Types of Electrical Plugs: Types, Uses, Features and Benefits
Mục Lục
Types of Electrical Plugs
Contact Companies
Please fill out the following form to submit a Request
for Quote to any of the following companies listed on
Get Your Company Listed on this Power Page
Introduction
This article takes an in-depth look at the types of
electrical plugs.
Read further and learn more about topics such as:
- What are Electrical Plugs
- Two-pronged and Three-pronged Plugs
- Types of Electrical Plugs
- Plug Adapters and Replacement Plugs
- And Much More…
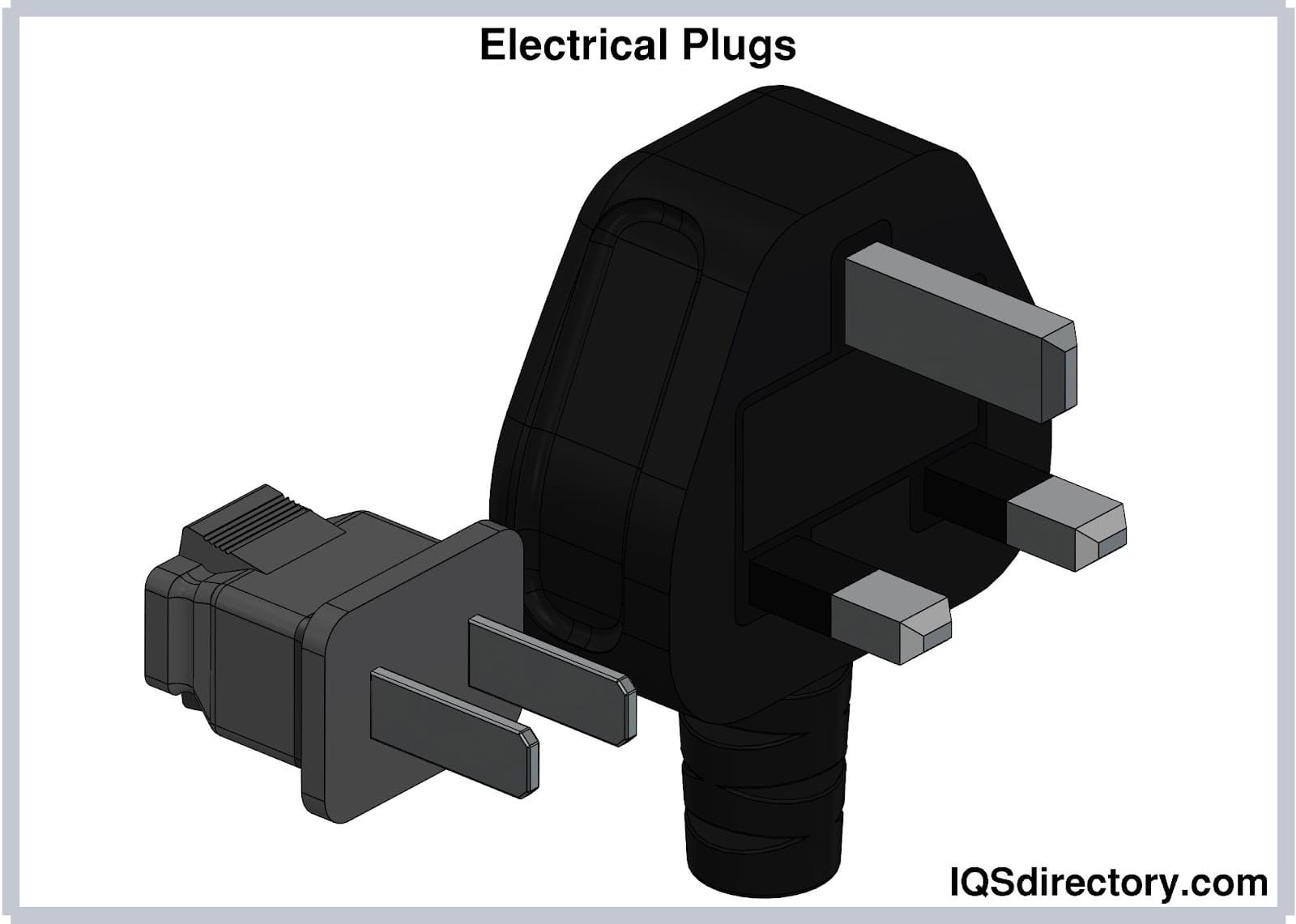
Chapter 1: What are Electrical Plugs?
Electrical plugs, commonly known as power plugs, are devices
responsible for supplying and drawing current from a receptacle
to the circuitry of an electrical appliance.
Electrical plugs consist of prongs or pins supported by plastic
support or casing. Prongs are inserted into the holes of an
outlet or receptacle to establish the electrical connection
between the appliance and the main power supply.
Many types of standard electrical plugs are found in residences,
industries, and commercial spaces worldwide. Electrical plugs
differ in the number and dimensions of the pins, voltage and
current ratings, and countries in which they are used.
Chapter 2: Two-Pronged and Three-Pronged Plugs
Electrical plugs have two or three prongs:
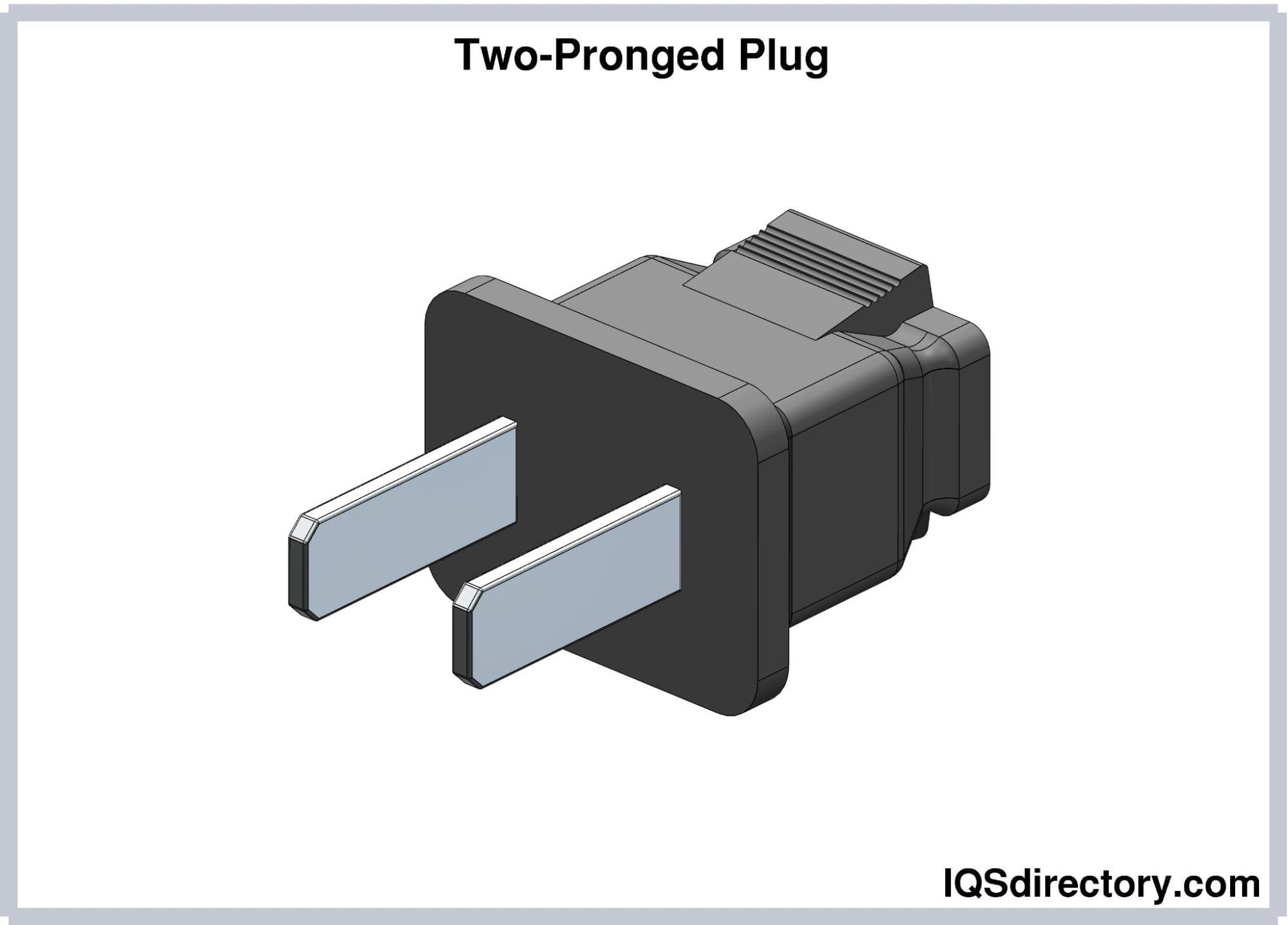
Two-Pronged Plugs
Two-pronged plugs have one prong or pin, each connected to the
“hot” and “neutral” slots of the receptacle. The hot pin is
connected to the hot slot of the socket. It draws current from
the receptacle, which flows to power the load. The neutral pin,
connected to the neutral slot of the socket, returns the current
to the receptacle and back to the power supply. Two-pronged
plugs can be readily inserted into two-slot receptacles.
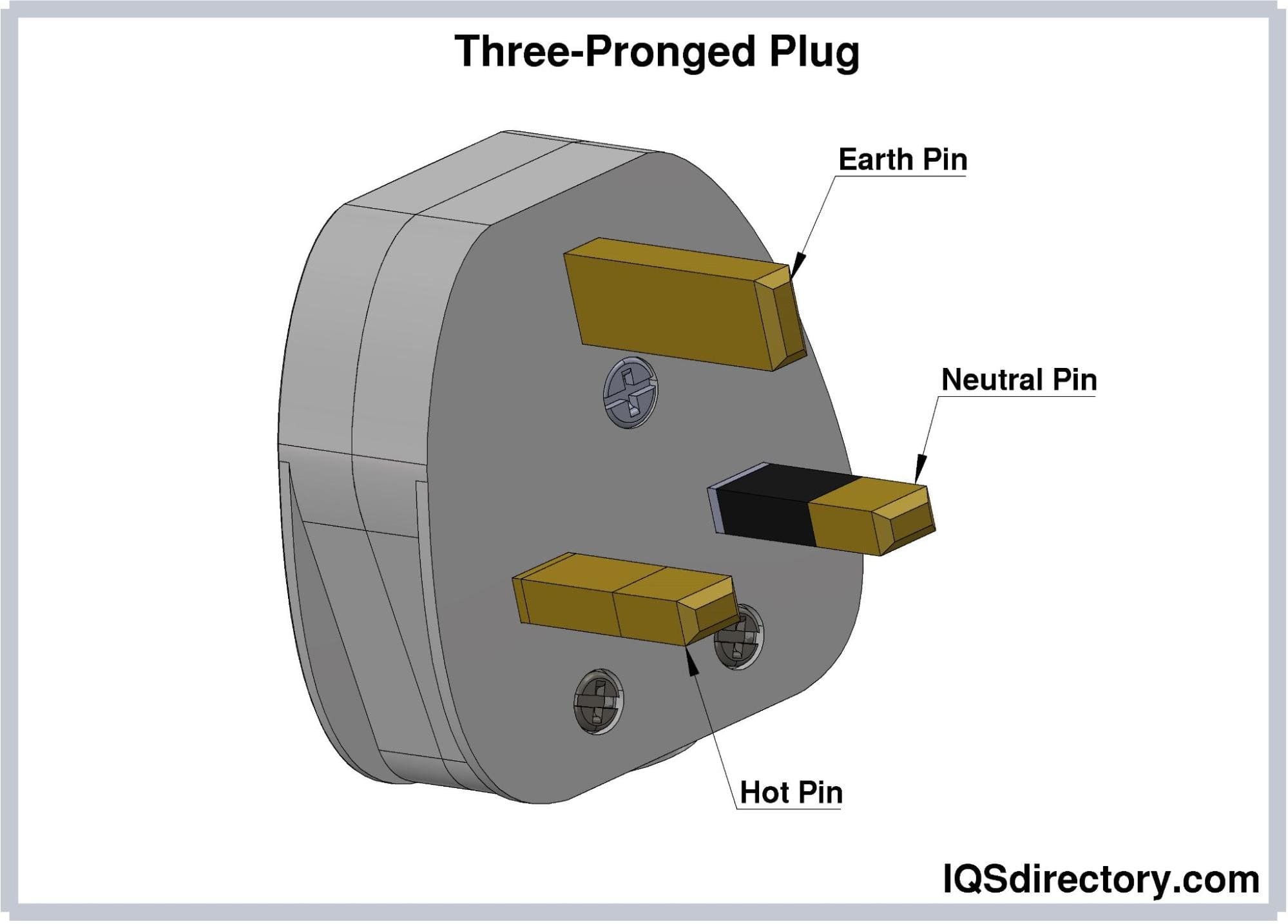
Three-Pronged Plugs
In three-pronged plugs, a grounding or earthing pin is
introduced. This pin is connected to an electrical system’s
ground wire. It is typically positioned under hot and neutral
pins. This pin does not carry current, and the ground connection
is added as a safety feature. In case of a faulty wire, short
circuit, or electrical surge, the ground connection will
transmit and neutralize the stray electricity to the power
supply and the ground. Therefore, the ground connection can
prevent electrocution, electrical fires, and damage to the
plugged appliance. Moreover, installing three-slot receptacles
is required nowadays in newly constructed buildings and
residences.
Three-pronged plugs are used in electrical appliances requiring
high power, such as flat irons, toasters, HVAC equipment,
industrial machinery, and other sensitive electronics. They are
used for devices contained in a metal housing (e.g., computers
and game consoles). Stray electricity can conduct through the
metal housing; thus, a ground connection can divert the path of
the stray current instead of electrically shocking a person.
