What is RTT(Round Trip Time)? – GeeksforGeeks
RTT also called round-trip time/delay is a crucial tool in determining the health of a network. It is the time between a request for data and the display of that data. It is the duration measured in milliseconds. RTT can be analysed and determined by pinging a certain address. It refers to the time taken by a network request to reach a destination and to revert back to the original source. In this scenario, source is the computer and the destination is a system which captures the arriving signal and reverts it back.
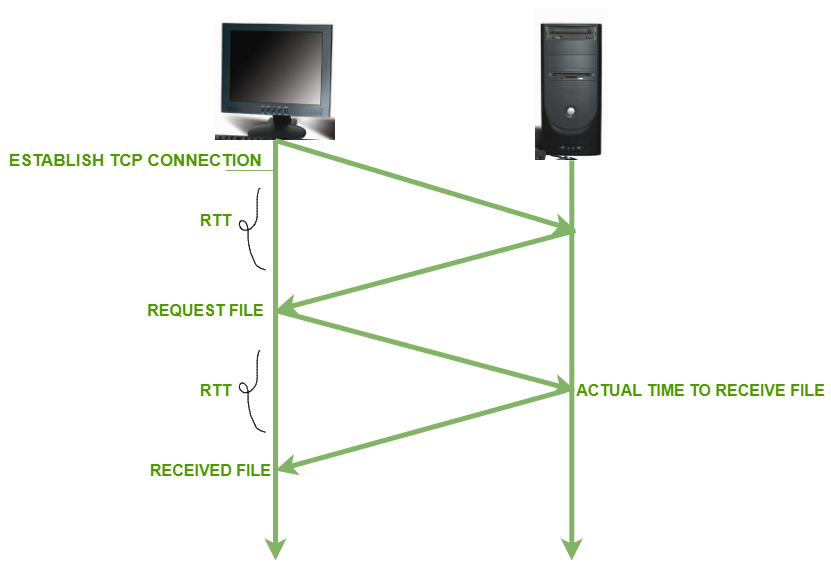
Figure – RTT Measurement
Factors that influences RTT:
There are certain factors that can bring huge changes in the value of RTT. These are enlisted below:
1. Distance, 2. Transmission medium 3. Network hops 4. Traffic levels 5. Server response time
Applications :
Round Trip Time refers to a wide variety of transmission such as wireless Internet transmissions and satellite transmissions. In Internet transmissions, RTT may be identified by using the ping command. In satellite transmissions, RTT can be calculated by making the use of Jacobson/Karels algorithm.
Advantages :
Calculation of RTT is advantageous because:
- It allows users and operators to identify how long a signal will take to complete the transmission.
- It also determines how fast a network can work and the reliability of the network.
Example:
Let us assume there are two users, one of which wants to contact the other one. One of them is located in California while the other one is situated in Germany. When, the one in California makes the request, the network traffic is transferred across many routers before reaching the server located in Germany. Once the request reverts back to California, a rough estimation of the time taken for this transmission could be made. This time taken by the transmitted request is referred to as RTT.
The Round Trip Time is a mere estimate. The path between the two locations can change as the passage and network congestion can come into play, affecting the total period of transmission.
Calculation of RTT :
Consider a topology where an appliance named “Exinda” is located between the client and the server.
The diagram shown below depicts how the concept of RTT works:
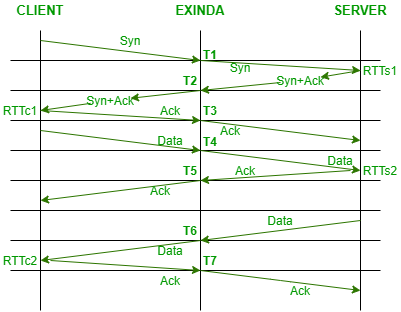
For the calculation of Average RTT, RTTS for server and client needs to be calculated separately. The performed calculations are shown below:
Server RTT: RTT1 = T2 - T1 RTT2 = T5 - T4 Client RTT: RTT3 = T3 - T2 RTT4 = T7 - T6 Average RTT: Avg Server RTT = (RTTs1 + RTTs2) / 2 Avg Client RTT = (RTTc1 + RTTc2) / 2 Avg Total RTT = Avg Server RTT + Avg Client RTT
Measures to reduce RTT :
A significant reduction in RTT can be made using Content Delivery Network (CDN). A CDN refers to a network of various servers, each acquiring a copy of the content on a particular website. It addresses the factors affecting RTT in the enlisted ways:
1. Points of Presence (PoP) 2. Web caching 3. Load distribution 4. Scalability 5. Tier 1 access
CDN have been largely successful in reducing the value of RTT and due to this, a decrease in RTT by 50% is achievable.
My Personal Notes
arrow_drop_up















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


