How does Google make money? What is Google’s Business Model?
Listen to the Story
The Internet is one of the world’s most potent equalizers; it propels ideas, people, and businesses, large and small. Google’s business model is built to provide users the tools they need to increase their knowledge, health, happiness, and success while providing businesses worldwide opportunities to connect with those users and make money.
Through this story, let’s understand the service architecture of Google’s business model and how does Google make money through those services?
Mục Lục
How is the business model of Google designed?
Google’s business model comprises two segments: Google Services and Google Cloud. Google reports all non-Google businesses collectively as Other Bets. Let’s dive deep into each component, and in the next section, we will see how Google makes money from those segments.
Google Services
Google Services’ core products and platforms include ads, Android, Chrome, hardware, Gmail, Google Drive, Google Maps, Google Photos, Google Play, Search, and YouTube, each with broad and growing adoption by users around the world.
These products and services have become an integral part of the modern world and have come a long way since the company was founded over two decades ago.
Rather than the ten blue links in Google’s early search results, users can now get direct answers to their questions using their computer, mobile device, or voice, making it quicker, easier, and more natural to find what they are looking for.
Google Cloud
Google was a company built in the cloud. Google invests in infrastructure, security, data management, analytics, and AI. Google feels there is a powerful opportunity to help businesses utilize these strengths with data migration, modern development environments, and machine learning tools to provide enterprise-ready cloud services, including Google Cloud Platform and Google Workspace.
Why did Google Plus Fail to take off?
Google Cloud Platform enables developers to build, test, and deploy applications on its highly scalable and reliable infrastructure. Google Workspace collaboration tools — apps like Gmail, Docs, Drive, Calendar, Meet, and more — are designed with real-time collaboration and machine intelligence to help people work smarter.
Because more and more of today’s digital experiences are being built in the cloud, Google Cloud products help businesses of all sizes take advantage of the latest technological advances to operate more efficiently.
How does Google make money?
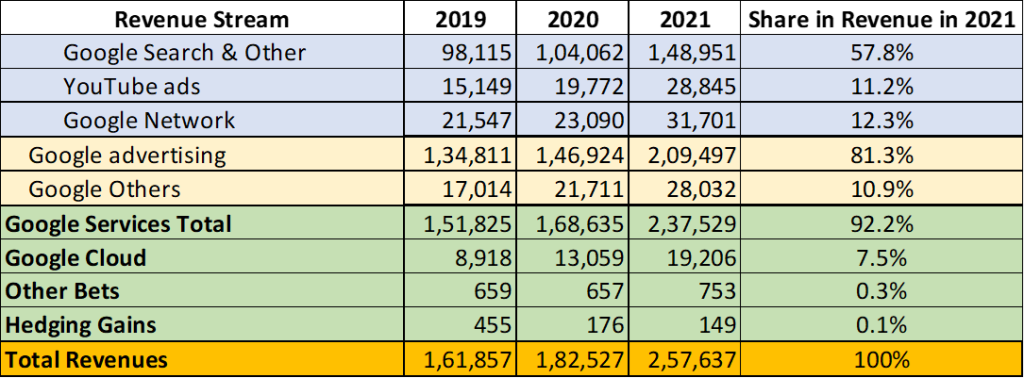
Google generated $257,637 billion in revenue in 2021. Google’s revenue streams are segmented into three areas: Google services, Google Cloud, and Other Bets. Google services are further segmented into Google advertising and Others. Advertising includes Google search, YouTube Ads, and Google Network.
Google Services
Google Services primarily generates revenues by delivering performance and brand advertising that appears on Google Search & other properties, YouTube, and Google Network partners’ properties (“Google Network properties”).
- Performance advertising creates and delivers relevant ads that users will click on, leading to direct engagement with advertisers. Performance advertising lets advertisers on Google connect with users while driving measurable results. Google’s ads tools allow performance advertisers to create simple text-based ads.
- Brand advertising helps enhance users’ awareness of and affinity for advertisers’ products and services through videos, text, images, and other interactive ads across various devices. Google helps brand advertisers deliver digital videos and different types of ads to specific audiences for their brand-building marketing campaigns.
Google Services revenues consist of revenues generated from advertising (“Google advertising”) as well as revenues from other sources (“Google other revenues”).
Google Advertising: Google advertising revenues are comprised of the following:
- Google Search & other, which includes revenues generated on Google search properties (including revenues from traffic generated by search distribution partners who use Google.com as their default search in browsers, toolbars, etc.), and other Google-owned and operated properties like Gmail, Google Maps, and Google Play;
- YouTube ads, which include revenues generated on YouTube properties; and
- Google Network includes revenues generated on Google Network properties participating in AdMob, AdSense, and Google Ad Manager.
Google uses specific metrics to track how well traffic across various properties is monetized as it relates to its advertising revenues: paid clicks and cost-per-click pertain to traffic on Google Search & other properties. In contrast, impressions and cost-per-impressions pertain to traffic on Google’s Network partners’ properties.
DoubleClick: An acquisition that skyrocketed Google’s ad business
Paid clicks represent engagement by users and include clicks on advertisements by end-users on Google search properties and other Google-owned and operated properties, including Gmail, Google Maps, and Google Play. Cost per click is defined as click-driven revenues divided by the total number of paid clicks and represents the average amount Google charges advertisers for each engagement by users.
Impressions include impressions displayed to users on Google Network properties participating primarily in AdMob, AdSense, and Google Ad Manager. Cost-per-impression is defined as impression-based and click-based revenues divided by the total number of impressions and represent the average amount Google charges advertisers for each impression displayed to users.
As the business model of Google evolves, it periodically reviews, refines, and updates its methodologies for monitoring, gathering, and counting the number of paid clicks and impressions and for identifying the revenues generated by the corresponding click and impression activity.
Google’s advertising revenue growth, as well as the change in paid clicks and cost-per-click on Google Search & other properties and the change in impressions and cost-per-impression on Google Network properties and the correlation between these items, have been affected and may continue to be affected by various factors, including:
- advertiser competition for keywords;
- changes in advertising quality, formats, delivery, or policy;
- changes in device mix;
- changes in foreign currency exchange rates;
- Fees advertisers are willing to pay based on how they manage their advertising costs;
- general economic conditions, including the effect of COVID-19;
- seasonality; and
- Traffic growth in emerging markets compared to more mature markets and across various advertising verticals and channels.
Google Other: Google’s other revenues are comprised of the following:
- Google Play, which includes sales of apps and in-app purchases and digital content sold in the Google Play store;
- Devices and Services, which includes sales of hardware, including Fitbit wearable devices, Google Nest home products, and Pixel phones;
- YouTube non-advertising, which includes YouTube Premium and YouTube TV subscriptions; and
- Other products and services.
Is Google Stadia a Success or a Fail?
Google Cloud
Google Cloud revenues are comprised of the following:
- Google Cloud Platform, which includes fees for infrastructure, platform, and other services;
- Google Workspace, which includes fees for cloud-based collaboration tools for enterprises, such as Gmail, Docs, Drive, Calendar, and Meets; and
- Other enterprise services.
Other Bets
Other Bets include earlier-stage technologies further afield from the core Google business. Revenues from Other Bets are generated primarily from selling health technology and internet services.
The following chart summarizes how much money Google makes through each revenue stream. (all figures are in $ million)















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


