How to restart network services in Linux – LinuxWays
Sometimes, when you changed the network configuration or due to some network problems, you may need to restart the network services again on your Linux system to solve your problem. In this article, we will talk about how to restart the networking services on in different Linux distributions (Ubuntu, Debian, LinuxMint and CentOS) by using the command line. We have implemented different commands on Ubuntu 20.04 and CentOS 8 system. All commands which we have executed on Ubuntu 20.04 can be also used for Debian and LinuxMint distributions.
Mục Lục
Get network Service Status
You can get the network services running status by using the following command:
For latest (Ubuntu/Debian/Mint)
To check the networking services are running on your system or not, by using the following ‘systemctl’ command you can view the networking service status on your Ubuntu/Debian/Mint system:
$ sudo systemctl status networking
Or
$ sudo systemctl status networking.service
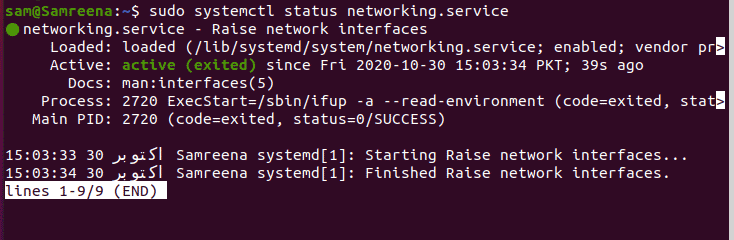
You can also display the networking service status by using the service command which is given as follows:
$ sudo service networking status
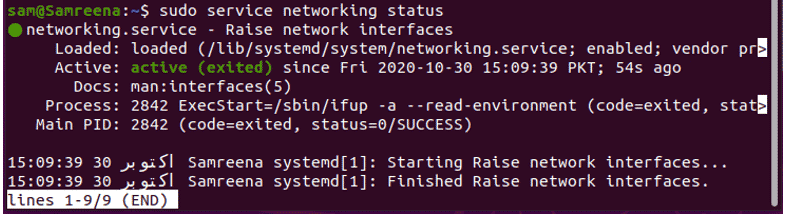
Or
$ /etc/init.d/networking status
For CentOS 8 / Fedora
If you are using CentOS 8 then you can check the network service status by using the following command:
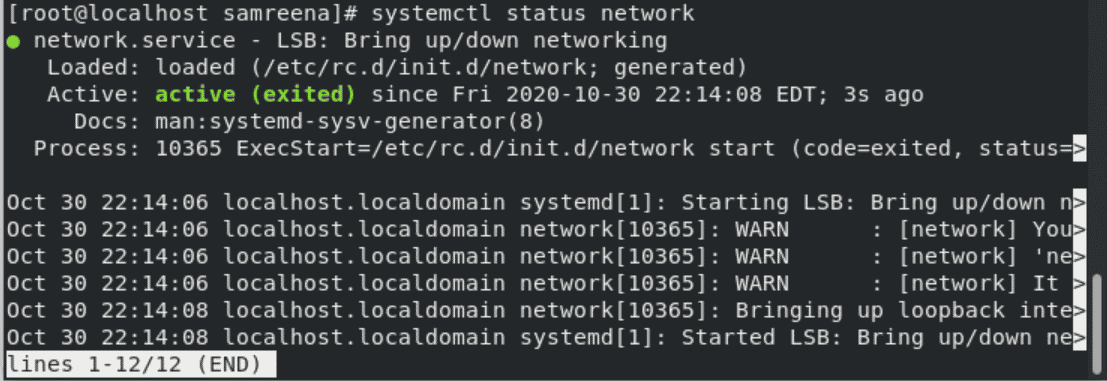
# systemctl status network

If you received an error like ‘network.service unit not found’ then, you will run the following command to start the network manager:
# systemctl start NetworkManager
![]()
Now, start the network services and you can get network status by using the above-mentioned command.
Stop Network Services
You can stop your network services through the method which is mentioned below. But, if you have a remote connection with SSH, we are not recommended you to stop the service because it may create problems.
For Ubuntu/Debian/Mint
You can use the ‘stop’ option with the above ‘networking’ command on Ubuntu, Debian, Kali, Mint distributions in order to stop network services.
$ sudo /etc/init.d/networking stop

