What is Network Monitoring? Why it’s important – ManageEngine OpManager
Mục Lục
Basics of Network Monitoring
Looking to start-off your network monitoring journey? Get your basics right, first!
Get started for free Schedule a live demo
What is Network Monitoring?
In today’s world, the term network monitoring is widespread throughout the IT industry. Network monitoring is a critical IT process where all networking components like routers, switches, firewalls, servers, and VMs are monitored for fault and performance and evaluated continuously to maintain and optimize their availability. One important aspect of network monitoring is that it should be proactive. Finding performance issues and bottlenecks proactively helps in identifying issues at the initial stage. Efficient proactive server monitoring can prevent network downtime or failures.
How to perform network monitoring effectively
For an efficient network monitoring, you need to cut-off the unnecessary load to the network monitor, at every step possible by:
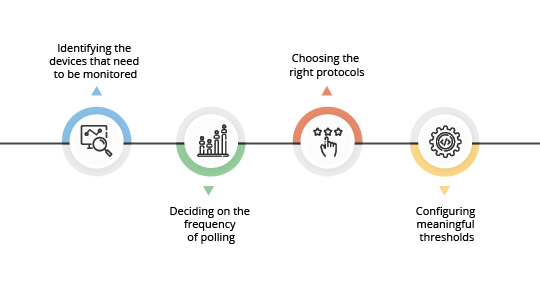
Monitoring essential network devices
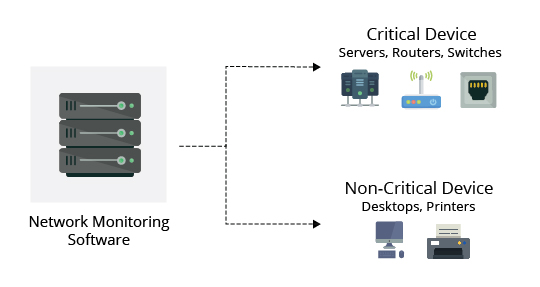
Faulty network devices impact network performance. This can be eliminated through early detection and this is why network device monitoring is of utmost importance. In effective network monitoring, the first step is to identify the devices and the related performance metrics to be monitored. Devices like desktops and printers are not critical and do not require frequent monitoring whereas servers, routers and switches perform business critical tasks but at the same time have specific parameters that can be selectively monitored.
Optimizing the network monitoring interval
Both the critical and non-critical devices however require monitoring, hence the second step, configuring monitoring interval. Monitoring interval determines the frequency at which the network devices and its related metrics are polled to identify the performance and availability status. Setting up monitoring intervals can help to take the load off the network monitoring and reporting tools and in turn, your resources. The interval depends on the type of network device or parameter being monitored. Availability status of devices have to be monitored the least interval of time preferably every minute. CPU and memory stats can be monitored once in every 5 minutes. The monitoring interval for other metrics like Disk utilization can be extended and is sufficient if it is polled once every 15 minutes. Monitoring every device at the least interval will only add unnecessary load to the network and is not quite necessary.
Choosing the right network protocol
With the devices identified and the monitoring intervals established, selecting the right network protocol is the next step. When monitoring a network and its devices, a common good practice is to adopt a secure and non-bandwidth consuming network management protocol to minimize the impact it has on network performance. Most of the network devices and Linux servers support SNMP(Simple Network Management Protocol) and CLI protocols and Windows devices support WMI protocol. SNMP is one of the widely accepted network protocols to manage and monitor network elements. Most of the network elements come bundled with an SNMP agent. They just need to be enabled and configured to communicate with the network management system (NMS). Allowing SNMP read-write access gives one complete control over the device. Using SNMP, one can replace the entire configuration of the device. The best network monitor helps the administrator take charge of the network by setting SNMP read/write privileges and restricting control for other users.
Setting up monitoring thresholds
Network downtime can cost a lot of money. In most cases, the end-user reports a network issue to the network monitoring team. The reason behind this is a poor approach to a proactive enterprise network monitor. The key challenge in real time network monitoring is to identify performance bottlenecks proactively. This is where thresholds play a major role in network monitoring application. Threshold limits vary from device to device based on the business use case.
