What is a Network Security Key in Home Wireless Networks?
Written By
It is fair to say that there are few things more important to your daily security than the security of your Internet connection and hence your privacy and sensitive data.
Everyone has heard horror stories of their information being stolen via covert means online, and nobody wants to be subject to the nightmares that can bring.
That means investing in the protection of your privacy and data, which in turn means looking into protecting your home wireless network as much as possible. This is where the WiFi Network Security Key comes into play.
I’m mentioning the wireless network here because nowadays almost all homes have a WiFi network running for all family members to enjoy fast Internet access and information exchange.
Still, if you’re not a tech-savvy individual, you may have a basic idea of why it’s important to protect your privacy and data, but not know how to do so, or what any of these terms mean.
This guide can, thus, give a bit of a primer on that while filling you in on some of these terms, what they mean, and how to approach them.
Moreover, we’ll discuss in detail how to find your WiFi Network Security Key, what it is, how to change it etc.
What Is a Network Security Key?
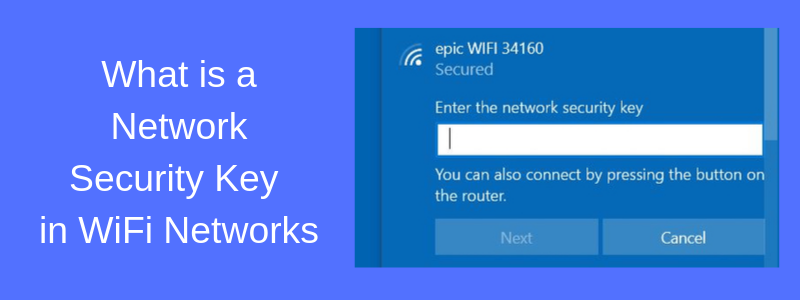
First thing’s first – what is the network security key shown in the picture below?
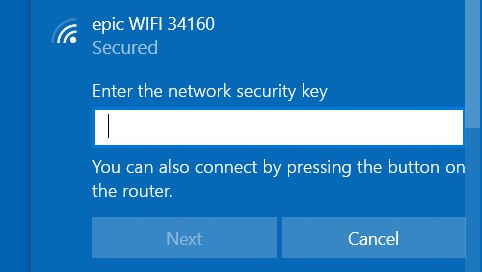
I’m sure you have encountered a window similar to the above (this is taken from my Win10 computer) when you try to connect to a WiFi network.
The short answer is that the “network security key” shown above is the password to your WiFi network.
Chances are, if you are reading this, you know what WiFi is. If so, you probably understand the importance of having a security key that keeps random people from having access to your network.
You want to make sure your network is password protected, and that’s precisely what your network security key allows. This must be a long and complex key (at least 12-14 random characters including alphanumeric symbols and special characters).
If you forget your network security key, you can typically find it on the router itself (some routers have a label on them with the key).
Moreover, if a member of your family or guest friend asks you to give them your network security key of your WiFi, you can find it from your computer as described below:
How to find your Network Security Key on Windows 10
Assuming you are already connected to your WiFi network, let’s see how to find the security key:
- Go to Bottom left of your windows screen > Type here to search > WiFi Settings