Leading Manufacturers and Suppliers
GET YOUR COMPANY LISTED ABOVE
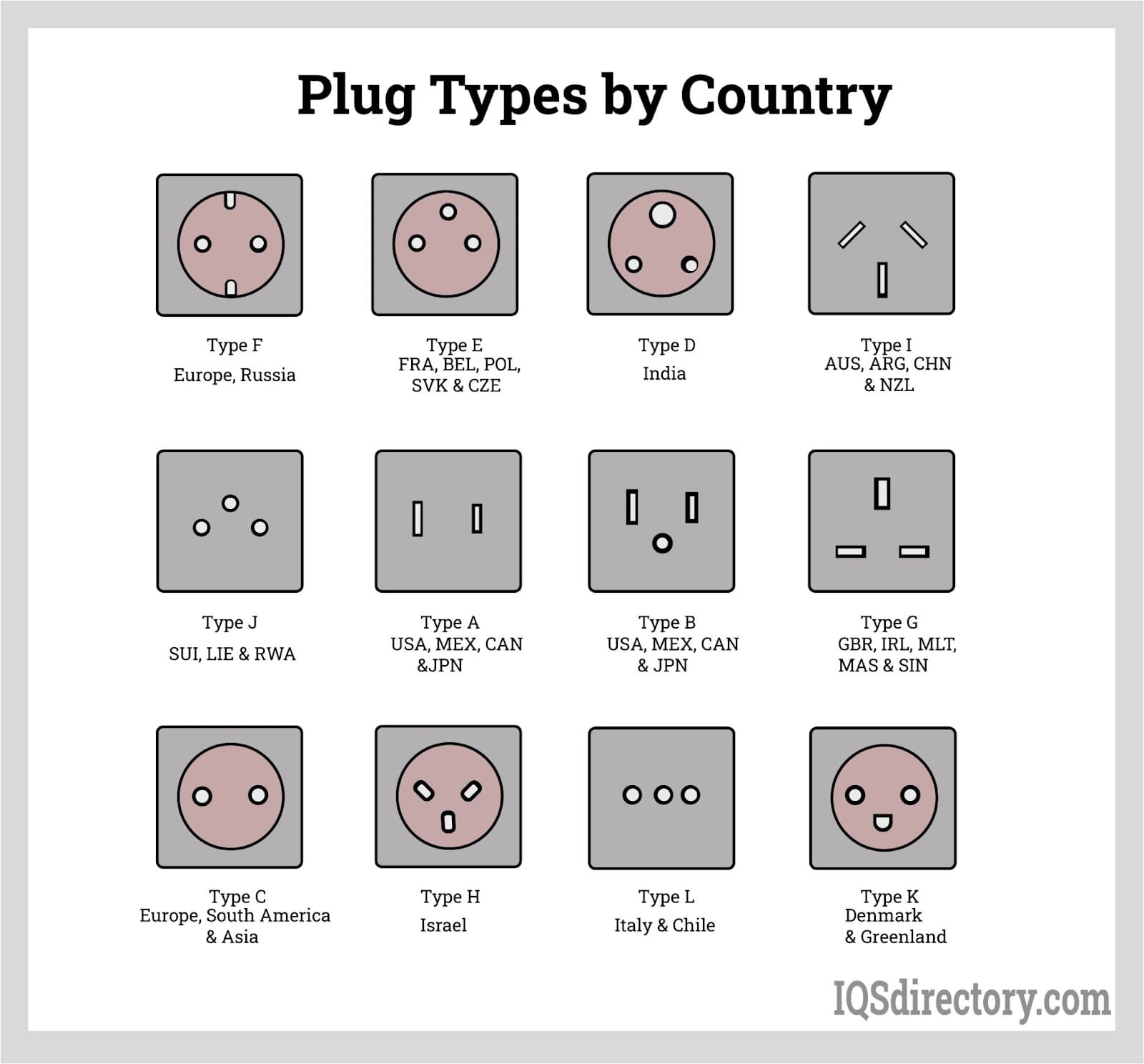
Chapter 3: Types of Electrical Plugs
There are fifteen (15) standard types of mains electrical plugs
worldwide recognized by the International Electrotechnical
Commission (IEC). These types are listed in the IEC 60083
standard. Each type has a letter designation and lists under a
standard, which we will be discussing in the succeeding
sections.
NEMA Plugs (Type A, B)
NEMA plugs are compliant with the standards and specifications
set by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA),
the largest trade association for electrical equipment and
medical imaging equipment. NEMA standards are prevalent in North
and Central America, but other countries also adopt these
standards. NEMA designates Type A and Type B plugs.
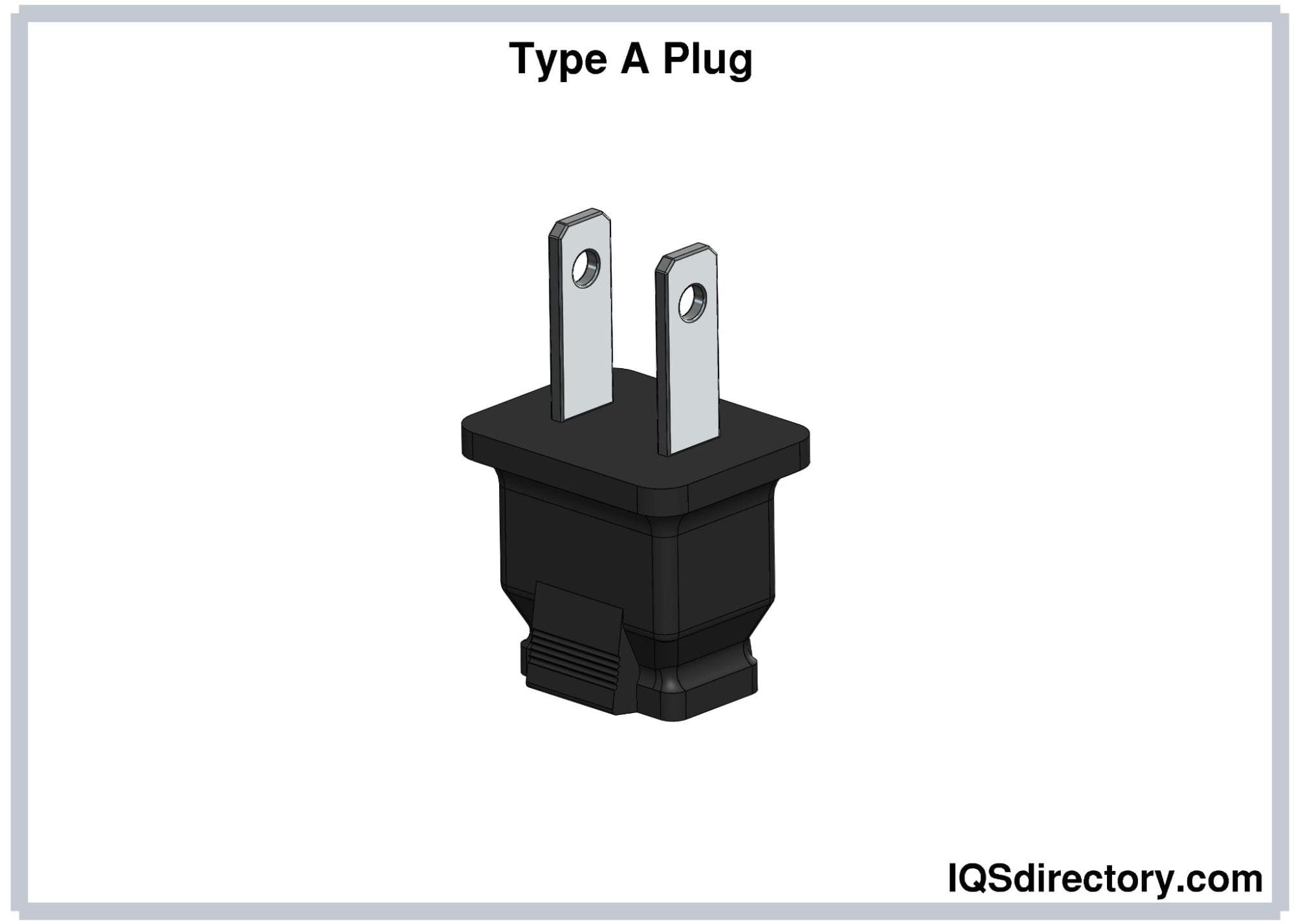
Type A (NEMA 1-15) Plugs
Type A electrical plugs are ungrounded plugs that consist of two
flat parallel prongs. These plugs have a current and voltage
rating of 15A and 125V, respectively. The length of the pins
varies from 15.9-18.3 mm, and their spacing is 12.7 mm.
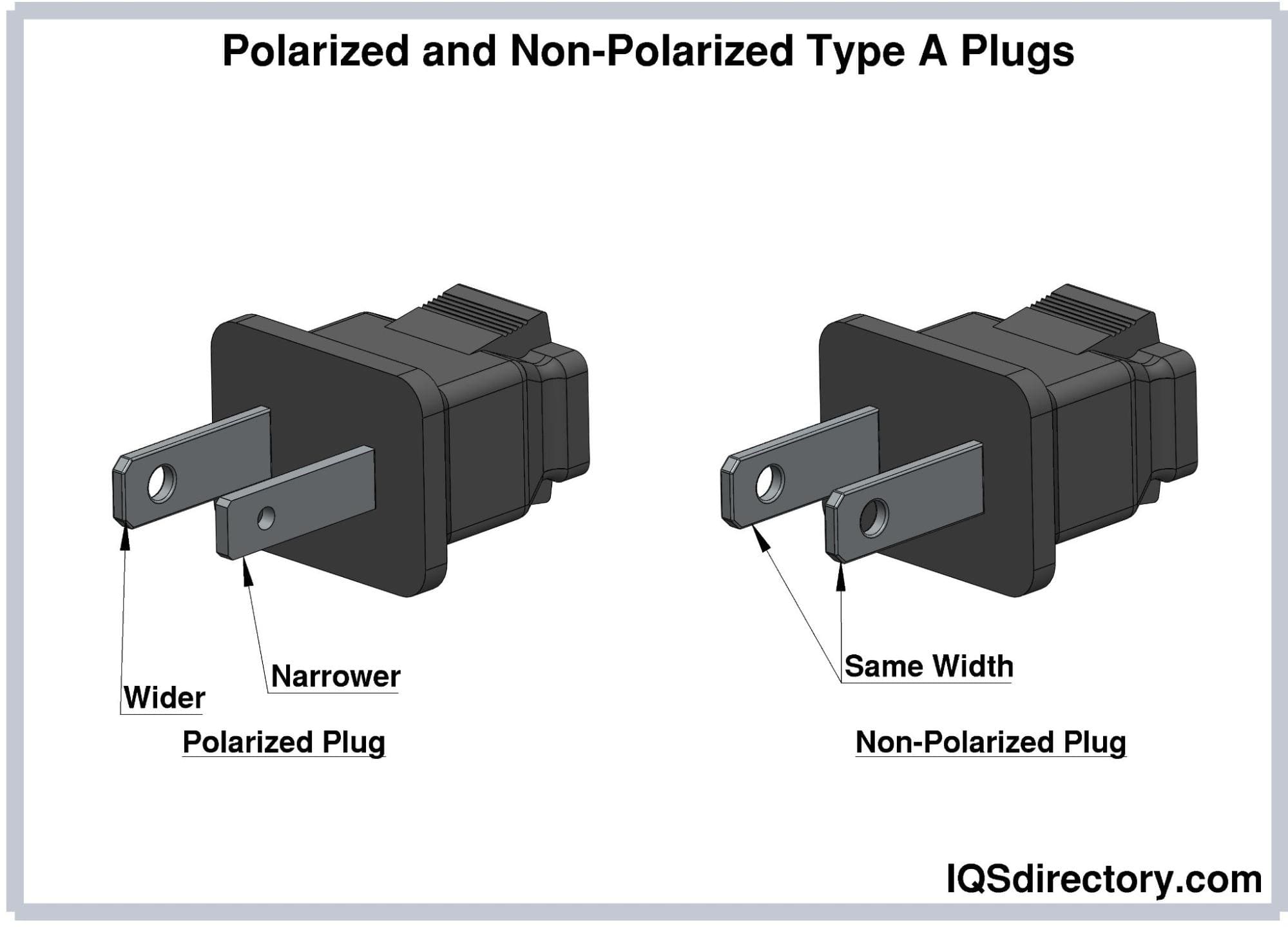
Type A plugs have polarized and non-polarized versions.
Polarized plugs have a neutral pin wider than the hot pin,
limiting their insertion to only one orientation. Polarized Type
A plugs are common in North America and Mexico. They have
neutral and hot pins measuring 7.9 mm and 6.3 mm wide,
respectively. Meanwhile, non-polarized plugs have prongs with
equal widths. They are widely used in Japan. Non-polarized plugs
can fit into polarized sockets, but not the other way around.
Type A plugs are compatible with Types A and B sockets.
In type A plugs, there are holes present near the tip of the
prongs. The bumps on the outlet’s contact wiper fill the prong
holes as the prongs are inserted into the receptacle. This
mechanism allows the outlet to grip the plug firmly and prevents
it from slipping out due to its weight. In some special sockets,
a rod can be inserted into these holes to lock the plug when it
is inserted. These holes also enable factory sealing.
Some sockets use two spring-action blades instead of a contact
wiper, which grip the prongs on their sides. This mechanism
makes the holes unnecessary.