Instant alerting based on threshold violations
Configuring thresholds helps in proactively monitoring the resources and services running on servers and network devices. Each device can have an interval or threshold value set based on user preference and need. Multi-level threshold can assist in classifying and breaking down any fault encountered. Utilizing thresholds, network monitoring alerts can be raised before the device goes down or reaches critical condition.
Primary factors to consider while monitoring network
Flexibility: For the customizations in network monitoring
Data becomes useful only when it is presented clearly to the right audience. It is important for IT administrators and users to know about critical metrics as soon as they log in. A network monitoring software should be flexible enough to provide an at-a-glance overview of the current status of your network, with critical metrics from routers, switches, firewalls, servers, services, application, URLs, printer, UPS and other infrastructure devices. Network monitor’s support for widgets to monitor the required specifics and real-time performance graphs can help administrators quickly troubleshoot problems and monitor devices remotely.
High availability: To ensure uninterrupted connectivity of a network monitor
What happens when your trusted network monitoring tool running on a server crashes or loses network connection? You will want to be alerted on this and also have the situation automatically remedied using a back-up/stand-by of another twin real-time network monitor application installation. High availability refers to the continuous availability of a network monitoring system. Every single network incident – device sickness, unhealthy bandwidth levels, DoS attacks etc., should be immediately brought to your notice so that counter-measures can be taken immediately.
Failover and fail-back functionality ensures an always-monitored network environment by utilizing a secondary standby server. If a failure occurs in the primary server, the secondary server is readily available to take over and the database is secure. This ensures a hundred percent network and device uptime.
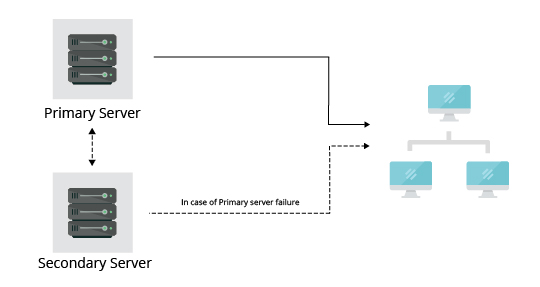
Benefits of the Failover system while monitoring network:
- Instantly recognize primary server failure.
- Immediate notification via email in event of a primary server failure.
- 100% uptime and uninterrupted network management.
- Automated, seamless switching between the Primary server to Standby server and vice versa.
Scalability: To extend the scope of network monitoring
Enterprises tend to expand with time to cope with the rising network demands and business operations. The constant addition of new devices to the network requires a network monitoring software that spots and adds them as soon as the devices are introduced to the network. Network monitors that are future-ready and scalable to any network infrastructure is what you need for the successful network monitoring.
On an Enterprise level, a network monitoring solution should allow you to deploy multiple probes in the same site or same network to distribute the monitoring load and offer enhanced scalability.
Security: To prevent unauthorized network access
The increased size and complexity of networks make it hard for the network admins to keep track of files and folders in the network, paving the way for malicious attacks or data breaches. It is a network monitor that should keep the network away from such threats. To achieve network security, network monitor lets you control the access level of individuals in the organization to the network monitoring tool, on a role basis. This prevents unwanted changes to the network and helps network admins stay on the same page. A network monitoring software should also ensure the authenticity of product files that are associated to the tool and external files that are originated from external sources, by conducting periodical checks to identify tampered files.
Multi-vendor compatibility: For the effortless enterprise network monitoring
In today’s hybrid network environment, where multiple vendors are into the play, a network monitor extending support to all the major vendors and device types is crucial especially for enterprise network monitoring. Each vendor will have unique OIDs which creates the need for multi-vendor backed network monitor to collect performance data of the network devices. For instance, OpManager, a potent network monitor, offers support to major vendors such as Cisco, HP, Huawei, Hitachi, IBM, and more.















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


