Static vs. Dynamic IP Addresses
An IP address is a unique number assigned to every device on a TCP/IP network . Just like your physical home address lets people know where to send your birthday card, IP addresses identify computers and devices and lets them communicate with each other.
Internally, IP addresses are stored as numbers. While computers are happy to use numbers, humans prefer names. The Internet uses the Domain Name System (DNS) as an internet address book so you can use use words (such as www.avast.com) instead of numbers to navigate the internet and to address the devices on your network. Those devices might be anything that connects online: computers, TV, smart speakers, perhaps even your refrigerator. These days almost anything electronic in your home could have an IP address.
When you type a URL into your web browser, it uses DNS to look up the IP address for that domain. For example, if you type www.avast.com into your browser, DNS returns one of several IP addresses, including 77.234.41.52.
There are two versions of IP addresses in common use: IPv4 and IPv6.
IPv4 has four hexadecimal numbers separated by periods – such as 192.168.0.1 – while IPv6 has six hexadecimal numbers separated by colons – such as 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334. There are almost 4.3 billion IPv4 addresses, and we’ve used almost all of them. There are far more IPv6 addresses. We’ll not run out of IPv6 addresses anytime before the heat death of the universe.
Mục Lục
What is a static IP address?
A static IP address is simply an address that doesn’t change. Once your device is assigned a static IP address, that number typically stays the same until the device is decommissioned or your network architecture changes. Static IP addresses generally are used by servers or other important equipment.
How to set a static IP address?
To get a static IP address, you need to contact your ISP (Internet Service provider) and request it from them. Then, you can change your regular IP address and set up a static IP address in Windows settings. Note that creating a static IP address is an advanced networking function, and it requires a basic knowledge of TCP/IP protocols.
With the static IP address assigned to you by your ISP, here’s how to enter your IP address manually on a Windows 10 device:
-
Click Start and then click Settings. Note that you need admin access.
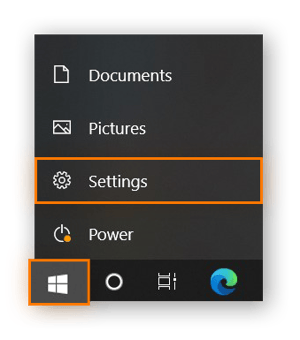
-
Choose Network & Internet in the Settings window.
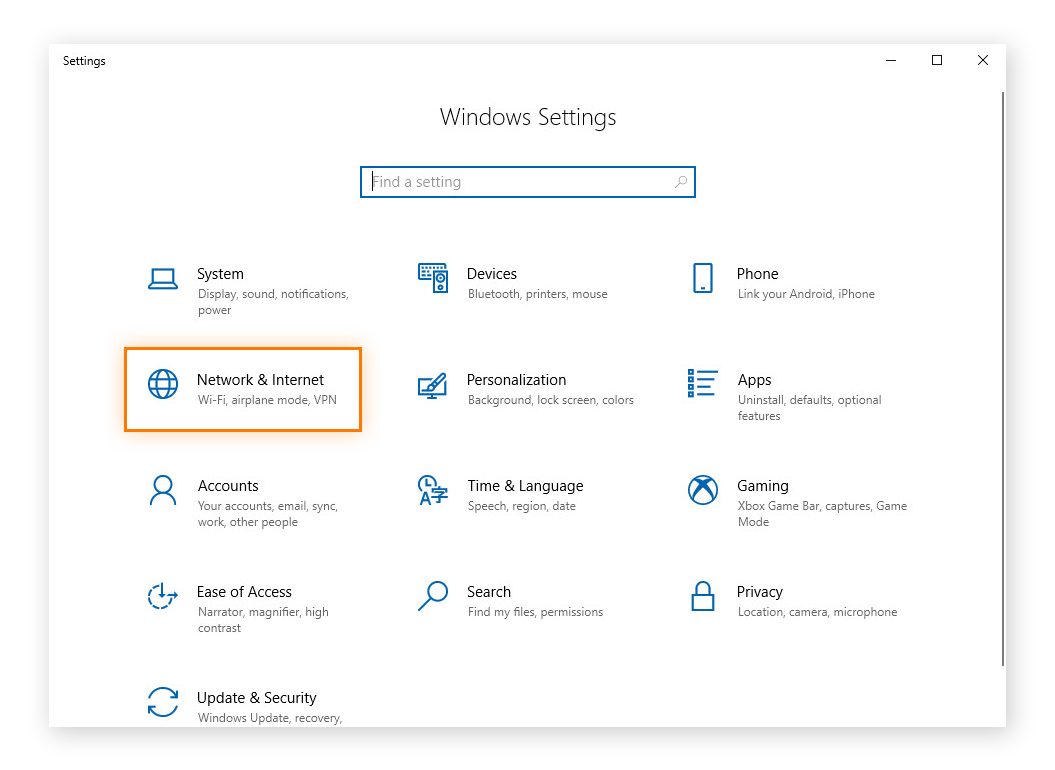
-
Click Properties under the local area connection field.