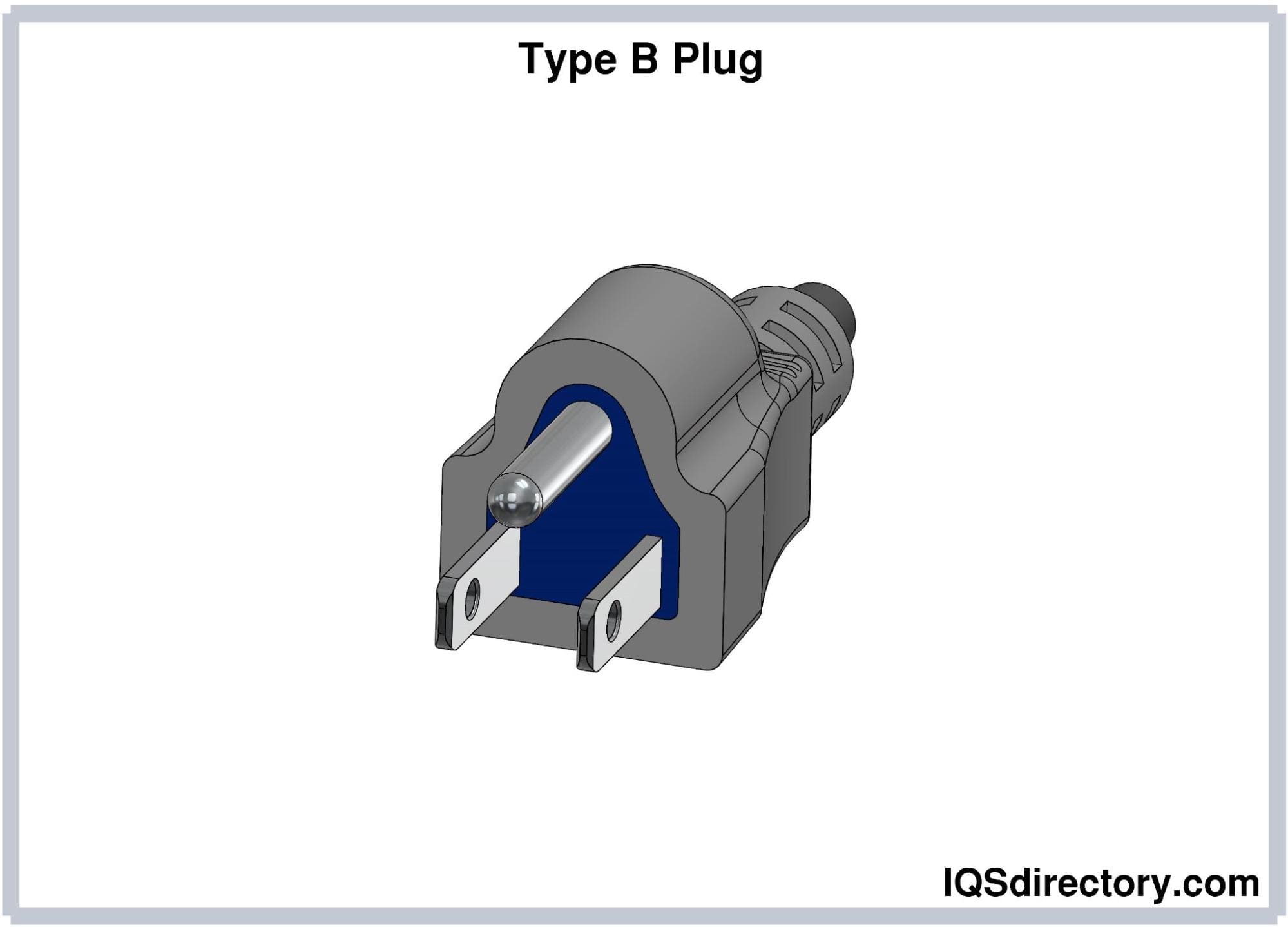
Type B (NEMA 5-15) Plug
Type B electrical plugs, also known as the North American 3-pin
plug, are grounded plugs. They consist of two flat parallel
prongs and a round pin for grounding. The ground pin is longer
than the hot and neutral pins so that a ground connection is
made before the connection to the voltage. The hot and neutral
pins measure 1.5 mm thick, 15.9-18.3 mm long, and 6.3 mm wide.
The ground pin has a diameter of 4.8 mm and is 3.22 mm longer
than the two flat pins.
Type B electrical plugs have a current and voltage rating of 15A
and 125V, respectively. They are widely used in North America,
Mexico, China, Japan, and other countries which use Type A
plugs. Like Type A, Type B plugs used in Japan vary in design
slightly than those used in the United States.
CEE 7 Standard AC Plugs (Type C, E, F)
CEE Publication 7 is the “Specification for plugs and
socket-outlets for domestic and similar uses .”This standard is
maintained by the IECEE and governs the domestic electrical
connectors used in Europe. The countries that do not use CEE 7
plugs and sockets as their primary power connectors are the
United Kingdom, Ireland, Malta, Cyprus, Switzerland, and Italy.
Type C (CEE 7/16 and CEE 7/17) Plugs
Type C is the most internationally used electrical plug. It is
an ungrounded and unpolarized plug and consists of two round
pins. There are two types of Type C plugs:
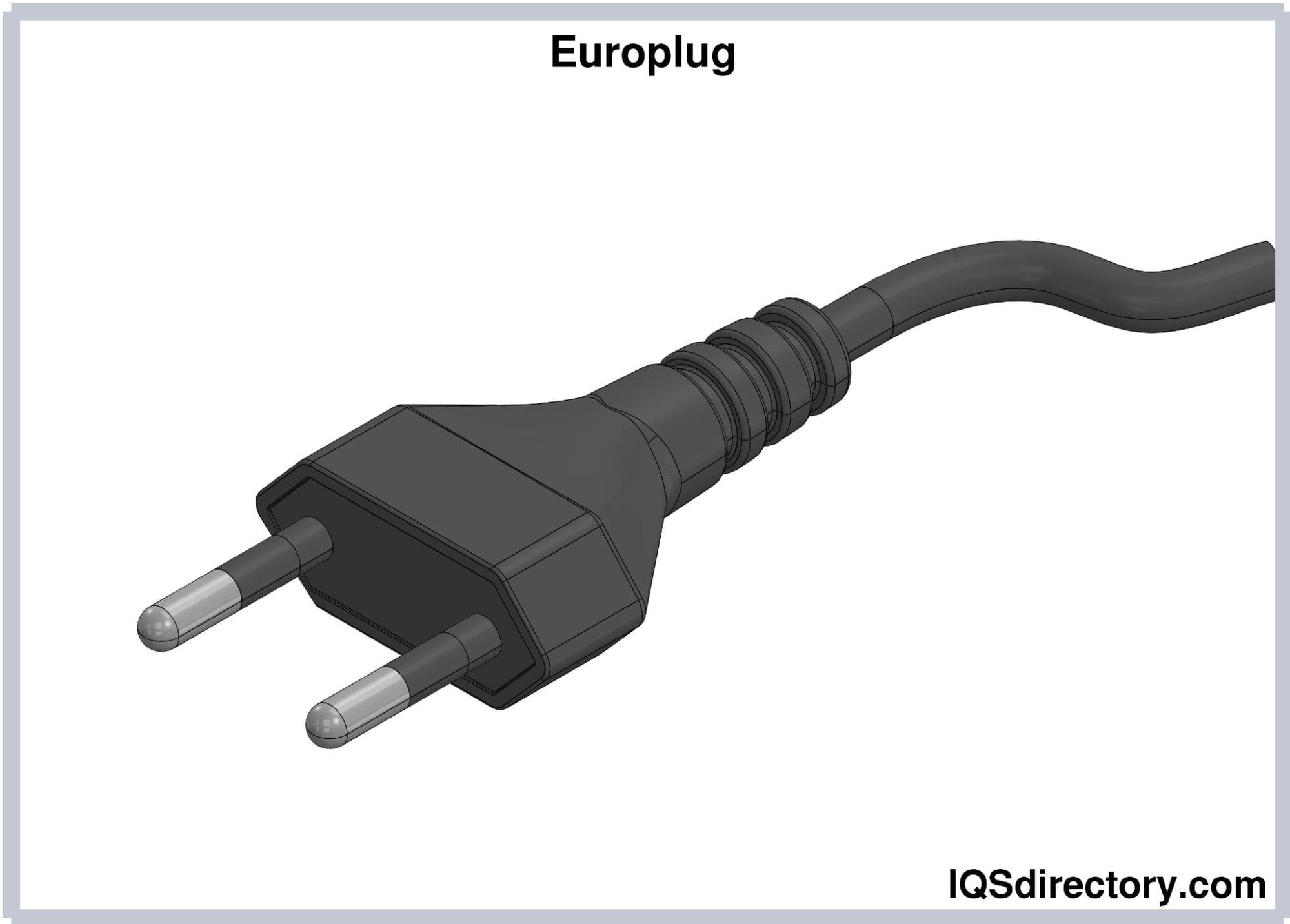
-
Europlug (CEE 7/16). Europlugs have two pins measuring
19 mm long and 4 mm in diameter. The pins are 18.6 mm apart
from the base and 17.5 mm from the tip. They have an insulated
covering 10 mm of their length from the base. The pins are
relatively flexible, which allows them to fit in sockets that
support rounded pins from 4.0 to 4.8 mm in diameter and whose
slots are 17.5-19 mm apart. Europlugs are rated with 2.5A; the
low current rating limits the Europlug to low energy
applications.
Europlugs are the more popular type of Type C plugs.
-
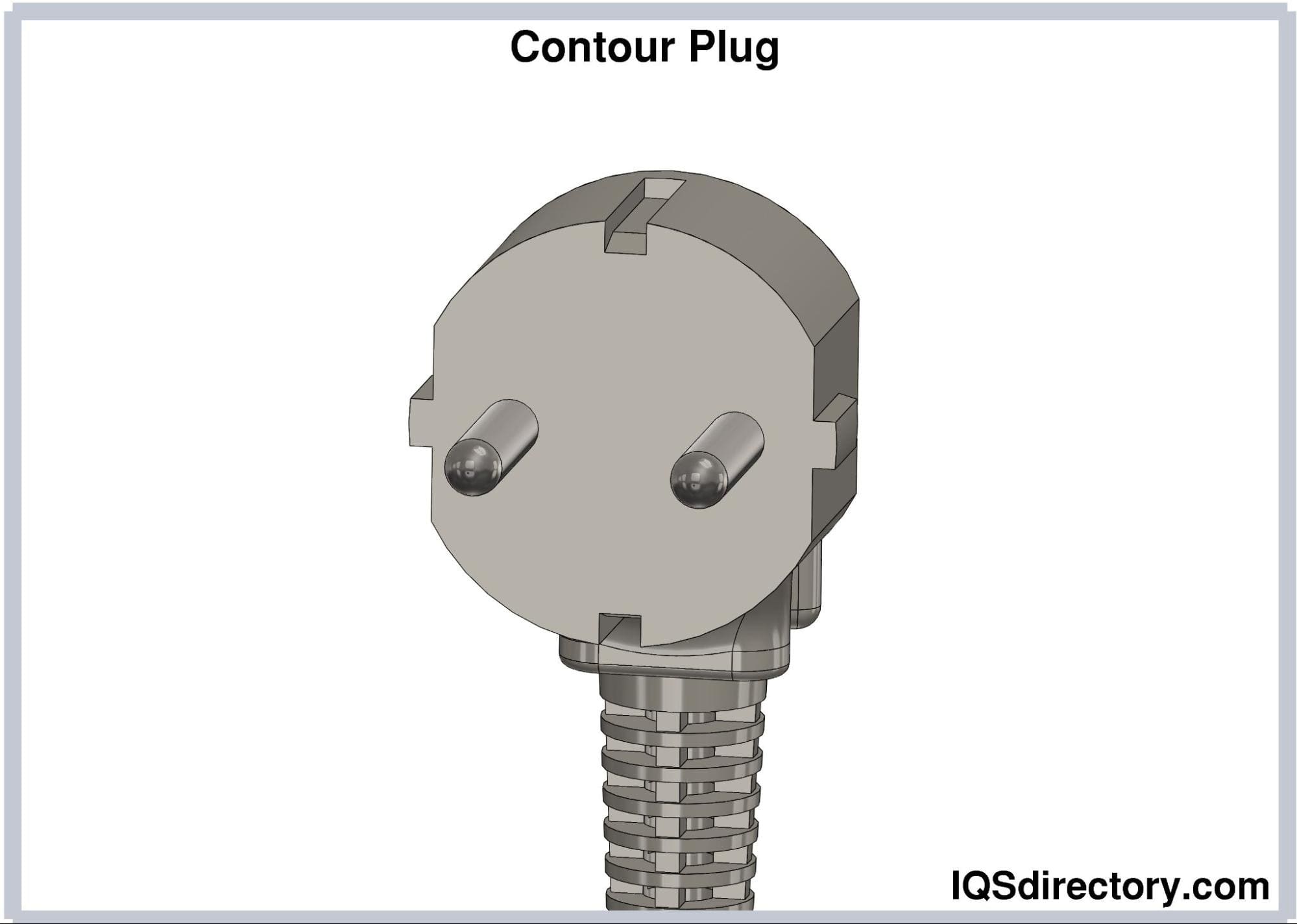
Contour Plug (CEE 7/17). Contour plugs have two pins
measuring 19 mm long and 4.8 mm in diameter. The pins are
spaced 10 mm apart. Unlike Europlugs, contour plugs do not
have an insulated sleeve. The insulated sleeve in electrical
plugs makes their operation safer.
Contour plugs are rated at either 10A or 16A; thus, they can be
used in high energy appliances.
