What is network-attached storage?
Hardware
Preconfigured storage software is installed on dedicated hardware. Known as a NAS box, NAS unit, NAS server, or NAS head, this hardware is essentially just a server containing storage disks or drives, processors, and random-access memory (RAM).
Software
The main differences between NAS and general-purpose server storage lies in the software. NAS software is deployed on a lightweight operating system (OS) that’s usually embedded in the hardware. General-purpose servers have full OSs that send and receive thousands of requests every second—a fraction of which may be related to storage—while a NAS box sends and receives only 2 types of requests: data storage and file sharing.
Protocols
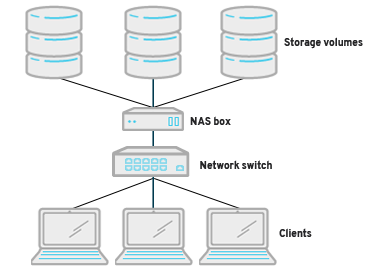
A NAS box is formatted with data transfer protocols, which are standard ways of sending data between devices. These protocols can be accessed by clients through a switch, which is a central server that connects to everything and routes requests. Data transfer protocols basically let you access another computer’s files as if they were your own.
Networks can run multiple data transfer protocols, but 2 are fundamental to most networks: internet protocol (IP) and transmission control protocol (TCP). TCP combines data into packets before they’re sent through an IP. Think about TCP packets as compressed zip files and IPs as email addresses. If your grandparents aren’t on social media and don’t have access to your personal cloud, you have to send them vacation photos via email. Instead of sending those photos 1-by-1, you can bundle them into zip files before sending them over. In similar fashion, TCP combines files into packets before they’re sent across networks through IPs.
The files transferred across the protocols can be formatted as:
- Network File Systems (NFS): This protocol is regularly used on Linux and UNIX systems. As a vendor agnostic protocol, NFS works on any hardware, OS, or network architecture.
- Server Message Blocks (SMB): Most systems that use SMB run Microsoft Windows, where it’s known as “Microsoft Windows Network.” SMB developed from the common internet file sharing (CIFS) protocol, which is why you might see it referred to as the CIFS/SMB protocol.
- Apple Filing Protocol (AFP):A proprietary protocol for Apple devices running macOS.















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


