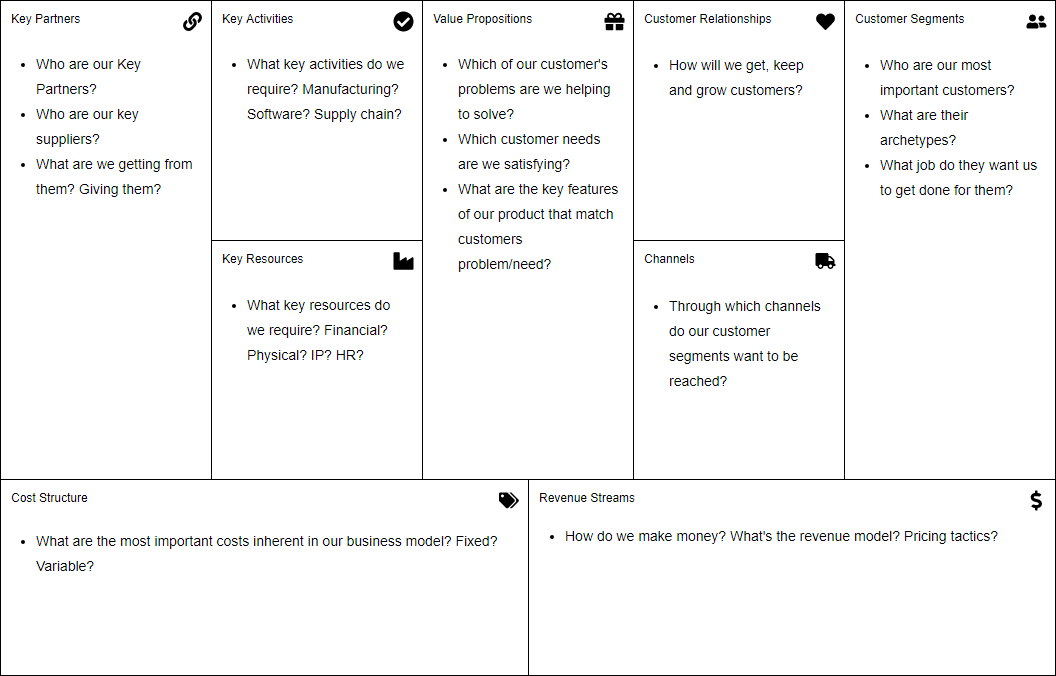
1. Value Propositions: these are the different products and services which the business offers and which create value in each of the customer segments. Value proposition enables the customers to go for the product or service that is being offered as compared to the others. It is the one that attracts the customers and which makes the customers return. Some of the characteristics of value proposition include the newness, customization, uniqueness, and quality of the product or service. Price, design, brand, and accessibility are some of the key attributes of a value proposition.
Guiding Questions:
- What is unique that is available to customers?
- Why do customers buy from your business?
- Which classes are you creating values for?
- What unique service do you offer to your customers?
2. Customer Segments: This refers to the market which the service or product is offered to. A customer segment is that part of the market targeted by the organization. In any business model, customers are at the center of the business. There is a need to classify these customers, identify their needs and satisfy the customers for the business to survive. There are different customer segments which include based on different market characteristics.
Guiding Questions:
- Who are the major customers of your business?
- What do customers say about your business?
- Are there any important customers?
3. Channels: These are the means by which the goods and services reach customers. Recently modern technologies have been used to easily and effectively reach customers.
Guiding Questions:
- What channels are used to reach customers
- What alternatives are available to reach customers?
4. Customer Relationships: this involves all the activities that are undertaken to motivate and impress customers. Different market segments have different relations which the business should identify and maintain.
Guiding Questions:
- What is been done to maintain customers
- What incentives and rewards are available for customers?
5. Revenue Streams: includes the means and sources that the business gets income from. These are the different ways that an organization would use to get revenue. Examples could be advertising, asset sale, subscription fees and renting.
Guiding Questions:
- What are the main revenue source
- What is the business doing to get more income?
6. Key Resources: Key resources are the main utilities that the business has and uses to achieve customer satisfaction. It includes the equipment, pool of assets and other products that the business uses to ensure that there are production and service delivery.