Or
$ sudo systemctl stop networking.service
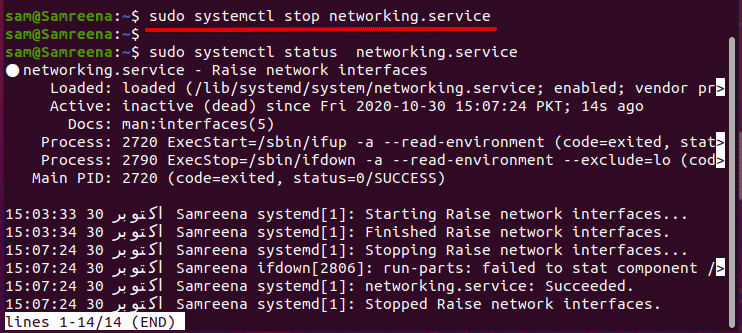
For CentOS 8/Fedora
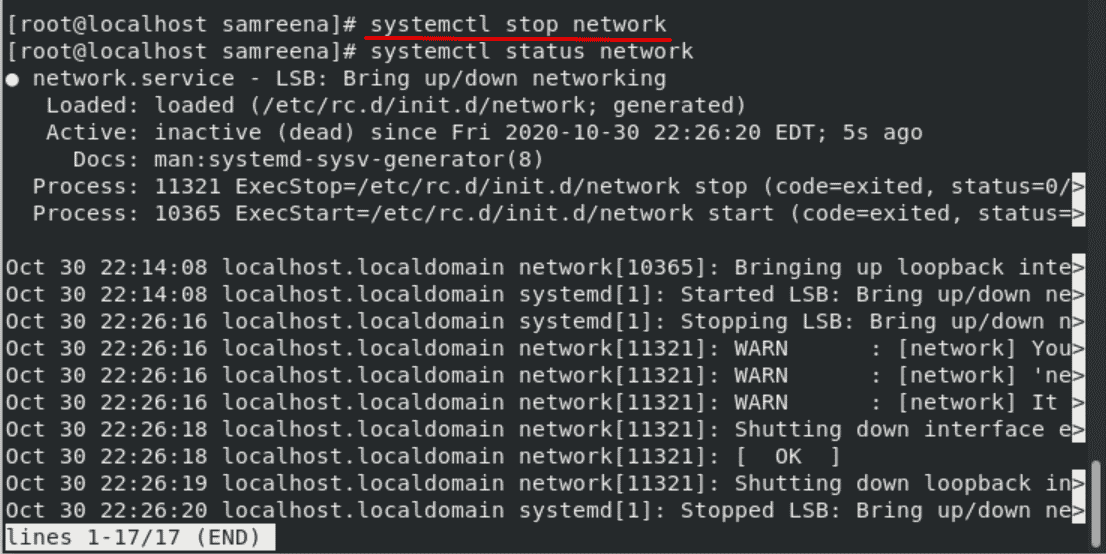
In CentOS 8, using the following command you can stop network services:
# systemctl stop network
Now, if you will check the network status you will see that network services are stopped on your system.
Start Network Service
If networking services are stopped on your system then, you start these services on the Linux system.
For Ubuntu/Debian/Mint
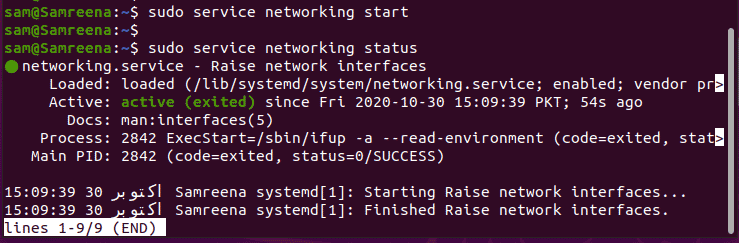
You can also start the network services by using the service command. Use ‘start’ option to start the network service on your Ubuntu. Debian and LinuxMint distributions.
$ sudo service networking start
Or
$ sudo systemctl start networking.service
Or
$ $ sudo /etc/init.d/networking start
For CentOS 8/Fedora
In CentOS 8, by using the following command you can start the network service on your system:

Restart Network Service
You can also restart the network service by using the following command on Linux distributions:
For Ubuntu/Debian/Mint
Type the following command to restart the network service on Ubuntu, Debian, and Linux Mint:
$ /etc/init.d/networking restart
Or
$ sudo systemctl restart networking.service
Or
$ sudo systemctl restart networking

For CentOS 8/Fedora
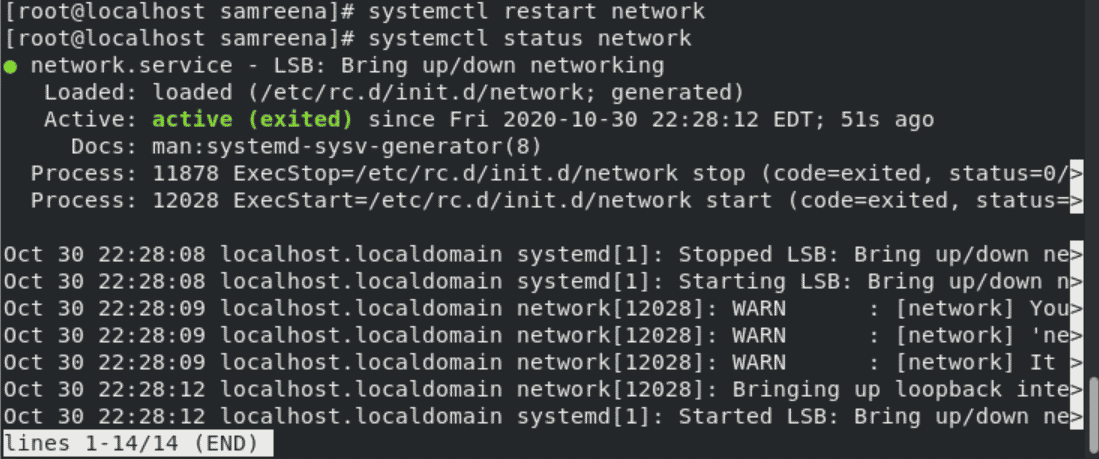
Use the following command to restart the network service on CentOS 8:
# systemctl restart network

If you get the following error on the terminal then, you need to start the NetworkManager services on your system by using the following command:
# systemctl start NetworkManager
![]()
Now, again restart the network service. You will see the following output on the CentOS system:
Conclusion
From the above information, we have explored how to start, stop, and restart the network service on different Linux distribution like Ubuntu, Debian, Linux Mint, and CentOS 8. Moreover, you can troubleshoot the network error through the NetworkManager tool on CentOS 8. If you need more details then, you can implement all command on your system and then let us know about your problems. Please don’t stop services if you have a remote ssh connection that may create a problem.
Samreena Aslam holds a master’s degree in Software Engineering. She’s a technical writer and has written various articles on different Linux flavours including Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS and Mint as well as programming guides in various programming languages















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


