Author : D. Robin Reni , AI Research Intern
Classification of Items based on their similarity is one of the major challenge of Machine Learning and Deep Learning problems.But we have seen good results in Deep Learning comparing to ML thanks to Neural Networks , Large Amounts of Data and Computational Power. We have mostly seen that Neural Networks are used for Image Detection and Recognition etc . But I am not going to explain how we execute it. But in brief, we can say that “ Neural Networks are extracting features by finding the patterns in large set of images using mathematical computation for detecting and recognizing“.
But
why Siamese Neural Network
s
?
and
What
are
Siamese Neural Network
s
?
. For many of them it
is
a
new word. Don’t worry
!
I will make it clear and easy
for you
. I
will
also explain
the same
with a small mini project.
But before that
,
you should understand some terminologies and topics behind it. Lets dive in!
Siamese Neural Network Definition :
A
Siamese
N
eural
N
etwork is a class of neural network architectures that
contain two or more
identical
sub networks
.
‘
identical
’
here means
,
they have the same configuration with the same parameters and weights. Parameter updating is mirrored across both sub networks.
It is used
to
find the similarity of the inputs by comparing its feature vectors.
One-shot Learning :
It is an object categorization problem, found mostly in Computer Vision. Wh
ere, m
ost Deep Learning based object categorization algorithms require training on hundreds or thousands of samples/images and very large datasets, one-shot learning
aims to learn information about object categories from one, or only a few, training samples/images
.
More about One-Shot Learning :
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FIjy3lV_KJU
Contrastive Loss or Lossless Triplet Loss:
Like any distance-based loss, it tries to ensure that semantically similar examples are embedded close together. It is calculated on
Pairs
(other
popular distance-based Loss functions are Triplet & Center Loss, calculated on
Triplets
and
Point wise
respectively)
More about Triplet Loss :
https://omoindrot.github.io/triplet-loss![]()

Reasons to Use Siamese Neural Network :
-
Need
s
less training Examples to classify image
s
because of One-Shot Learning
-
Learn by Embedding of the image so that it can learn Semantic Similarity
-
It helps in ensemble to give the best classifiers because of its correlation properties.
-
Mainly used for originality verification .
That’s i
t! T
hese are the main terminologies that you should know before you get started with Siamese Networks . Now we can learn about architecture and inner working of the network .
Siamese Neural Network Architecture :

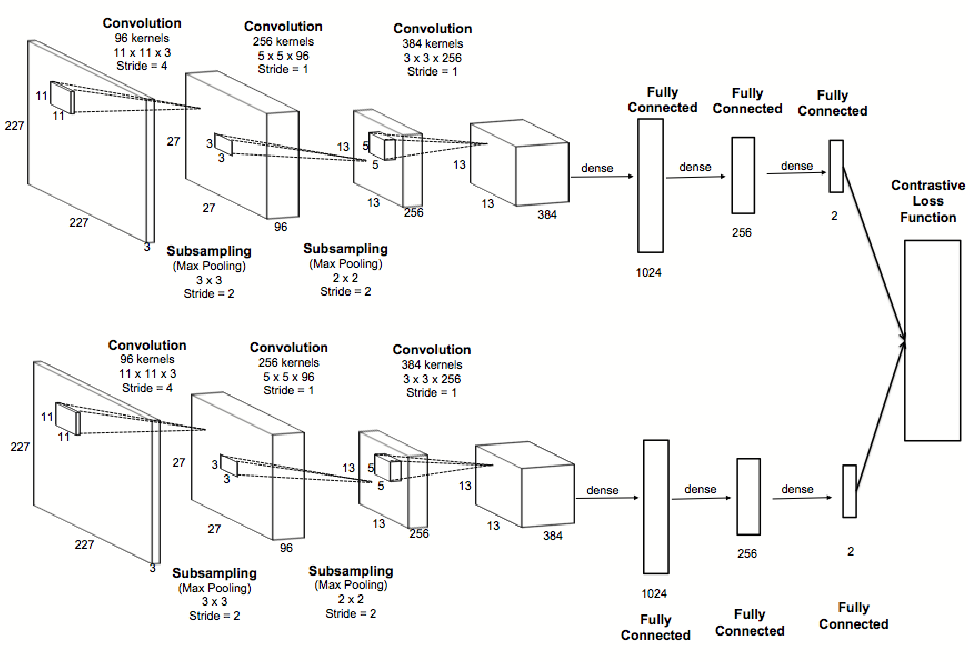
Don’t get panic by seeing its architecture. It
’
s an elaborated structure of two identical CNN which is placed parallel. All the layer definitions of the CNN are depends upon the developer and the domain for what they are developing . The only thing you have to note from this architecture is
Two Identical CNN’s placed in parallel.
If you are not familiar about Convolutional Neural Network read this blog :
https://medium.com/@phidaouss/convolutional-neural-networks-cnn-or-convnets-d7c688b0a207
.
Working with Siamese Neural Network :
In general, we learn image representations via a supervised metric-based approach with siamese neural networks, then reuse that network’s features for one-shot learning without any retraining.
Also we use
large Siamese Convolutional Neural Networks
because learning generic image features, easily trained and can be used i
rrespective of the
domain.
-
Preprocessing :
First step,
Collect and Preprocess
your data .