Guiding Questions:
- What are the main assets and resources for the business?
- What do you need to be able to satisfy customers’ needs?
7. Key Partnerships: includes all the key stakeholders that the business requires to be able to perform its activities. These may include manufacturers, suppliers and other businesses in the same category of other entities that a business can collaborate with.
Guiding Questions:
- Who are the main stakeholders?
- What are the motivations for the partnerships?
8. Key Activities: these are the major functions of the organization. These are key activities that a business engages in, to ensure survival in the market.
Guiding Questions:
- What are the main functions of the business?
- What does your business do?
9. Cost Structure: describes all costs incurred to operate a business model. Such costs include the costs incurred during the creation and delivery of value, enabling customer value and getting income.
Guiding Questions:
- What are the business’ major cost drivers? How are they linked to revenue?
- What are the main expenses for the business?
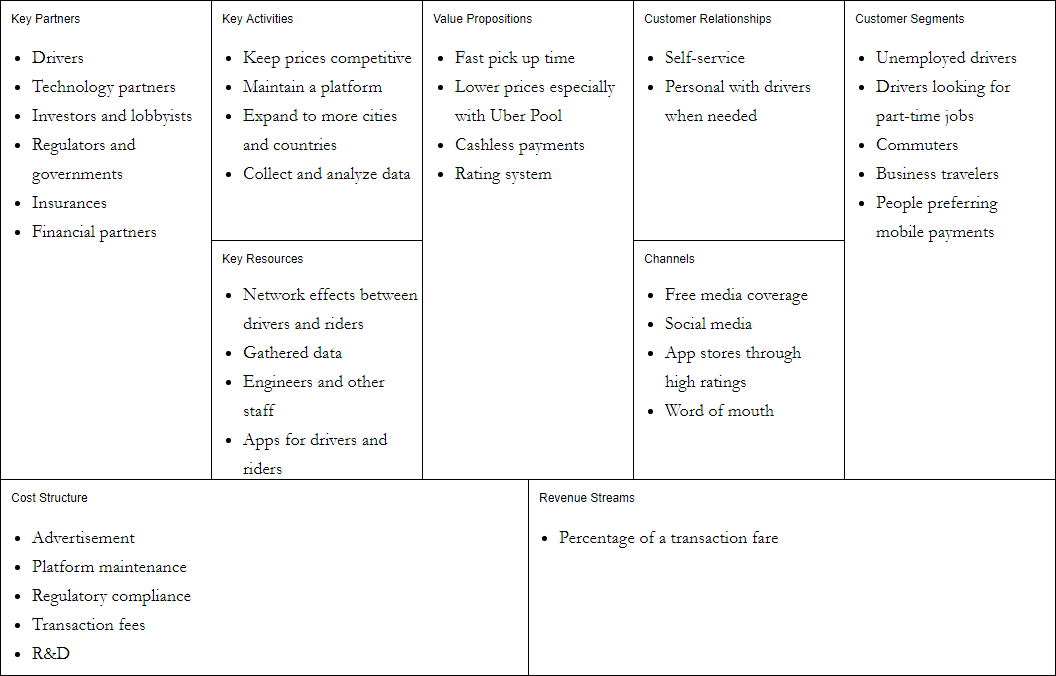
Business Model Canvas Example – Uber Platform
Business Model Canvas provides a holistic view of the business as a whole. It is crucial when it is used in a comparative analysis regarding the impact of company investments and other contributing factors.
Be creative and write your ideas down on colorful memo notes using the Business Model Canvas tool.
- Create a blank Business Model Canvas.
- Choose a memo you wish to use then drag and drop it onto the drawing canvas.
- Customize the memo and sticky via the Format panel.
- When you are done, save it (File > Save as) to our cloud repository for future access. You can also export your diagram into an image (PNG, SVG, JPG, PDF and more) and share it with your co-workers.
Business Model Canvas helps you discover who your clients are, search for a solution for your target customers, and explore what they are interested in and why they would choose your product. In this Business Model Canvas example below, you can see the Uber segmentation is also geo-demographic as the service seems to employ drivers who live in areas with the highest unemployment rates.
Edit this Diagram















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