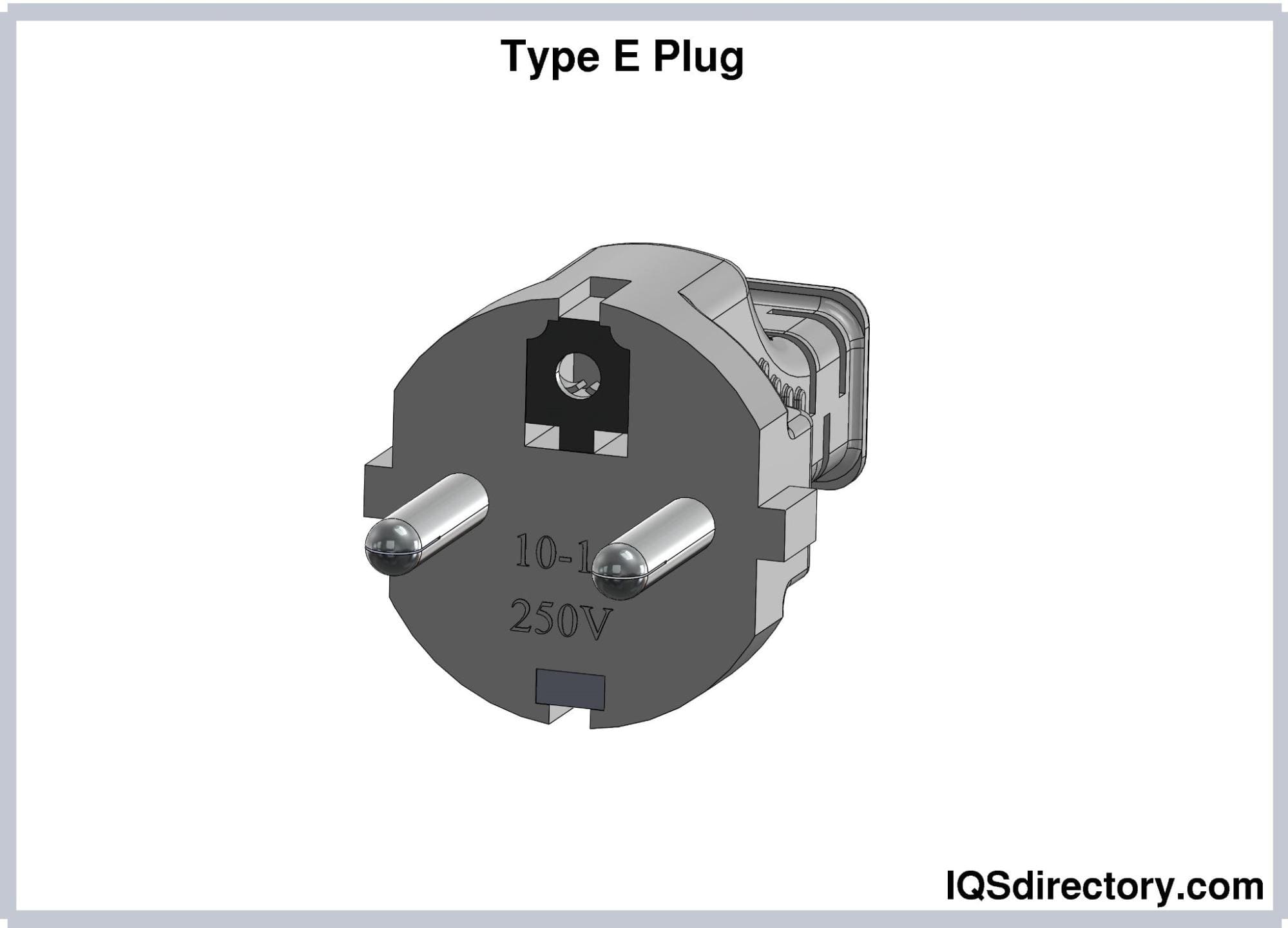
Type E (CEE 7/5) Electrical Plugs
Type E electrical plugs consist of two round pins, measuring 19
mm long, 4.8 mm in diameter, and 19 mm apart. It has a female
contact or hole that accommodates the socket’s earthing pin
measuring 14 mm long and 4.8 mm in diameter. This contact is
located beneath the plug pins. The asymmetrical arrangement of
the pins in Type E plugs does not allow polarity reversal.
Type E plugs have a current rating of 16A. They are compatible
with Types E and F sockets. These plugs are also known as
“French plugs” and are widely used in France, Belgium, Slovakia,
and Tunisia.
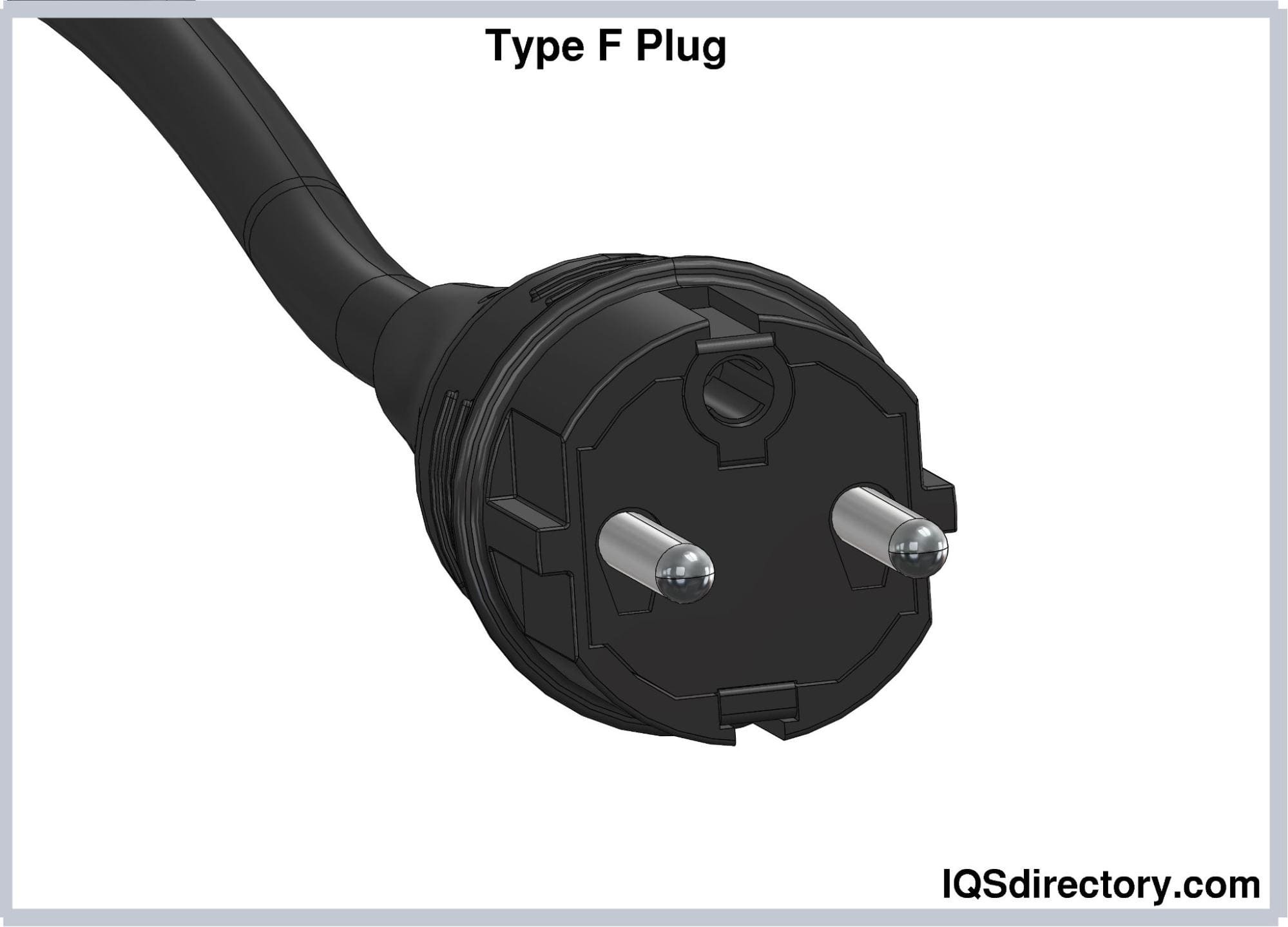
Type F (CEE 7/4) Plugs
Type F electrical plugs have almost the exact pin dimensions as
Type E plugs, except the pins are not perfectly rounded. Type F
plugs have two earthing clips instead of female earthing
contact. These clips are located on the upper and lower sides of
the plug housing, which is 16 mm from the midpoint of the
imaginary line connecting the pins. These plugs also have a pair
of plastic notches on the left and right sides to provide
additional stability when used as a large built-in plug.
Type F plugs also have a current rating of 16A. They are not
compatible with Type E sockets. These plugs are also known as
“Schuko plugs” and are widely used in Germany, Austria, the
Netherlands, and Spain.
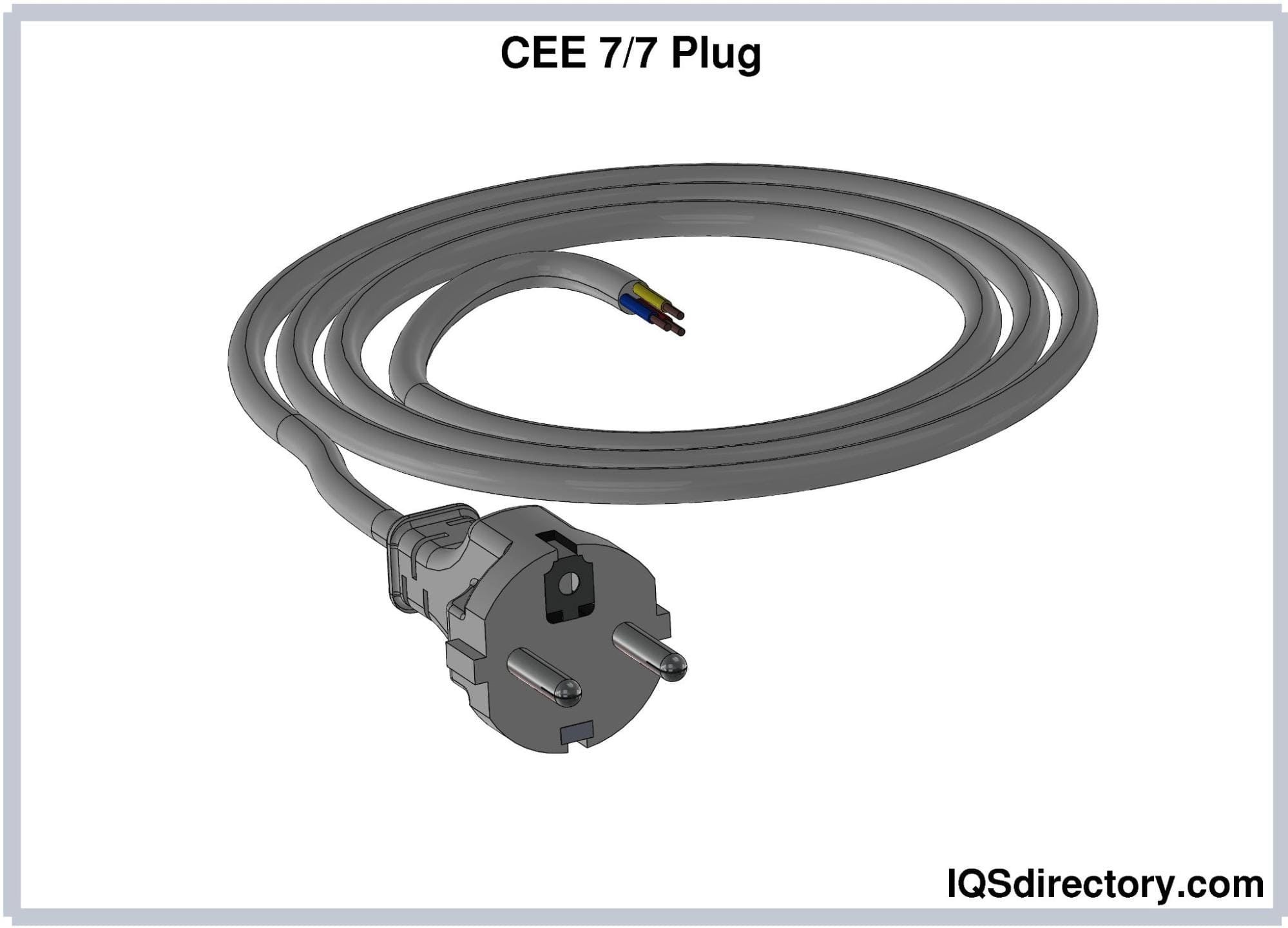
CEE 7/7 Plugs
CEE 7/7 plug is a hybrid version of Type E and F plugs to fit
both socket types. This plug has a female earthing contact to
accept the grounding pin of the Type E socket and two earthing
clips at the plug housing that works with Type F sockets. CEE
7/7 plugs are commonly found in countries that use Type E and
Type F plugs.

British Standard Plugs (Type D, M, G)
BS 1363 is a British standard that specifies the safety,
construction, electrical and mechanical testing, dimensional
accuracy, and marking requirements for the plug and socket
systems in the UK. Other countries such as India, Malta, and
South Africa have also adopted this standard.
