How to Set Goals You Can Achieve
Setting achievable goals is one of the key skills necessary for managing a business. However, as leaders try to envision their future, they can often stumble in determining what goals are achievable within a given time frame. They can also go wrong by being too vague or too easy.
- Business goals should be specific and challenging to maximize your chances for success.
- SWOT analyses and other methods can help companies determine the right goals to pursue.
- After setting goals, businesses must track their performance and progress to stay on track.
- This article is for business owners and leaders seeking to set ambitious, attainable goals for their organizations.
No matter their industry or offerings, all companies need realistic goals to fuel business growth and success. By setting goals, organizations can allocate resources appropriately and get team members on the same page about priorities. Established businesses may have long track records to guide them on realistic goals, while startups must employ more guesswork.
We’ll explore how to set specific, challenging, and achievable business goals to help organizations map their blueprint for success.
Mục Lục
What are achievable business goals?
Achievable business goals are targets an organization sets for a specific period, such as a quarter or year. They’re realistic, not vague or hopeful expectations. When setting achievable goals for your business, it’s crucial to make them specific and challenging.
Many organizations use frameworks to help them set detailed, precise business objectives.
1. SMART Goals is a common goal-setting framework.
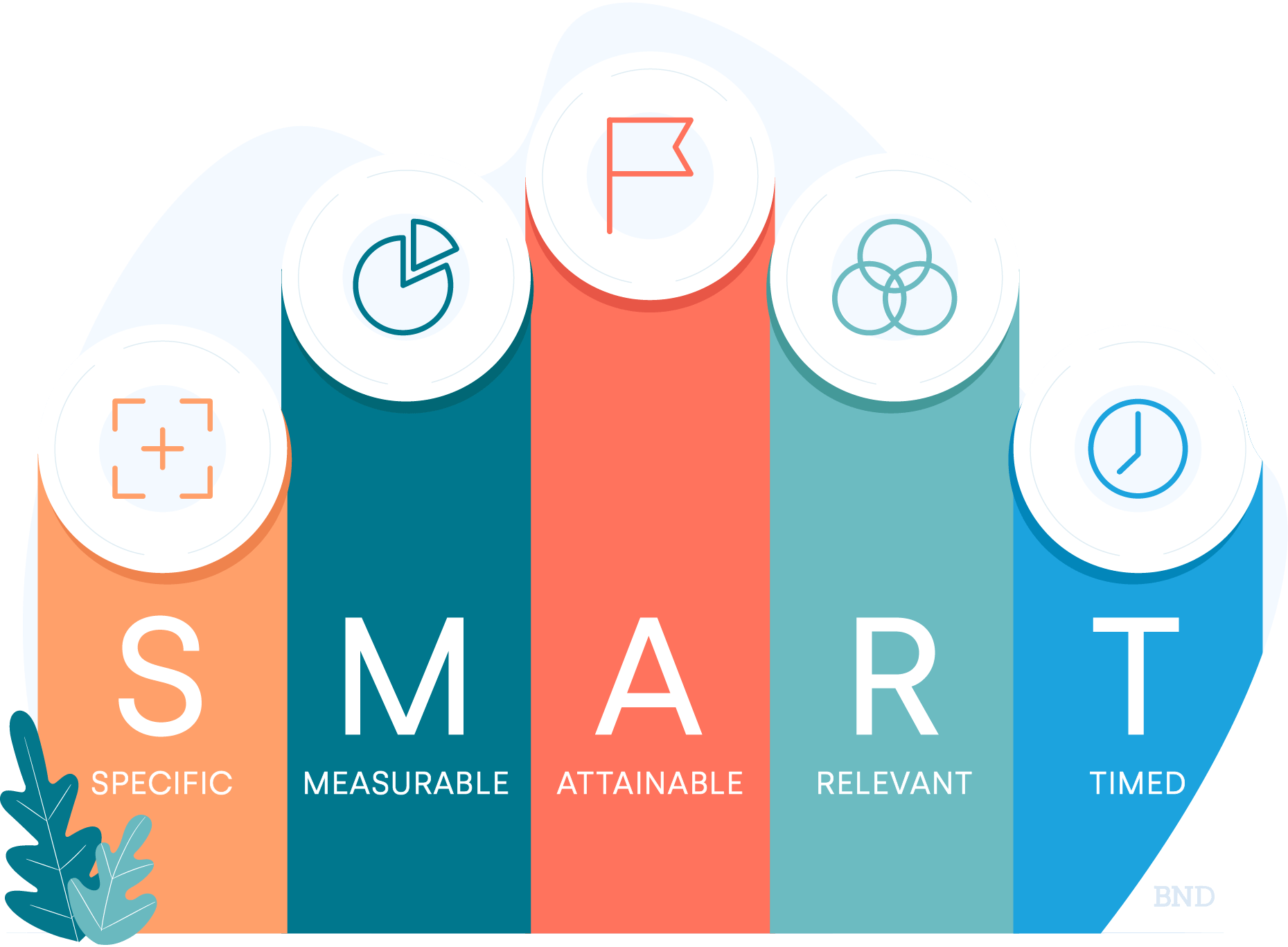
A popular business goal-setting framework is SMART Goals. SMART stands for specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-based. The SMART Goals framework aims to help organizations stay on target with systematic goal achievement.
For example, say your business wants to expand its operations. It’s unhelpful to set a goal of “make more money” or “have 10 times as many clients this year.” Both goals are too vague. Additionally, the first goal is too easy because making $1 more could count, while the second goal is difficult and overreaching. All three factors – being too vague, easy, or difficult – decrease the likelihood you’ll follow through as planned.
The SMART Goals framework urges you to consider your goal as an action plan. Be as specific as possible about what you will do, when it will happen, and how you’ll work toward it. Motivate yourself by aiming for achievements that are challenging but feel possible.
For example:
- I will have a blueprint for a new workshop written out by March, test it with my local chamber of commerce in April, and start selling regionally in May.
- I will improve my media presence by signing up for HARO and responding to three to five queries per week.
- I will finish my e-book by March, send it to an editor in April, and start selling it on my website by June.
- I will pitch three new clients every week until I have doubled my client load.
Widely cited research on goal setting and task performance states that 90 percent of the time, setting specific, challenging goals leads to higher success rates.
Did You Know?
Tech-based goal-tracking tools include reminders, performance analytics, and integrated dashboards to help make tracking goals easier and more efficient.
2. Some businesses prefer other goal-setting frameworks.
Depending on the organization type and its objectives, other goal-setting frameworks may be a better fit, including:
- WOOP. This framework stands for Wish, Outcome, Obstacle, and Plan. It’s the brainchild of German academic and psychologist Gabriele Oettingen. WOOP is a practical, motivational strategy that asks participants to imagine their future along with potential obstacles. It claims to help people reduce stress, increase engagement, and solve problems better.
- Micro goals. Some businesses prefer setting micro goals rather than one overarching goal. This involves breaking a long-term goal into achievable steps and setting daily intentions to help you reach your overarching goal more quickly.
Tip
To help achieve sales goals, create a sales plan dedicated to selling your offering to your target market and use emotional intelligence to build customer relationships.
How to determine the right business goals to pursue

