Internal and External IP Addresses
Although you may not know it you have two IP addresses, an Internal IP address (Private ) and an external IP address (Public).
So why do you need two IP addresses and what is the difference between an Internal and external IP address?
Mục Lục
What Is an External IP Address?
The external IP address or Public IP address is the IP address of the router interface that is connected to the Internet.
Here is a diagram to illustrate the IP address allocation on a typical home or small business network.
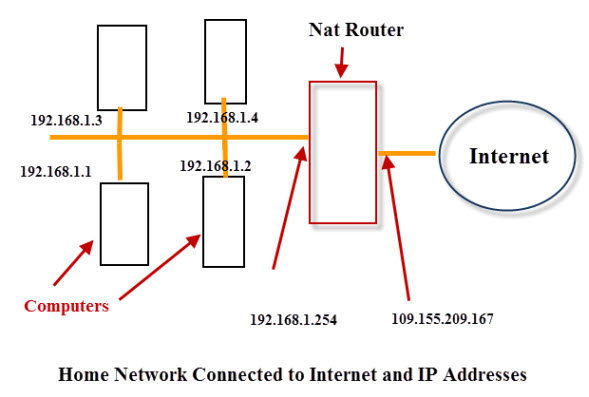
A router will typically have two network interfaces.
- An Internal Interface
- An external Interface
Each of these interfaces will have an IP address. The IP address assigned to the external Interface will have a routable IP address and will be assigned by your ISP.
This is the external address and is also known as the public address.
Public address ranges are assigned to ISPs by Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA).
On Home/home office networks that use a NAT router the internal IP addresses use a special IP address range.
NAT allows thousands of computers on an internal network access the Internet using a single external IP address.
This address range is specifically reserved for internal addresses and the IP addresses will not be forwarded by routers on the Internet.
Internal Addresses are also called Private addresses as they are restricted to private networks.
All of the devices on my home network have addresses like 192.168.1.x but externally they have the address 109.155.209.167
Home networks usually use addresses in the .192.168.0.* or .192.168.1.* address range.
The 192.168.0.0 network address range is a designated non route-able private network address.
However they are not the only non route-able private address ranges that you can use. Others address ranges that can be used are:
- 10.x.x.x is a 24 bit address block
- 172.16.x.x to 172.31.x.x is a 20 bit address block.
See wiki private networks for more details
Note: You may want to read the IP4 Addresses and classes tutorial if you are unfamiliar with network addresses.
Finding Your External (Public) and Internal (Private) IP Addresses
What is my external IP address?– To find your external IP address do a search for your IP address in Google then you will probably see a screen like this:
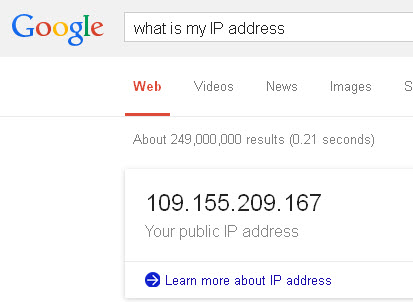
Google shows an IP address:
109.155.209.167
This is your external IP address.
What is my internnal IP address? -Open a command line and type:
ipconfig
You should see something like this:
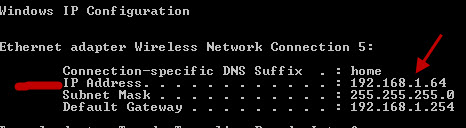
This time your IP address is 192.168.1.64
This is your Internal IP address.
The internal IP address, is used on your local internal network and the external IP address is used when communicating with machines on the Internet.
Allowing Access from The Internet To Your Network
Because of the NAT router there is no direct connection between the Internet, and a computer on the local network.
All communication between your Internal network and the Internet must be initiated by a device on your Internal network.
Generally this isn’t a problem, and is a security advantage.
However online gamers, and those who would like to host a website or other services on their own network will need to allow external devices on the Internet to access them.
To accomplish this NAT routers can be configured to use a technique called port forwarding.
Port forwarding allows an internal device to to appear to have an external IP address, and allows incoming connections from the Internet.
Summary
Home and business networks use private or internal addresses from a reserved non route-able address range.
On Home and Small Office networks a NAT router connects the internal network to the Internet using a single route-able external or public IP address assigned by the ISP from it’s allocated address block.
The NAT router allows connections to be established only from the internal network to the external network and not vice-versa unless techniques like port forwarding are employed.
Common Questions and Answers
Q- My External IP Address Keeps Changing. Is this normal? Can I stop it?
A- Most ISPs will allocate dynamic IP addresses to their customers. This Address will become the External IP address assigned to your router, and hence it could change.
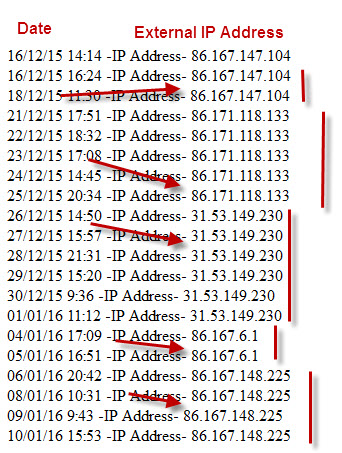
This is a screenshot showing how my own external IP address has changed over a month.
Some ISPs will allow you to have a static IP address but usually at a premium ( Business broadband)
Static IP addresses do not change.
If you intend providing access to your network from the Internet, then you really need a static external IP address.
However an alternative for home and small business networks is to use a dynamic DNS service.
A dynamic DNS service doesn’t stop the external address from changing, but instead it tracks these changes automatically and updates the DNS records automatically when the IP address changes.
Video
For those who prefer video then I’ve create a video on YouTube that covers the main points above.
Common Questions and Answers
Q- Can You Use an internal IP address on the Internet?
A- No – The internal IP address ranges discussed above are blocked by Internet routers.
Q- How does a message reach an Internal IP Address from an external one?
A- This is done using a translation table on the NAT router, and is covered in understanding port forwarding.
Q- Does in make any difference if I use the 10. IP address range and not the 192.168.0.0 address range.
A – No none at all. However most home routers are preset to use the 192.168 address range.
Q- Who assigns my external IP (Public) address?
A- It is assigned by your ISP.
Q- How do I know if my External Address has changed?
A- You will need to check it using the technique shown earlier.
Q- Can I change my External IP Address?
A- No
Related Articles and Resources:
Please Let me Know if you found it Useful
[Total:
41
Average:
4.6
]















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