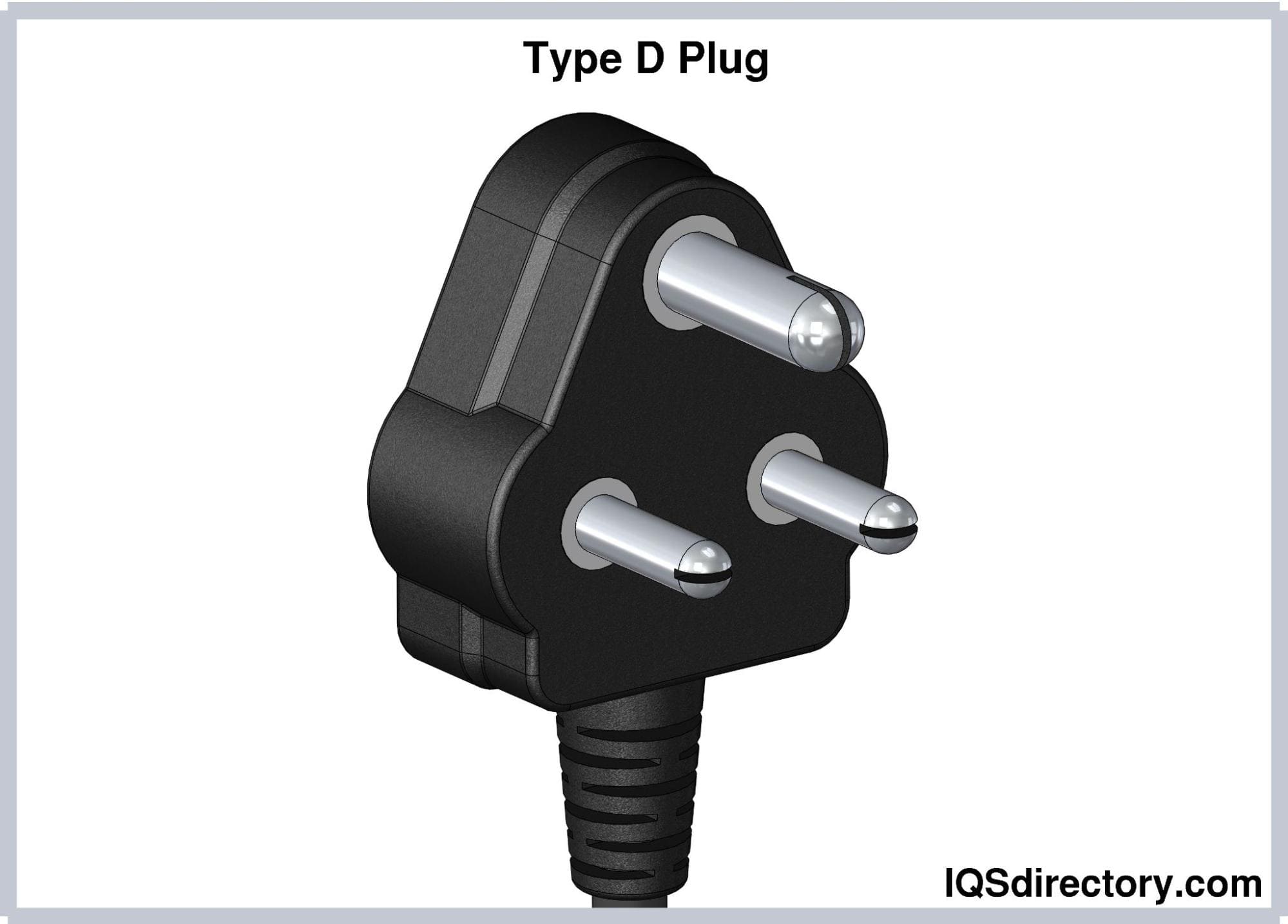
Type D (BS 546) Plugs
Type D electrical plugs consist of three round pins that form a
triangular arrangement. The central earthing pin is 20.6 mm long
and 7.06 mm in diameter, while the hot and neutral pins are 14.9
mm long, 5.08 mm in diameter, and spaced 19.1 mm apart. The
asymmetrical arrangement of the pins in Type D plugs protects it
from polarity reversal. Type plugs are rated at 5A. Type D plugs
are widely used in India, Sri Lanka, Namibia, and Nepal.
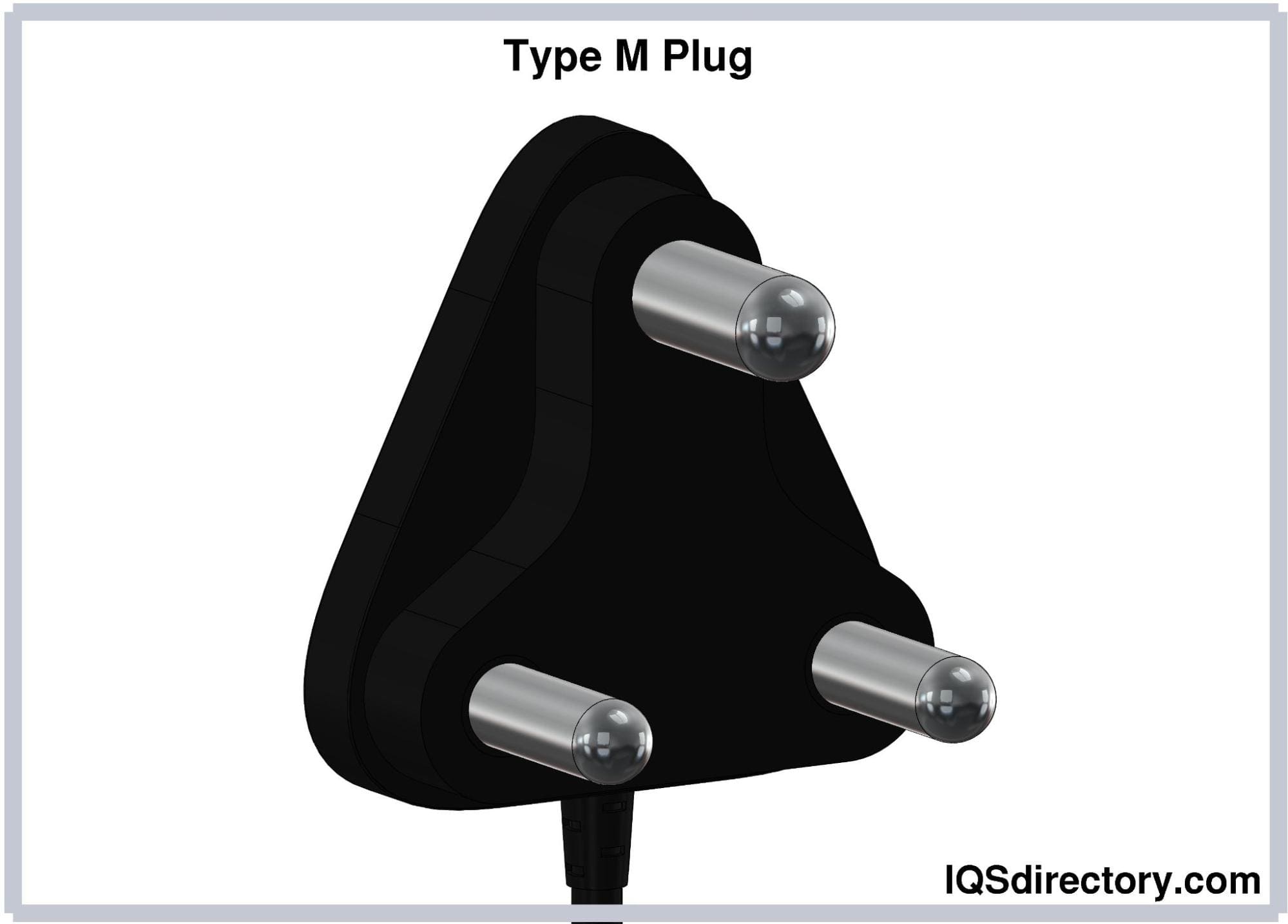
Type M (BS 546) Plugs
Type M electrical plugs have the same arrangement as Type D
plugs and are also protected from polarity reversal. They are
distinguished from Type D plugs by their larger pins and current
rating of 15A. The central earthing pin is 28.89 mm long and
8.71 mm in diameter, while the hot and neutral pins are both
18.94 mm long, 7.06 mm in diameter, and spaced 25.4 mm apart.
Due to their larger current rating, these plugs are used
alongside type D plugs in running appliances with large power
requirements. Type M plugs are used in South Africa, Swaziland,
Lesotho, the UK, Israel, and UAE. The South African variation of
this type features an insulated sleeve and a bare connector on
both pins.
Type G (BS 1363) Electrical Plugs
Type G electrical plugs consist of three rectangular pins that
form a triangular arrangement and an incorporated fuse. The
central earthing pin measures 4 mm by 8 mm by 22.7 mm. The hot
and neutral pins are 4 mm by 6.35 mm by 17.7 mm long, and their
center-to-center distance is 22.2 mm. The hot and neutral pins
have an insulated sleeve covering half their length, while the
earthing pin is uninsulated. British sockets have shutters that
prevent foreign objects on hot and neutral pins.
Type G plugs include a fuse rated at 3A or 13A. The higher
current rating is used in heavier-duty appliances. Hence, the
Type G plug and socket system is considered the safest for both
the user and equipment. However, Type G plugs are exclusive for
Type G sockets and are not compatible with other types.
Type G plugs are also known as the “Commonwealth Plug .” They
are widely used in the UK, Ireland, Hong Kong, Singapore,
Cyprus, and Malta.

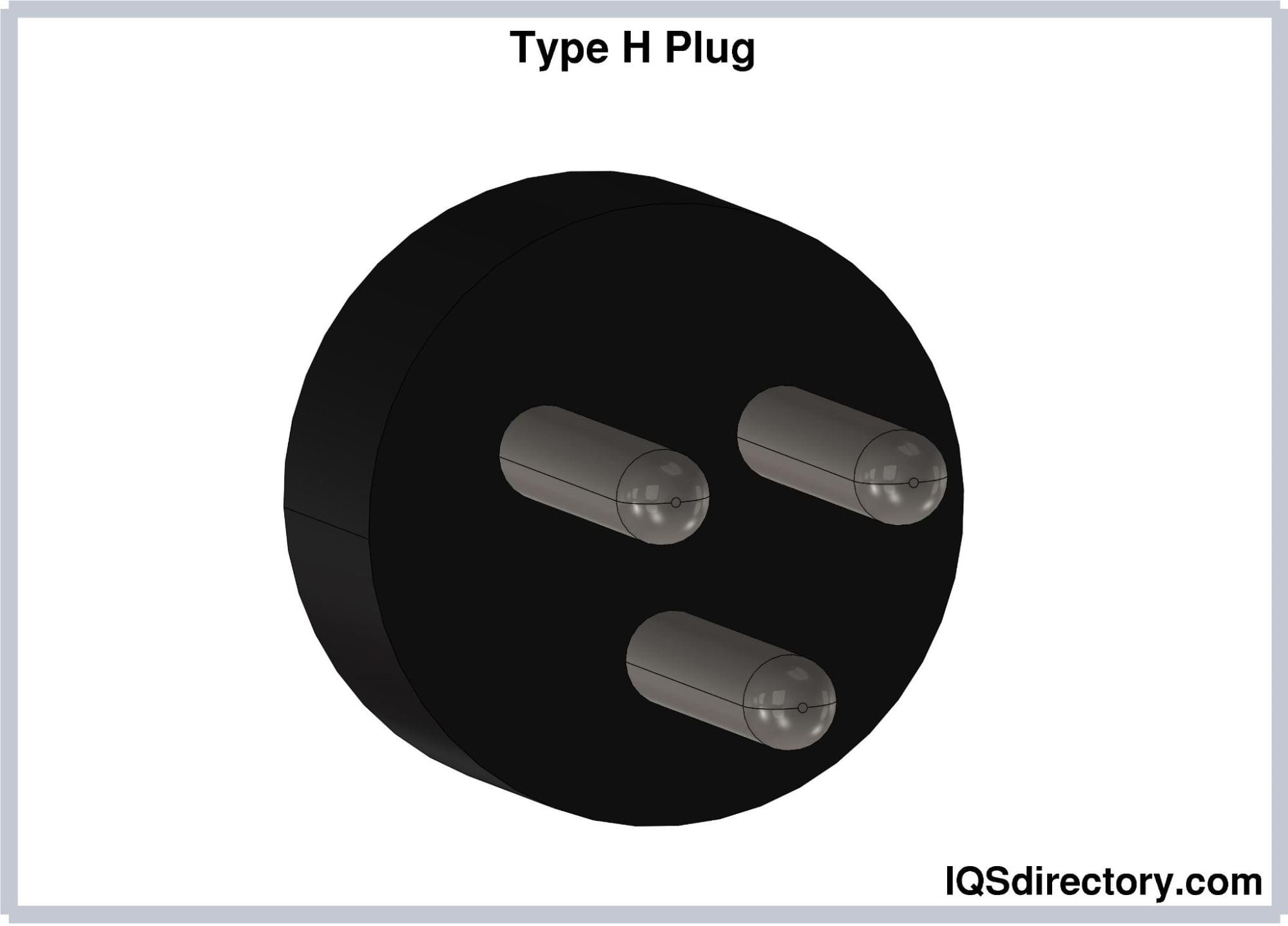
Type H (SI-32) Plug
Type H electrical plugs consist of three round pins arranged in
a triangular configuration, with a diameter of 4.5 mm and a
length of 19 mm. The center-to-center distance between the hot
and neutral pins is 19 mm. The center of the earthing pin is 9.5
mm away from the midpoint of the imaginary line connecting the
hot and neutral pins. Type H plugs are grounded and rated at
16A.
Type H plugs are only compatible with Type H sockets. Type H
sockets are compatible with Type C plugs but are unsafe with
Type E and Type F plugs. Type H plugs do not have an insulated
sleeve, making them hazardous when partially unplugged.
Type H plugs are exclusively used and only found in Israel and
Palestine.