When you own a business, it’s tempting to compare yourself to other entrepreneurs and small business owners and think you should be doing the same things. For example:
- If another business opens franchises, you may think it’s time for you to pursue franchise opportunities.
- If a colleague recently partnered with an investor, you may think you should also set a goal to land new funding.
- If one of your competitors starts a podcast, you start looking into podcast opportunities.
There’s nothing wrong with any of these goals if you really do want to do any of these things, such as start a podcast, franchise your business, or pitch your business idea to investors. However, if you’re pursuing goals just because that’s what you see other business owners do, you’ll quickly lose motivation and get discouraged.
Instead, focus on what you want for your own business goals and career goals. Choose goals you feel passionate about and genuinely want to achieve instead of trying to check boxes you don’t care about.
Methods for determining the right goals
Many businesses use structured methods to help them determine the right business goals to pursue. SWOT analyses and Porter’s Five Forces are examples.
- SWOT analysis. A SWOT analysis is a method many businesses use to determine the right goals to pursue. By breaking opportunities down into Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats, they can map out a path with the biggest upside and the fewest inherent risks. SWOTs are valuable because they break down the complex terrain all businesses face into four easy-to-understand concepts.
- Porter’s Five Forces. As businesses set their path, Porter’s Five Forces is a technique for better understanding the broader marketplace. Originally developed by Harvard Business School professor Michael E. Porter, the five forces look at specific factors determining whether a business can be profitable and which business goals are most likely to succeed. The five forces are:
- Competitive rivalry
- The bargaining power of suppliers
- The bargaining power of customers
- The threat of new entrants
- The threat of substitute products or services
Tracking business goals and progress
As they move forward, businesses must measure their performance relative to their goals. Many businesses utilize key performance indicators (KPIs) and data reporting.
- KPIs. KPIs are the most essential data points for measuring a business’s growth. While revenue can be a KPI, KPIs can measure almost every aspect of a business’ progress. For example, if a company wants to expand its marketing reach, KPIs might include email marketing metrics, like how many people saw an online ad, how many clicked on it, and the price per click.
- Data reporting. After determining the right KPIs for a specific goal and collecting data, businesses must organize and analyze that data. If they do so correctly, the resulting information can help them adjust their processes to maximize the outcome.
What to do when business goals fail

Business goals fail for myriad reasons. The goal itself might be the problem, or there may be issues with the people pursuing them, tenacious competitors, market trends, among many other factors. However, when a company plans precisely and methodically, it’s likely better prepared to understand what went wrong and adjust accordingly.
When a business goal fails, consider the following actions:
- Reassess your goal. Take another look at your goal and consider if it’s inherently problematic. Was it too vague? Was it unrealistic? If the goal is still valid and extenuating circumstances undercut it, it may be worthwhile to try it again. If it was too vague or challenging, reset your parameters and revise your goal.
- Set a new goal. If you decide it’s time for a new goal, evaluate your goal-setting process and focus on a new goal that’s specific, challenging, and realistic.
- Work with a support team. Working toward your business goals in isolation may lower your accountability. It can also prevent you from taking advantage of others’ experiences and creative suggestions when facing challenges. Share your goals with partners and employees so everyone works with the same blueprint and understands how their individual contributions fit into the big picture. Track the company’s progress, and celebrate achievements to stay accountable.
Key Takeaway
To help your team work together more effectively, foster a culture of teamwork, get everyone on the same page with priorities, and value everyone’s input.
Realistic goal setting is essential to success
Setting achievable goals doesn’t guarantee business success, but it’s almost impossible to succeed without them. SMBs make many small business decisions every day. Having clear, attainable goals keeps entrepreneurs moving in the right direction and lets them know when they’ve gone off course.
Katharine Paljug contributed to the reporting and writing in this article.















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


