What is Network Latency and How to Improve It? [2023]
This guide takes a deep look at network latency and explores the possible ways to reduce it for a better end-user experience.
In this world wide web, data travels from one point to another, bringing delays. While it seems insignificant from a normal life perspective, it makes a whole lot of difference in how the internet operates.
What is Network Latency?
Simply put, network latency is the round-trip time it takes a signal to leave a user for the server and return.
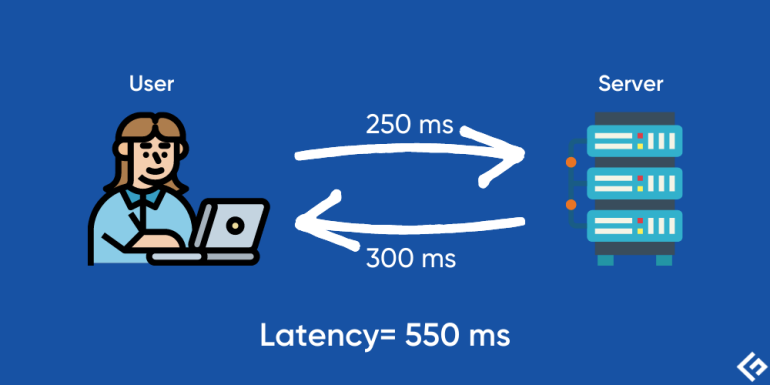
But it’s not as simple as it looks in the above image.
What did it miss were the junctions through which the signal hops between the two endpoints. This routing is the major cause of network latency.
It would help to know that latency is almost double of ping, which is the time taken for the data to move from the user to the server. Still, some use latency and ping interchangeably, which is conceptually wrong.
And though somewhat confusing to some, latency is different from throughput and bandwidth.
Zero-latency is what we all aim for. But the distance and the connections in-between induce unavoidable lag. Still, network admins target the lowest possible latencies for various internet applications such as gaming, video calling, etc.
Causes of Network Latency
The number one culprit of high latencies is the distance. Greater distance between the origin and the server means more intermediaries. These junctions have their individual bottlenecks adding a small number of delays to the overall latency.
Another major cause can be an unoptimized website. This may be caused by several issues like the presence of large media files, tracking cookies (from services like Google Analytics), poor web-hosting service, etc.
Besides, it can also be a user with inefficient hardware (like low RAM), causing high latencies.
Finally, every element in the network, like the cables, routers, server, client hardware, software, etc., add some lag.
Measuring Network Latency
Mục Lục
Traceroute
This is the most common way to measure it right from your computer. Open Command Prompt, and type tracert followed by the destination address.
For instance, tracert geekflare.com will give all the junctions from my computer on the way to the Geekflare website.
C:\Users\Hitesh Sant>tracert geekflare.com
Tracing route to geekflare.com [2606:4700:839a:d810:7339:41f:a5a:b5b7]
over a maximum of 30 hops:
1 <1 ms <1 ms <1 ms 2401:4900:1c1a:404d::1
2 7 ms 5 ms 6 ms 2401:4900:1c1a:8fff::1
3 8 ms 5 ms 6 ms 2404:a800:1a00:802::a5
4 36 ms 36 ms 37 ms 2404:a800::2
5 36 ms 37 ms 38 ms 2404:a800:0:29::b1
6 34 ms 45 ms 33 ms 2400:cb00:202:3::
7 33 ms 34 ms 33 ms 2606:4700:839a:d810:7339:41f:a5a:b5b7
Trace complete.The total latency, in this case, will be the average of the summation of individual columns, which indicate the round trip times (RTT) between consecutive hops.
Nirsoft Latency View
While the traceroute is handy for a single endpoint with less than 30 hops, Nirsoft Latency View reveals the lags of all outbound connections.
In addition, this completely free tool gives you the average latency value of all the connections to the same destination.
Take a look:

SolarWinds Traceroute NG
Traceroute NG is another excellent tool for running multiple latency tests aimed at a single server.

This keeps checking latency values until you stop. The dashboard gives you instant and average lag values for a specific destination.
Similarly, there are many utilities for finding out network paths and latency.
Effects of High Latency
You might be wondering why latency is so important. Not just gamers, our complete internet experience depends on it.
High latency values can make every internet-connected service load slow till the point the user switches to the computer.
For instance, would you use Facebook if it takes a good 30 seconds to load every time? Statistics show that each extra second in website loading translates into high bounce rates, and even a two-second loading time will result in almost 10% fewer users.
Increase this to seven seconds, and you’ll see a 32% drop in web traffic.
Not just the visitors, high lag values affect whatever you do online, be it video calls, presentations, payments, etc.
This will also shrink the data transferability per unit time (aka throughput) even if the network capacity (aka bandwidth) is substantial.
Conclusively, only low latency networks are useful, and network admins constantly try to bring this down to boost productivity.
Reducing Network Latency
While you can’t update or improve all of the networks between the endpoints, there are a few things to take care of.
The mechanism to optimize a network starts with targeting its biggest enemy–distance. The best practice is to host your business where you have the majority of the clients.
But in case you have a global clientele, then opting for a content delivery network (CDN) might just solve this. Beware, though there are free CDNs in the market, using them can negatively affect your web property.
So if you use one, it’s better to perform a website audit to verify the changes.
Regular updating of the software can be the next in line to improve high network latency. In addition, make sure your hardware is capable enough to utilize the full network potential.
Besides, wireless networks generally have a greater amount of lag. So, try to use wired connections wherever possible. Besides, going for best-in-class fiber networks will further help to minimize lag.
Additionally, using HTTP/2 also cuts down latency by simultaneously loading various page elements, among other things. You can check this by Geekflare’s HTTP/2 test.
Finally, try to implement data caching and optimize the media for a minimum lag.
Conclusion
Great user experience is a key to success for any organization. And if you are an online business, better take the speed aspect seriously.
But there are a few more things you should look at to optimize your website.















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