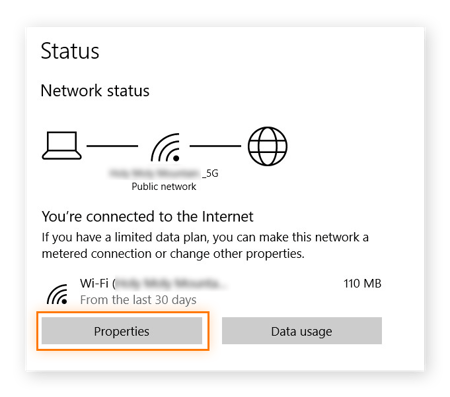
-
Click Edit under IP assignment.

-
Choose Manual, turn on the IPv4 button, and enter the IP address. Click Save.
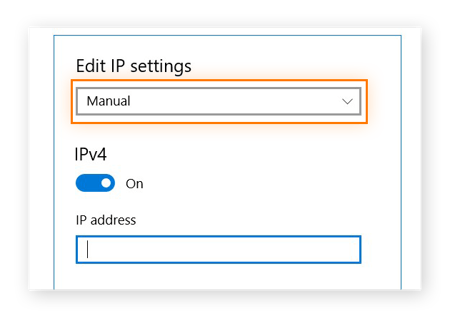
Follow these step-by-step instructions on how to enter your IP address manually on other devices.
Static IP addresses are assigned by Internet Service Providers (ISPs). Your ISP may or may not allocate you a static IP address depending on the nature of your service agreement. We describe your options a little later, but for now assume that a static IP address adds to the cost of your ISP contract.
A static IP address may be IPv4 or IPv6; in this case the important quality is static. Some day, every bit of networked gear we have might have a unique static IPv6 address. We’re not there yet. For now, we usually use static IPv4 addresses for permanent addresses.
What is a dynamic IP address?
As the name suggests, dynamic IP addresses are subject to change, sometimes at a moment’s notice. Dynamic addresses are assigned, as needed, by Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) servers.
We use dynamic addresses because IPv4 doesn’t provide enough static IP addresses to go around. So, for example, a hotel probably has a static IP address, but each individual device within its rooms would have a dynamic IP address.
On the internet, your home or office may be assigned a dynamic IP address by your ISP’s DHCP server. Within your home or business network, the dynamic IP address for your devices — whether they are personal computers, smartphones, streaming media devices, tablet, what have you — are probably assigned by your network router. Dynamic IP is the standard used by and for consumer equipment.

Static vs. dynamic: Which is best for me?
There is no perfect IP address solution for all people and all occasions. Sometimes, it is better for a computer or device to use a static IP address; sometimes a dynamic IP address works best.
Deciding whether dynamic or static IP addresses are better for you also depends on the nature of the connection. A static IP address is more likely to be relevant for a business, while a dynamic IP address is appropriate for a home network.
Advantages of a static IP
There are numerous advantages to using a static IP address. Among these benefits are:
-
Better DNS support: Static IP addresses are much easier to set up and manage with DNS servers.
-
Server hosting: If you are hosting a web server, email server, or any other kind of server, having a static IP address makes it easier for customers to find you via DNS. Practically speaking that means it’s quicker for clients to get to your websites and services if they have a static IP address.
-
Convenient remote access: A static IP address makes it easier to work remotely using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) or other remote access programs.