- Click to WiFi Settings and a new window will open. Scroll down to WiFi settings window and click on “Change Adapter Options” as shown below:
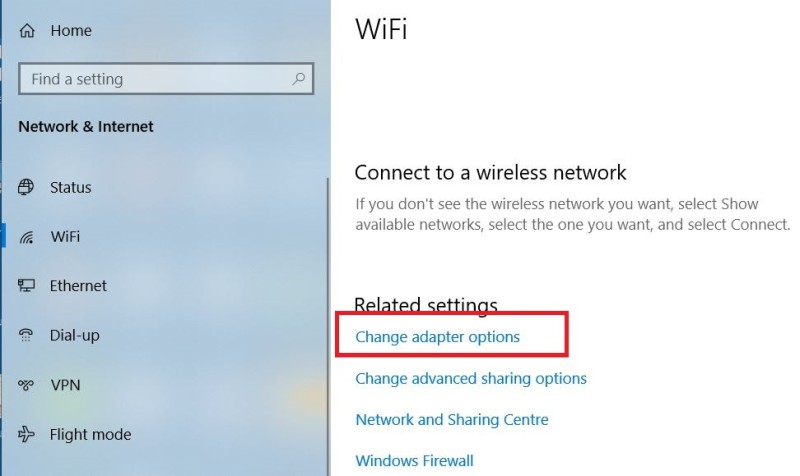
- A new window will open with all of your network adapters (wired and WiFi adapters). Right click on the WiFi adapter and select “status”
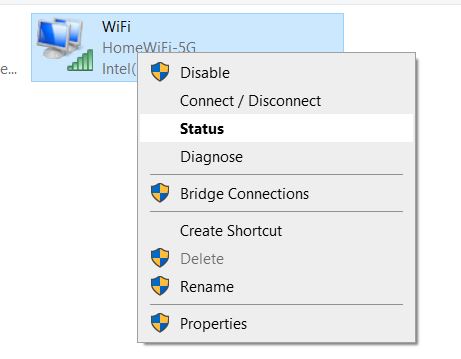
- At the new window, click to “Wireless Properties” as shown below:
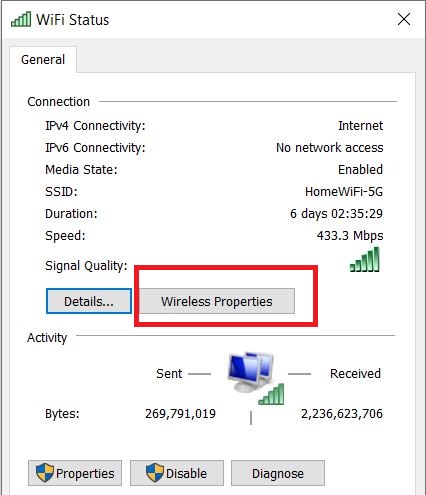
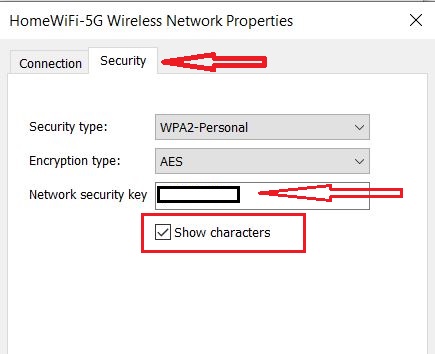
- At the new window, select the “Security” tab and also click “Show characters”. This will show the current Network Security Key of your WiFi network.
Types of WiFi Encryprion and Security Protocols
There are four main wifi security protocol standards – WEP, WPA, and WPA2 are the existing ones but there is also a new standard called WPA3 as we’ll discuss below.
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
WEP makes use of a 40-bit key for the purpose of encryption of wireless traffic. This is paired with another key, a 24-bit IV, which combines to give the 64-bit WEP key.
That said, WEP suffers from several shortcomings, including slow speed and weaker passwords.
While it was an important step instead of no-encryption in wifi, it is no longer considered a choice among those looking to safeguard their connection and data. In summary, DO NOT use WEP when selecting the security protocol on your router.
WPA and WPA2 (WiFi Protected Access)
WPA came next, and was intended to be a stopgap replacement for WEP to address its shortcomings. In that respect, it largely succeeded, offering faster and better encryption. Even so, it has since been outstripped by its intended successor, WPA2.
For example, WPA still makes use of the same RC4 stream algorithm which has had a history of being insecure and causing problems with WEP. That said, it does provide extra security in the form of TKIP.
By contrast, WPA2 uses AES encryption standard, an improvement over the instability and weaknesses of RC4. In addition, it replaces the TKIP used by WPA with CCMP. It is, thus, able to offer better and faster security than WPA, and is recommended over both that and WEP.
WPA3
That said, WPA3 has come out, and is superior to all of the above, offering the fastest and most secure encryption options yet.
WPA2 and WPA3, thus, remain the most secure options for WiFi encryption, with WPA to be avoided but it is still occasionally used.
You’ll, thus, want to take these factors into consideration and choose one of these (preferably WPA2 or WPA3) when encrypting and protecting your WiFi connection. Note however that currently not all wifi routers support WPA3.















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