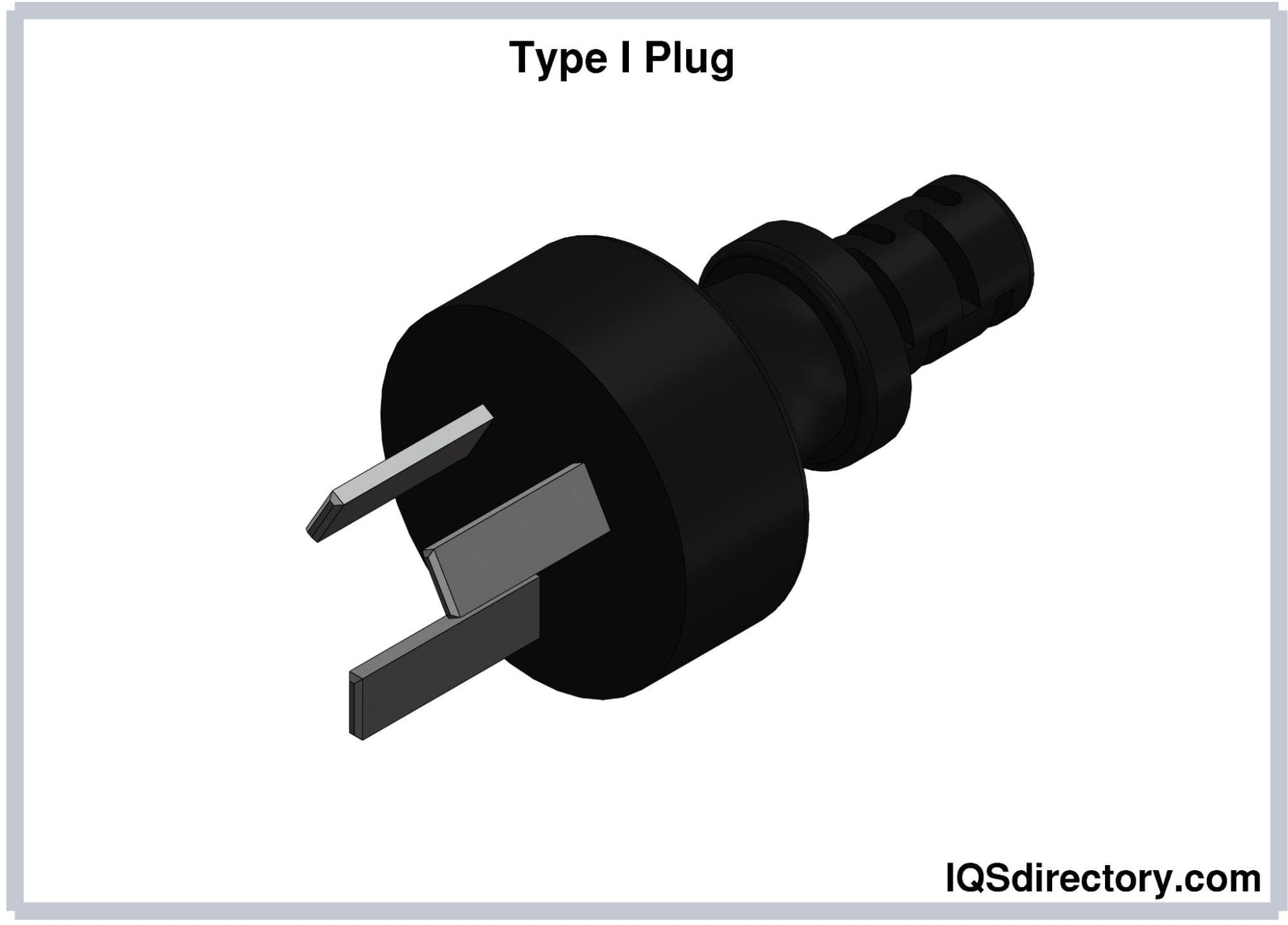
Type I (AS 3112) Electrical Plug
Type I electrical plugs consist of two flat pins rotated 300
from the vertical, forming an inverted-V arrangement and a flat
earthing pin. The hot and neutral pins measure 17.3 mm long, 6.3
mm wide, and spaced 13.7 mm. The pins are insulated. The
earthing pin measures 20 mm long and is away from the middle of
the plug by 10.3 mm. The width of the earthing pin depends on
the current rating. For Type I plugs rated at 10A and 15A, the
width is 6.3 mm and 8 mm, respectively. 20-A Type I plugs also
exist with wider prongs. A lower current rating plug can fit a
socket with a higher rating. Ungrounded Type I plugs also exist.
Type I plugs are mainly used in Argentina, Australia, New
Zealand, Papua New Guinea, China, and other Pacific Island
countries. In Type I plugs used in China, the earthing pin is
above the other two pins, and all pins are 1 mm longer than the
conventional. Type I plugs in Australia can mate with Type I
sockets installed in China.
Type I plugs are documented in AS/NZS 3112, the harmonized
Australian and New Zealand standard for plug and socket systems.
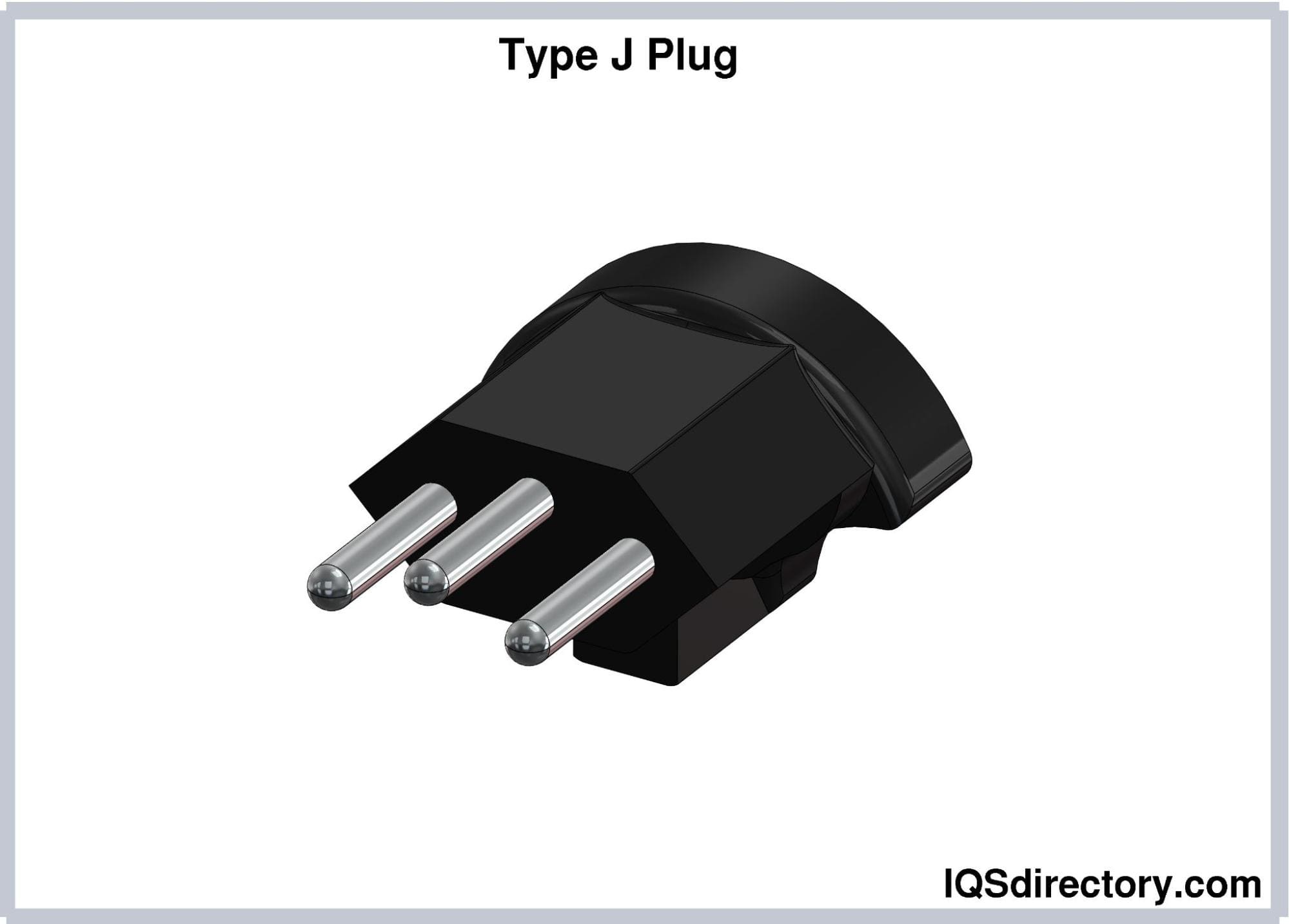
Type J (SN 441011) Electrical Plugs
Type J electrical plugs consist of three round pins whose
dimensions are almost the same as Type C plugs. The hot and
neutral pins are spaced 19 mm apart. The center of the earthing
pin is 5 mm offset from the midpoint of the imaginary line
connecting the hot and neutral pins. All pins have the same
lengths and diameters of 19 mm and 4 mm, respectively. All pins
are also insulated. The design of Type J plugs prevents polarity
reversal. These plugs are rated at 10A.
Type J plugs look similar to the Brazilian Type N plugs.
However, they do not fit into Type N sockets since their
earthing pins are farther from the imaginary centerline.
Type J plugs are used in Switzerland and Liechtenstein. This
type is listed in SEV 1011, the Swiss standard for domestic plug
and socket systems, as the Type 13 plug.
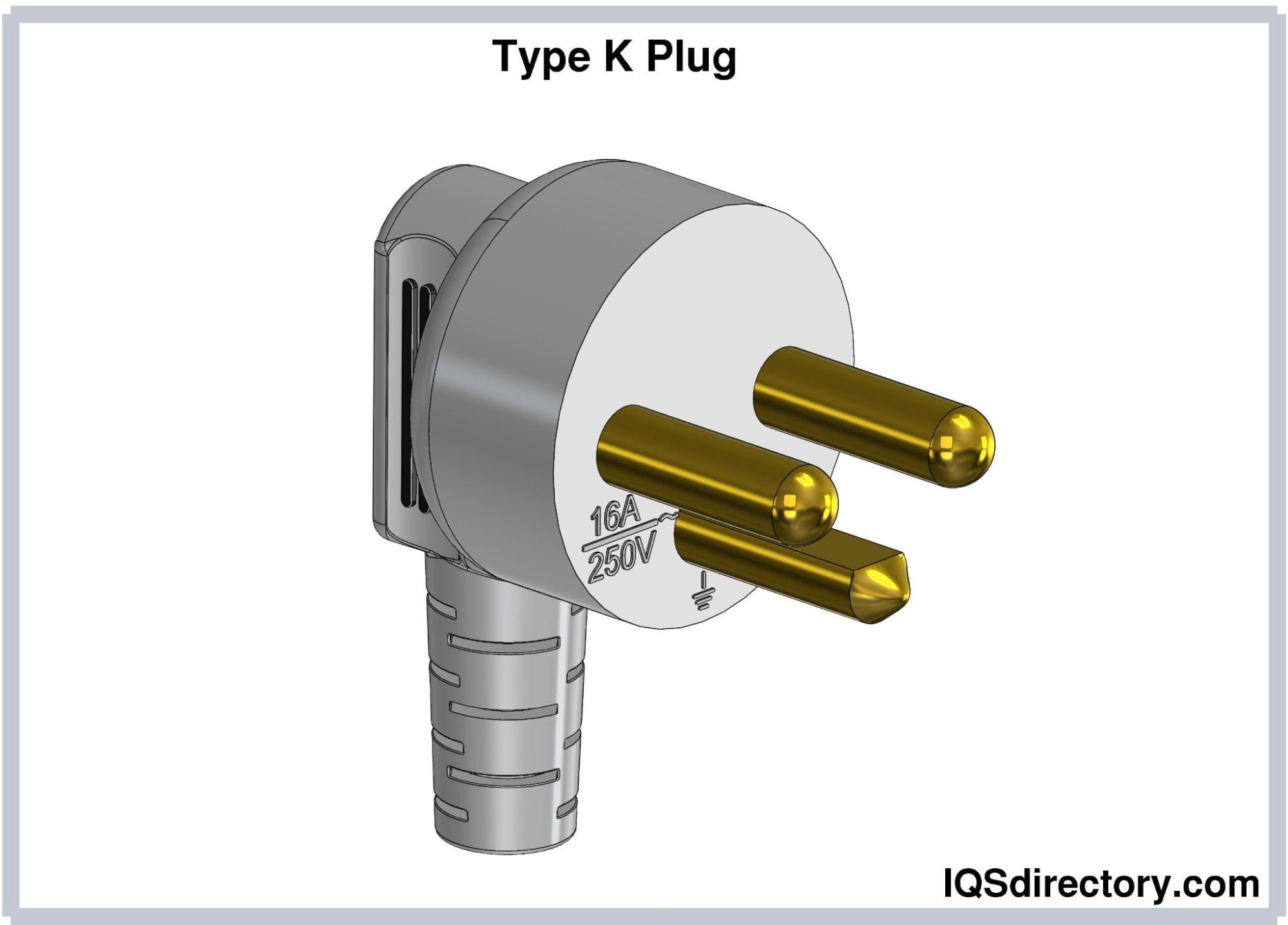
Type K (DS 60884-2-D1) Plugs
Type K electrical plugs consist of two round pins and a U-shaped
earthing pin. The hot and neutral pins have 4.8 mm diameter, 19
mm length, and 19 mm center-to-center distance. The U-shaped
earthing pin has a 6.5 mm diameter, 14 mm length, and 4 mm
thickness. These plugs resemble Type E plugs except for the
gender and shape of the earthing contact. The design of Type K
plugs disables polarity reversal. These plugs are rated at 16A.
Type K plugs are used in Denmark and Greenland. This type is
specified under DS-60884-2-D1, the Danish Standard for plugs and
socket-outlets for household and similar purposes.