-
Feature Extraction :
Next create sequence model for the same architecture which is to pass
Input 1
and
Input 2.
It is the step where Siamese theory is implemented and final layer of both the architecture should return a feature vector of the passed input images
Feature Vector of Image 1
and
Feature Vector of Image 2
.
-
Similarity Score :
Then to calculate the similarity of the the two feature vectors we use some
similarity functions
such as
Cosine Similarity , Euclidean Distance
etc and this function gives similarity score of the feature vectors and based upon the threshold of the values classification is done .
-
Loss Function :
To find the loss on the Validation Set , we use
triplet loss function , contrastive loss
,
regularized cross entropy
etc to find out the loss and calculate the accuracy .
-
Optimization :
So , to improve the accuracy we will backpropagate the network and optimize the loss using optimization techniques such as
RMSprop, Mini Batch Gradient Descent , Adam Optimizer
etc.
-
Training :
Now our complete flow for training is set . Train the model with the preprocessed images until a fixed epoch.
Test your accuracy if it
’
s low then try
Hyper Parameter Optimization
to improve it.
Also
increasing your data and image augmentation
may help you in increasing the accuracy.
-
One-Shot Learning :
Now we have a mastered trained Siamese Network for classification or Verification.
We have a
test image X
and we wish to classify into
one of C categories
. For each C categories we have Xc= { X0 , X1 , X2 , …. , Xc-1 } images.Calculate the
similarity score for X and Xc images
.Then
predict the class corresponding to the maximum similarity
. This step is known as One Shot Learning.
That’s it ! These are the important working principles which you have to know when you ar
e
to implement Siamese Neural Network for your problem. Its time to make your own Siamese Neural Network.
Lets get your hands dirty with some python codes.
Hands-On with Siamese :
We know that Siamese is basically for
classification using similarity score.
In this blog we just represent the main part of Siamese Network. We considered
Offline Signature Classification
based upon Similarity Score as proof of concept. The Siamese architecture is inspired by
Signet Paper
. The dataset we used is
ICDAR 2011 Dataset
since its the classic and valid open source data.
Siamese Code Structure
class SiameseNetwork(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(SiameseNetwork, self).__init__()
# Setting up the Sequential of CNN Layers
self.cnn1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 96, kernel_size=11,stride=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.LocalResponseNorm(5,alpha=0.0001,beta=0.75,k=2),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2),
nn.Conv2d(96, 256, kernel_size=5,stride=1,padding=2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.LocalResponseNorm(5,alpha=0.0001,beta=0.75,k=2),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2),
nn.Dropout2d(p=0.3),
nn.Conv2d(256,384 , kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(384,256 , kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2),
nn.Dropout2d(p=0.3),
)
# Defining the fully connected layers
self.fc1 = nn.Sequential(
# First Dense Layer
nn.Linear(30976, 1024),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout2d(p=0.5),
# Second Dense Layer
nn.Linear(1024, 128),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
# Final Dense Layer
nn.Linear(128,2))
def forward_once(self, x):
# Forward pass
output = self.cnn1(x)
output = output.view(output.size()[0], -1)
output = self.fc1(output)
return output
def forward(self, input1, input2):
# forward pass of input 1
output1 = self.forward_once(input1)
# forward pass of input 2
output2 = self.forward_once(input2)
# returning the feature vectors of two inputs
return output1, output2
Contrastive Loss Definition
class ContrastiveLoss(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, margin=2.0):
super(ContrastiveLoss, self).__init__()
self.margin = margin
def forward(self, output1, output2, label):
# Find the pairwise distance or eucledian distance of two output feature vectors
euclidean_distance = F.pairwise_distance(output1, output2)
# perform contrastive loss calculation with the distance
loss_contrastive = torch.mean((1-label) * torch.pow(euclidean_distance, 2) +
(label) * torch.pow(torch.clamp(self.margin - euclidean_distance, min=0.0), 2))
return loss_contrastive
Oneshot Learning :
Oneshot learning is like extracting the feature vectors of the input images from the trained model to say
how much both of the images are dissimilar
without training the images of large datasets
.
def oneshot(model,img1,img2):
# Gives you the feature vector of both inputs
output1,output2 = model(img1.cuda(),img2.cuda())
# Compute the distance
euclidean_distance = F.pairwise_distance(output1, output2)
#with certain threshold of distance say its similar or not
if eucledian_distance > 0.5:
print("Orginal Signature")
else:
print("Forged Signature")
That
’
s it from codingside ! For making the model into production you can follow lot of articles and production documents.
Major Applications Siamese Neural Network :
-
Face Recognition based upon Similarity
-
Object Classifier
-
Detect minute changes in Documents
-
Blood Cell Classification
To View Full Code and Model , Run this in your
Google Colab
Account :
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1FsixLon5Zz3_rFA0xIHzc8Tvnnw8FLr8
Reference :
1.
https://medium.com/@subham.tiwari186/siamese-neural-network-for-one-shot-image-recognition-paper-analysis-44cf7f0c66cb
2.
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1707.02131.pdf
3.
https://hackernoon.com/one-shot-learning-with-siamese-networks-in-pytorch-8ddaab10340e
4.
https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~rsalakhu/papers/oneshot1.pdf
5.
http://cs231n.stanford.edu/reports/2017/pdfs/801.pdf
Hope you got lot of insights from this blog. Feel free to share your comments and acknowledge your support by sharing.



















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