-
More reliable communication: Static IP addresses make it easier to use Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) for teleconferencing or other voice and video communications.
-
More reliable geo-location services: With a static IP address, services can match the IP address with its physical location. For example, if you use a local weather service with a static IP address you’re more likely to get the weather report you need instead of the one for the next city over.
Disadvantages of a static IP
A static IP address isn’t ideal for all situations.
-
Static IPs are more hackable: With a static IP address, hackers know exactly where your server is on the Internet. That makes it easier for them to attack it. Avast Internet Security can help you in this regard.
-
Higher cost: ISPs generally charge more for static IP addresses, particularly with consumer ISP plans. Business ISP plans often include static IP, at least as an option, but they are more expensive than end-user plans; be sure to ask if it’s an extra cost.
-
Real-world security concerns: Anyone with the right network tools can find where you and your computers are located. VPNs, such as Avast SecureLine VPN, can help alleviate this concern by hiding your physical location.
Advantages of a dynamic IP
Dynamic IP addresses are easier to manage and cheaper to deploy than static IP addresses.
-
Easy, automatic configuration: With a dynamic IP address, the DHCP server automatically assigns the device the next available IP address. You don’t need to do a thing.
-
Lower fees: Typically, you save money by using a dynamic IP address.
-
Unlimited IP addressing: Dynamic addresses allow you to reuse IP addresses. Within a network, your devices are automatically configured with a fresh dynamic IP address as needed. So, for example, if you bring home a new computer you don’t have to manually delete the old one or assign it a number; the network or router takes care of it. That prevents confusing conflicts when two computers try to use the same IP address.
-
Potentially better security: With a dynamic IP address it’s harder for a potential attacker to target your networked equipment. You can also add to your security by obscuring your network address with a VPN for PC.
-
Better physical security: It’s much harder for a snoop to find out exactly where you’re located. A VPN can help with this as well.
Disadvantages of a dynamic IP
Dynamic IP addresses are not ideal for all situations. They don’t work well for internet-facing services such as the web or email.
-
Unlikely to work well for hosted services: If you plan to host a website, email server, or so on, using a dynamic IP address may be troublesome. DNS doesn’t work well with dynamic IP addresses since the address is always changing. There are Dynamic DNS services that take care of this problem; however, they add expense and complexity. This can be a serious downside.
-
May limit remote access: Depending on your remote access software, your program may have trouble connecting if you use a dynamic IP address. That’s where VPN programs like Avast SecureLine VPN really shine.
-
Potentially more downtime: While it doesn’t happen often, sometimes your ISP is unable to assign you a dynamic IP address. This can interrupt your internet connection. For an individual consumer, that’s a temporary annoyance. It’s a much bigger problem if it knocks your company website offline.
-
Less accurate geolocation: A dynamic IP address can make your geo-location services fail because you can keep a dynamic address that no longer reflects your real-world location.
Conclusion
Typically, static IP addresses are best for businesses, which host their own websites and internet services. Static IP addresses also work well when you have remote workers logging into work via a VPN.
Dynamic IP addresses are usually fine for most consumers. They are cheaper and typically pose a bit less of a security risk.
Which type of IP address do you have?
Now that you understand the differences between static IP and dynamic IP, you may realize that it never mattered before which kind you are using. One quick way to find your IP address and its type is to use a free online tool like Avast’s IP checker.
Is it difficult to change your IP address?
If you get your internet service through an ISP or cable company, in most cases they assign you a dynamic IP address.
Within your own network, by default your devices are assigned dynamic IP addresses. It is usually not much of a problem to switch to a static IP address. You do this by going to your router’s interface, finding the device for which you want to assign a static IP address, and then assigning it one (usually by manually typing in a number). The details vary from router to router. On a network with an administrator, you need to have the system administrator do this for you.
How to protect your IP address, whether it’s static or dynamic
No matter whether your internet IP address is static or dynamic, your ISP — and tech-savvy bad guys — can tell approximately where you’re located and what you’re trying to do on the internet. You may want to hide your IP address — no matter what kind — from snoopers. A VPN, such as Avast SecureLine VPN, can help protect both your security and your privacy.















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


