Making the right choice: static IP vs dynamic IP explained
Internet Protocol (IP) addresses are like street addresses in the digital world. They identify devices on TCP/IP networks and make it possible for other devices to locate them.
Every internet-connected device has a unique IP address. All of these addresses can be converted into text formats via the Domain Name System (DNS) format. This forms the basis of the World Wide Web. But underneath every website name, you will find at least one IP address.
There are two main types of Internet Protocol addresses: static and dynamic IP addresses. Both versions have specific roles. Both have strengths and weaknesses, and choosing the right type for your networking needs is important.
This article will explain how dynamic and static addresses work, their use, and how to choose between them.
Mục Lục
What is a static IP address?
The word “static” means unchanging, which describes how a static IP address works. It performs the IP address functions discussed previously and tells other computers or servers on the internet where a specific computer is located or connected. As it doesn’t change, external devices can always use the same IP address to reach the same destination.
This makes static IPs useful in business environments when setting up hosting, email, FTP servers, or remote access. Network administrators often use static IP addresses to make their resources available only to the allowlisted IP addresses.
Benefits of static IP
Obtaining a static IP address is a separate process that requires additional involvement from the organization’s or network administrator’s part. Here are some examples of why a static IP might be a beneficial addition to your organization.
Allows hosting
A static IP address comes into its own when used with web servers. With a static address, site visitors will find it easier to locate a website on the internet. Connection speeds may also be slightly quicker.
Streamlines resource access
When securing internal networks, administrators often introduce various barriers. IP addresses denylists often fit into this equation as remote users can request temporary access with their used dynamic IP. However, this window can be quite short for safety reasons, and it’s generally a very inefficient system.
Fixed IPs allow a centralized mechanism through connections to a shared gateway, allowing a much more solid system. Additionally, various security posture checks can be added to increase security layers.
IP allowlisting
If remote workers have a static IP address, security teams can use that address to filter legitimate traffic. Allowlisting supplements, firewalls, and VPNs. It effectively hides network resources from outsiders whose IP is not allowlisted. In turn, this promotes better data security and shuts down unauthorized pings.
How to set up a static IP address
While it’s possible to alter the addresses assigned to devices on the internal network, the IP address assigned to your router is subject to change at your internet service provider’s (ISPs) discretion. Therefore, static IP addresses must be requested by signing up for a special service plan and paying an extra fee. This will provide you with a unique fixed IP address no one uses.
In addition, it’s possible to obtain a fixed IP address by turning to VPN service providers. The service provider can then set up a dedicated server with a fixed IP address that’s reserved for exclusive use. Connecting to such a server allows routing all traffic through an intermediary server with an assigned static IP address. This allows obtaining a static IP address without changing your ISP’s plan.
What is a dynamic IP address?
A dynamic IP address is a temporary address assigned to devices connected to a network. They are rotated within various time periods as they are pulled from a pool of other IP addresses. It’s much more cost-effective to cycle through IP addresses for multiple users to ensure that each is always in use.
Still, dynamic IP addresses can’t be used for some use cases. This often incentivized businesses to opt-in for static IP.
Benefits of dynamic IP
Here are the main benefits associated with dynamic IP address usage.
Cost-efficiency
A dynamic IP address is usually cheaper to use than static alternatives. There is no regular fee. Addresses are assigned as part of ISP packages and work automatically without additional user involvement.
Security benefits
Hackers may obtain static IPs and use them to breach network resources. Because a dynamic IP address changes regularly, it presents a moving target. This makes life harder for potential attackers when targeting home users.
How does dynamic IP work?
Dynamic IP is based on the principle of scarcity. For instance, IPv4 is written in decimal digits for 8-bit fields. This means that a finite number of possible combinations can be used. As a workaround, ISPs limit the number of static IP addresses while trying to maximize the use of the remaining IP addresses pool by recycling them. When a requesting Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) computer is assigned one of them — it’s a dynamic IP address assignment in action.
After the session duration expires or a specified amount of time runs out, the same IP address returns to the same pool of addresses. When the next user begins a session, the ISP can retrieve and assign an IP address. This cycle continues continually rotating IP addresses among its users.