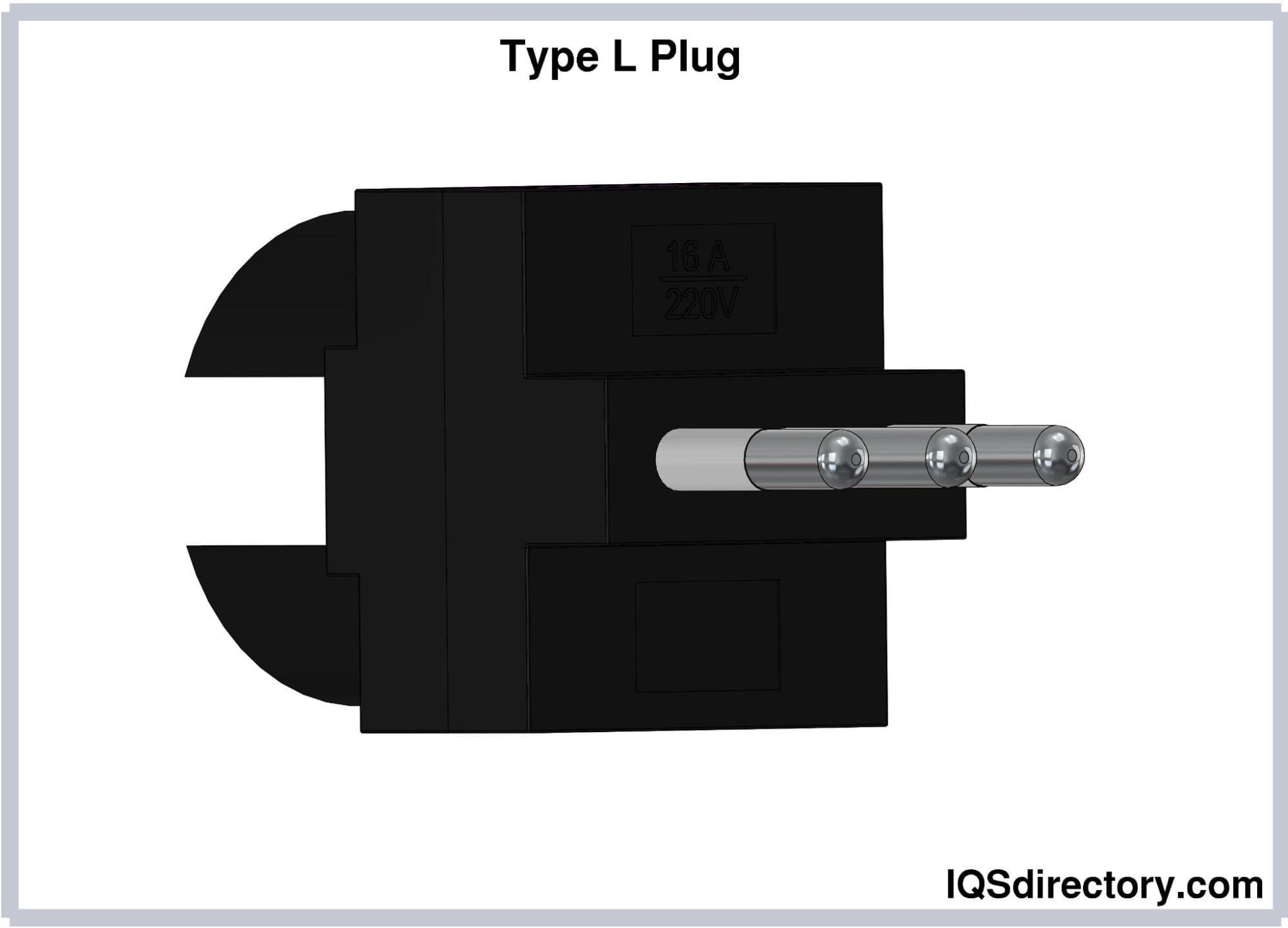
Type L (CEI 23-16-VII) Electrical Plug
Type L electrical plugs consist of three round pins placed in a
straight line. The earthing pin is positioned between the other
pins. These plugs come in two variants which vary in the current
rating and dimensions:
-
The 10A variant has pins measuring 4 mm in diameter and 19 mm
long. The centers of the hot and neutral pins are spaced 19 mm
apart, while the distance of the center of the earthing pin to
the center of the hot or neutral pin is 9.5 mm. -
The 16A variant has pins measuring 5 mm in diameter and 19 mm
long. The centers of the hot and neutral pins are spaced 26 mm
apart, while the distance of the center of the earthing pin to
the center of the hot or neutral pin is 13 mm.
The 10A plugs are incompatible with the 16A sockets and vice
versa since both variants differ in dimensions. The design of
Type L plugs is symmetrical, which allows them to be inserted in
any orientation. Thus, these plugs are unpolarized.
Type L plugs are used in Italy, Chile, Uruguay, and some
countries of North Africa.
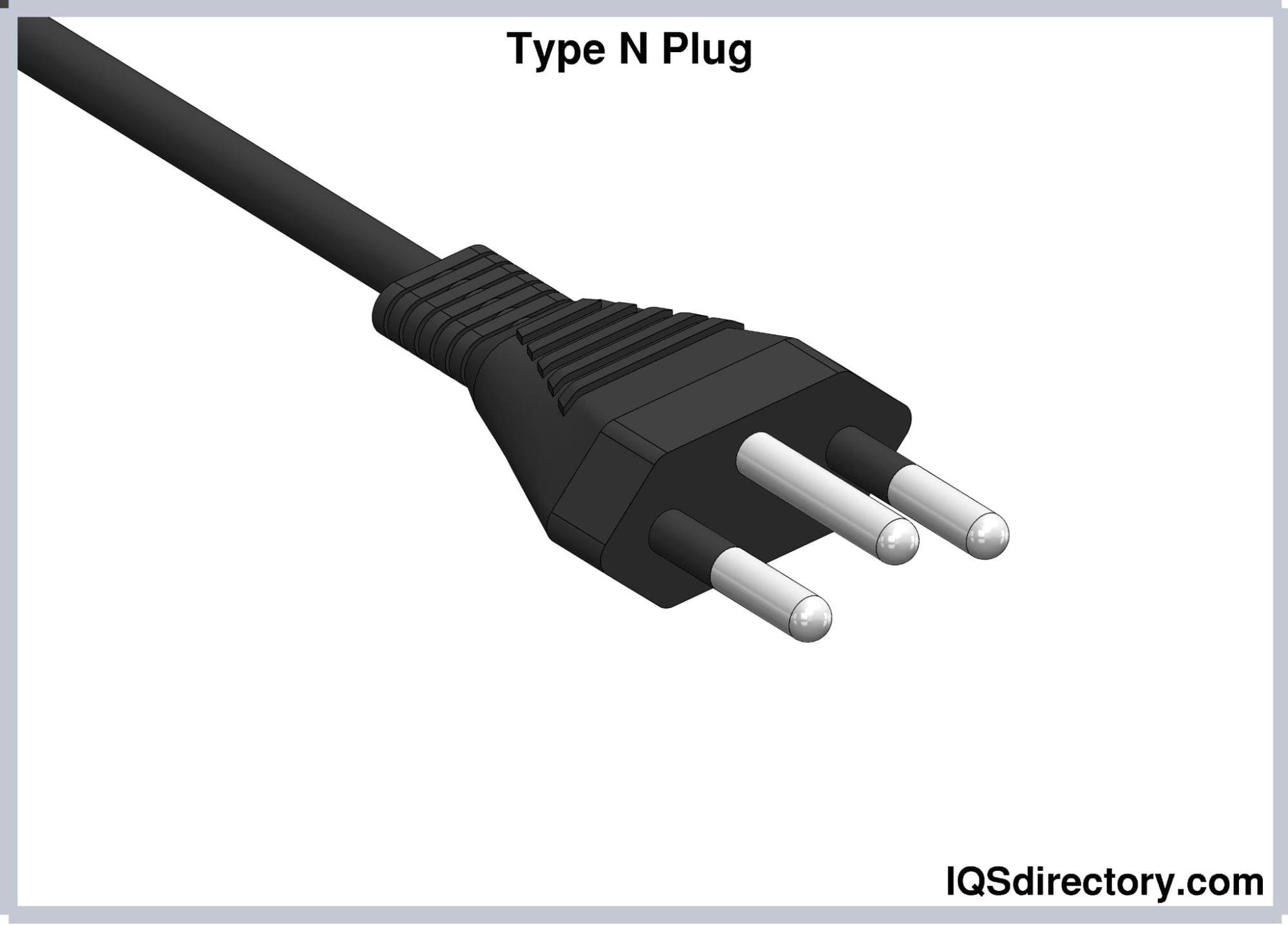
Type N (IEC 60906-1) Electrical Plugs
Type N electrical plugs consist of three round pins arranged in
a triangular configuration. This type has three variants rated
at 10A, 16A, and 20A. The pins of all variants are 19 mm long.
However, the diameters are 4 mm, 4.5 mm, and 4.8 mm for the 10A,
16A, and 20A versions, respectively. The pins are covered with
an insulated sleeve measuring 10 mm of their length. The
center-to-center distance of the hot and neutral pins is 19 mm
apart. The center of the earthing pin measures 3 mm away from
the midpoint of the imaginary line connecting the hot and
neutral pins. Hence, Type N plugs are not compatible with Type J
plugs because this measurement is smaller compared to the latter
(5mm).
The 10A and 20A Type N plugs are used in Brazil, while the 16A
version is used in South Africa.
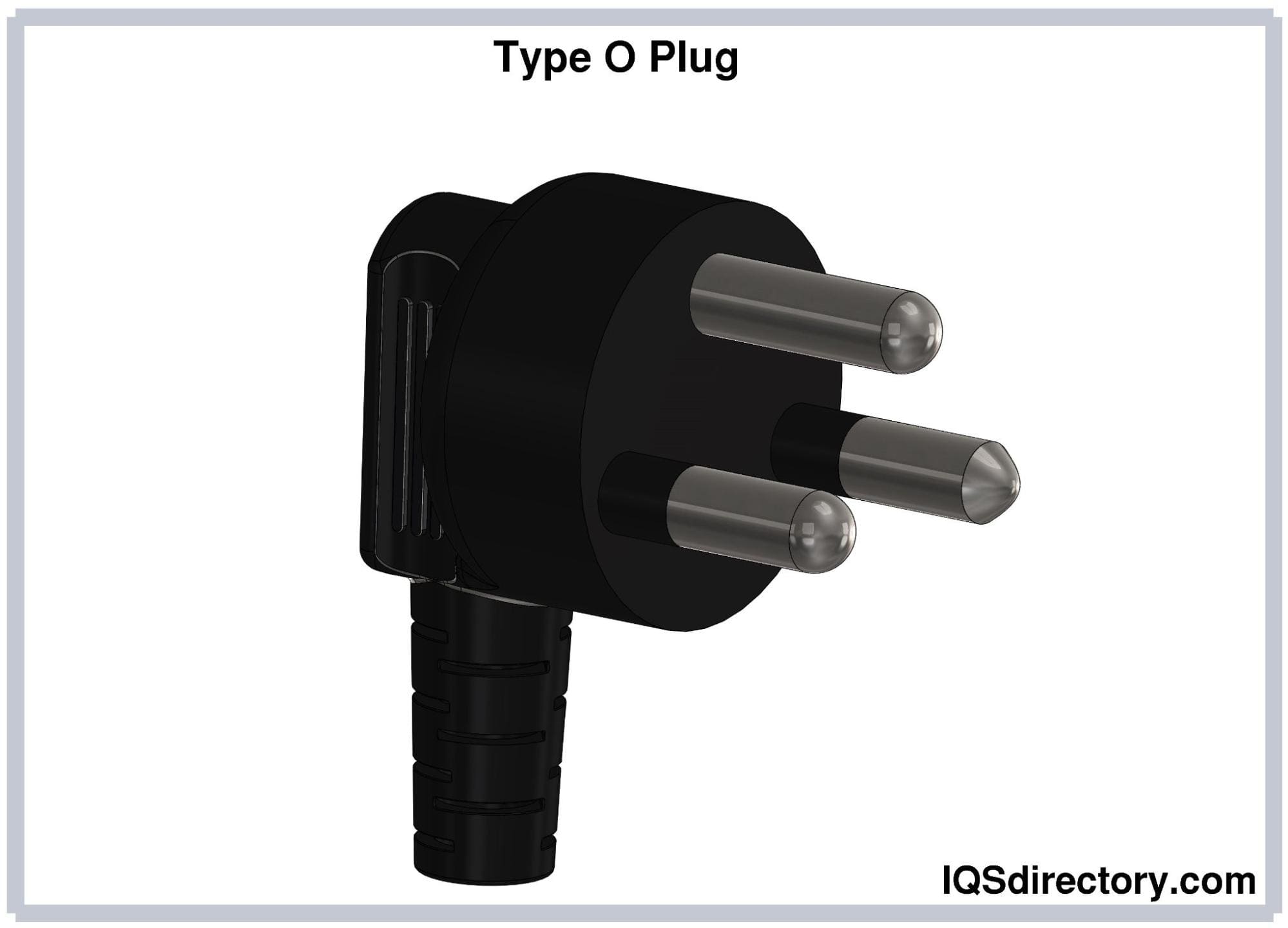
Type O (TIS 166-2549) Electrical Plugs
Type O electrical plugs consist of three round pins measuring
4.8 mm in diameter. The hot and neutral pins measure 19 mm long
and have an insulated sleeve covering 10 mm of their length. The
earthing pin is 21.4 mm long. The center-to-center distance
between the hot and neutral pins is 19 mm. The earthing pin is
11.89 mm offset from the center of the imaginary line connecting
the hot and neutral pins. Type O plugs are rated at 16A.