Comparison of static and dynamic IP addresses
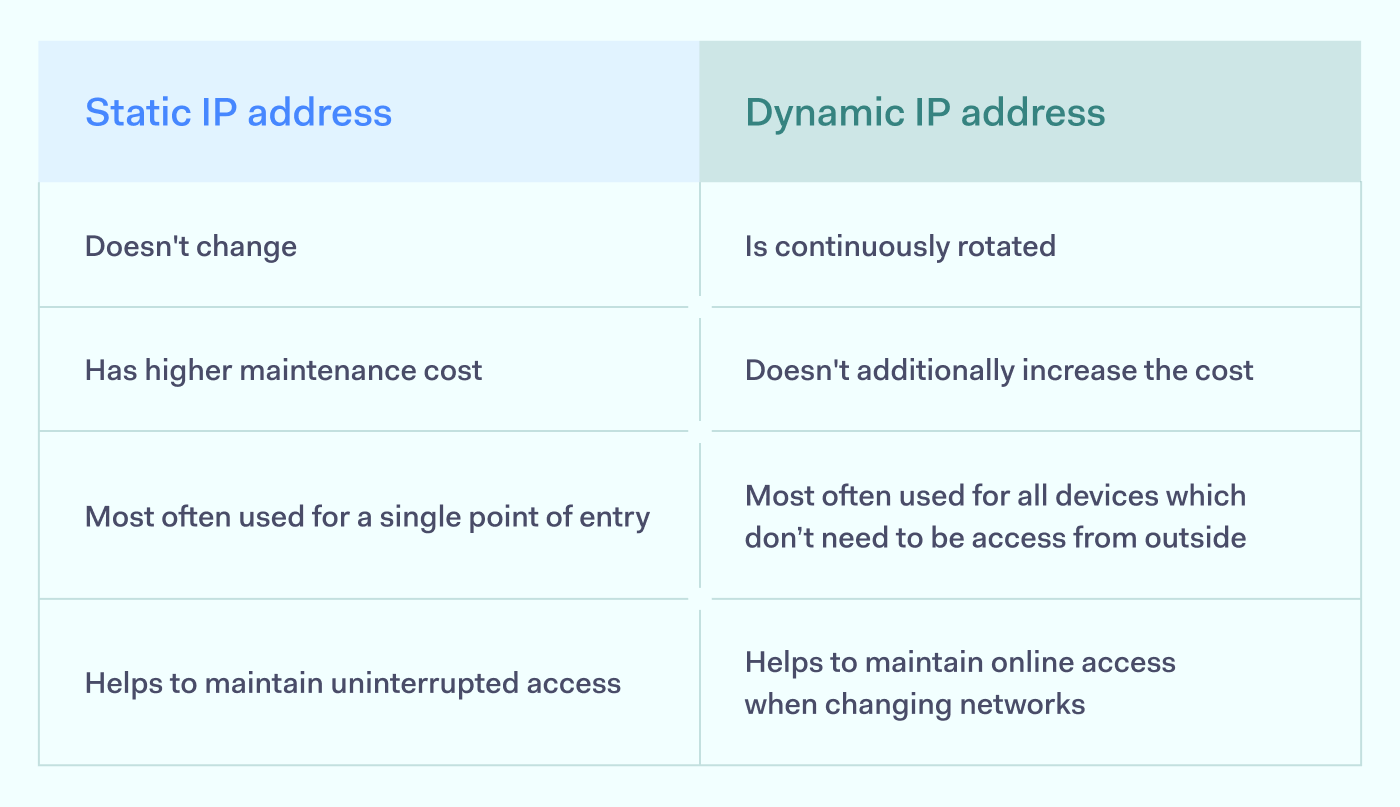
The main difference between static and dynamic IP addresses is their availability. What’s different is that these different availability modes also lead to different use cases. As static IP is a much more expensive option, it’s primarily used when some configurations require connecting with the same IP address. Business users usually favor static IP routes when setting up access to internal resources. In this sense, static IP is treated as an additional condition for access.
Dynamic IP address facilitates network communications, mainly used by home users who just need internet access. The address change doesn’t affect the user in any way, and ISP can change the IP address even as the user is browsing.
When to use a static or dynamic IP address?
Here’s a short rundown of static IP vs. dynamic IP addresses and their use cases.
When to use a static IP address
Businesses generally prefer static IPs. Unchanging IP addresses are ideal for hosting websites because they suit DNS server architecture.
Your web or email server will be easier to find with a static IP. External partners can use a single point of contact to interact with servers or databases. And that address only changes if you want it to.
If you plan to connect an email server or design a remote work system, static IP addresses will probably work best.
It is also easier to apply IP allowlisting with a static IP address. Allowlisting adds an extra layer of network protection. Security teams can add static addresses to firewall rules and block everything else. Remote workers can identify themselves easily. Wherever they are, the network will recognize them as authentic users.
When to use a dynamic IP address
Dynamic IP is generally found in the home and consumer settings. The low cost and convenience are a good fit for everyday device usage. Dynamic IP addresses are also popular for private settings and organizations that cannot invest in enterprise security solutions.
Some device types also tend to use dynamic IP for reasons of convenience. For instance, routers may not need a static address. Dynamic DHCP-assigned addresses can be cheaper and simpler to configure.
How can NordLayer help?
Choosing the right IP address format is an important part of network architecture. Businesses can optimize their web presence, improve app performance, and realize security benefits by applying static IPs.
However, these benefits require careful implementation. NordLayer is ready to help companies as they secure their network assets.
Our dedicated server with a fixed IP enables concealing traffic and filtering access requests. Assign a static IP to your VPN coverage, and block unauthorized traffic from outside the network without denting network performance. Users can combine static IPs with network segmentation, access controls, DNS filtering, and many other security features.
With NordLayer, you can build a user-friendly security architecture that makes life easy for authenticated users and blocks malicious traffic. To find out more, contact the NordLayer team today.















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