Type O plugs are exclusively used in Thailand, and this type is
described in TIS 166-2549. The Type O plug and socket system was
introduced in 2006 and is currently being phased in.
Chapter 4: Plug Adapters and Replacement Plugs
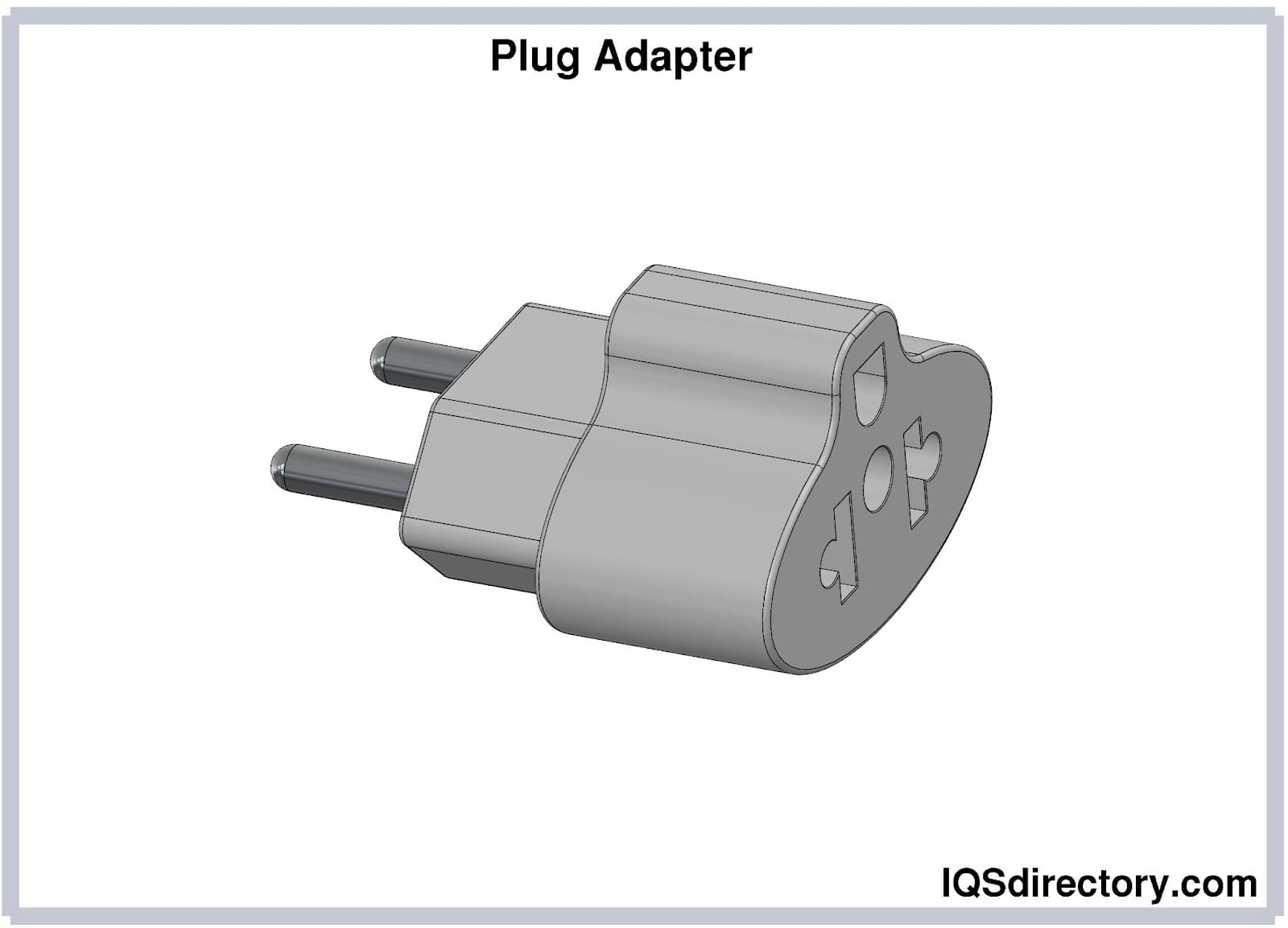
Plug Adapters
Plug adapters are small devices that make it possible to insert
a plug into a receptacle with a different number of prongs or
shapes. They are used to insert a plug into an incompatible type
of receptacle, and this instance is frequently encountered when
you visit a different country. However, they are not designed to
convert voltages and current. Plug adapters are also known as
power adapters, travel adapters, and ground plug adapters.
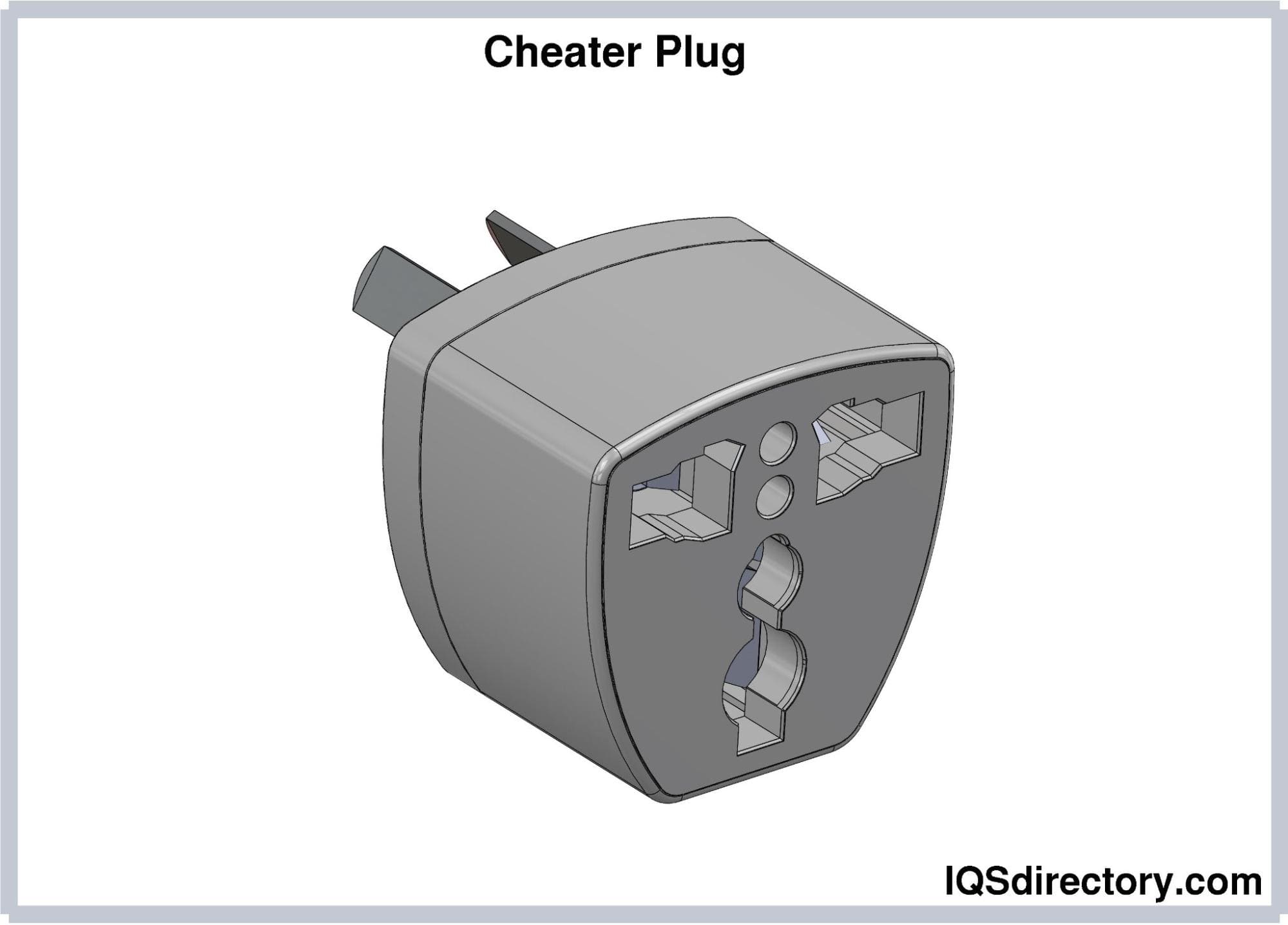
Cheater plugs, or three-to-two prong plug adapters, can
allow a three-pronged plug to a two-slot receptacle. They run
your electrical appliance normally, but they disable the
grounding feature of the three-pronged receptacles. Therefore,
these adapter plugs must not be used for a long time and be
operated with extra precaution.
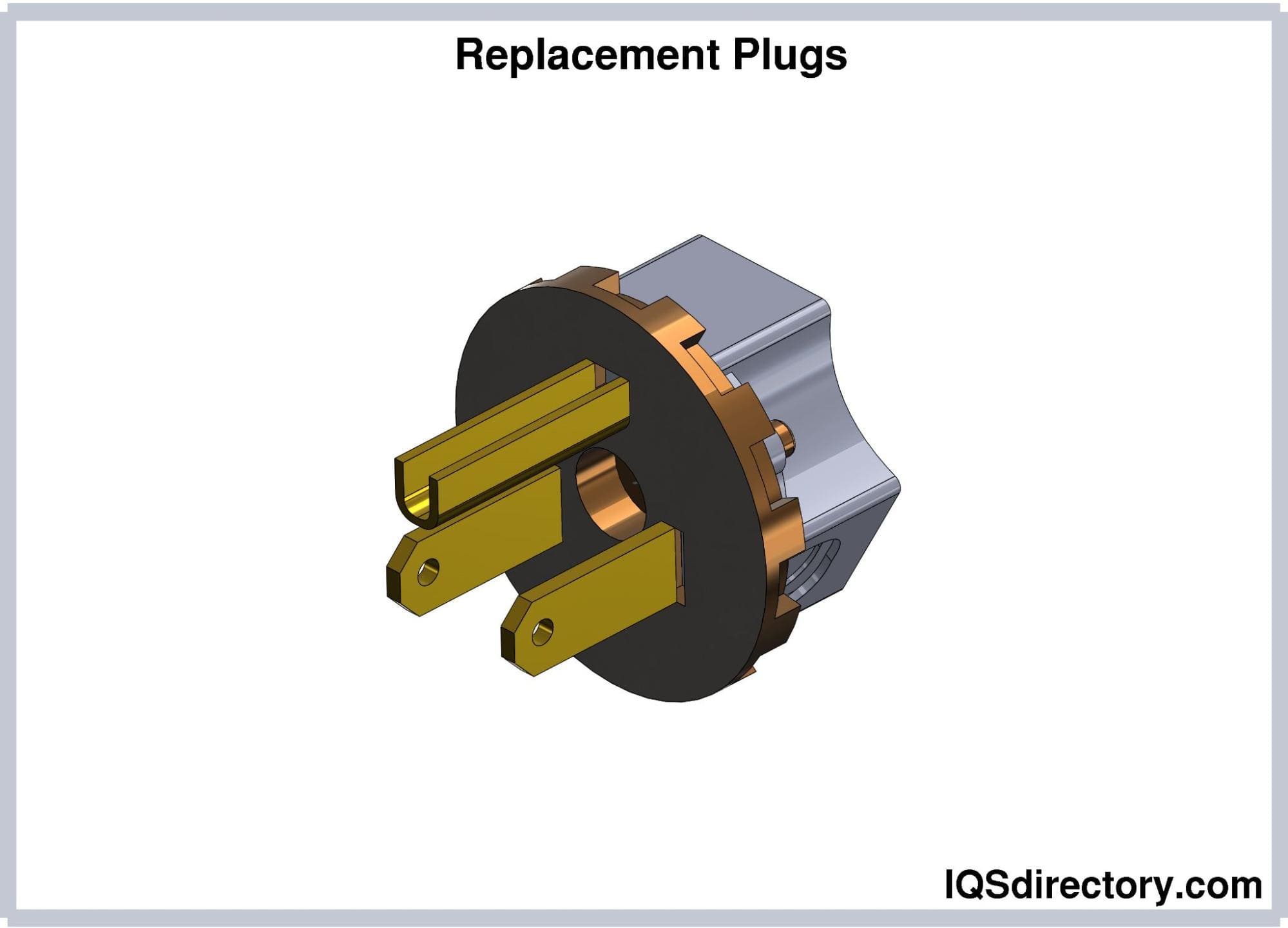
Replacement Plugs
Replacement plugs are used to replace worn-out or damaged plugs
of an electrical cord. They consist of terminals for the hot,
neutral, and grounding terminals contained in a plastic housing.
No appliances or cords are attached at the end of these devices.
The replacement plug must be of the same type and rating as the
original cord. The electrical cord must be unplugged from the
outlet before installing the replacement plug. The old plug is
cut from the cord, and the outer jacket and wire insulations are
stripped to expose the wires. The bare wires are then connected
to the corresponding terminals in the dismantled replacement
plug. Finally, the wires are locked in place, and the housing is
reassembled.
Conclusion
-
Electrical plugs are devices responsible for supplying current
from the receptacle to the circuity of an electrical
appliance. -
Electrical plugs have two or three prongs. Hot and neutral
pins are present in both two- and three-pronged plugs. A
grounding pin is introduced in three-pronged plugs as a safety
feature. -
There are fifteen standard types of mains electrical plugs
recognized by the International Electrotechnical Commission
(IEC) and listed under the IEC-60083 standard. Each type has a
letter designation. These types differ in the dimensions, the
number of contacts, current and voltage ratings, and the
countries in which they are used. -
Plug adapters enable the insertion of a plug into an
incompatible socket. -
Replacement plugs are devices that replace worn-out or damaged
plugs of an electrical cord.
Leading Manufacturers and Suppliers
GET YOUR COMPANY LISTED ABOVE















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


