Facebook Messenger for business [2023 guide] – Zendesk
Mục Lục
How to set up Facebook business Messenger
Setting up Messenger for business may sound daunting. But by following these steps, you can jump right in and use the platform.
1. Choose the right customer support software
Most teams use a CRM or other support platform for customer service. Your existing software will track and manage new Messenger conversations. Pick a platform suited to your business model and needs. From there, make sure it integrates with Messenger.
2. Connect Facebook Messenger to a unified workspace
Once you select a service platform, connect it with Messenger. By default, Facebook Messenger offers private messaging with customers. During setup, ensure your integrations offer public messaging with customers.
Different platforms follow their own integration process. Using Zendesk Agent Workspace as an example, administrators can give agents access to Messenger channels. You can add the channel by following these steps:
- In the Admin Center, click on Channels in the sidebar.
- Select Messaging and social, and then Messaging.
- On the Add Facebook Messenger page, click Continue with Facebook.
- Log in to your Facebook account as a user with admin permissions for all accounts being added. The on-screen instructions will help authorize access between Zendesk and your Facebook account.
- Toggle page permissions to Yes on the Facebook pages you want to manage with Zendesk.
- Name your channel, pick a brand, and save your settings.

3. Adjust your Facebook Messenger rules and views
Customer service agents need to follow the rules for routing messages. Support macros enforce routing rules, but admins can also make manual assignments. Chat routing rules cover:
- How agents accept tickets after creation
- How agents view unassigned tickets
Manual and automatic ticket assignment to agents - Ticket triaging and level of priority
Businesses also need to consider views, which organize tickets by grouping them into lists based on specific criteria. Views reinforce your workflow by creating an order of priorities on your tickets, streamlining operations, and ensuring agents have access to the same information.
You can create views based on these categories:
- Unsolved tickets
- New tickets in need of triage
- Pending tickets assigned to one or more agents
- Tickets awaiting a response from the client
- Tickets that arrived through a certain channel, as seen below:

4. Set your agents up to use the correct channels
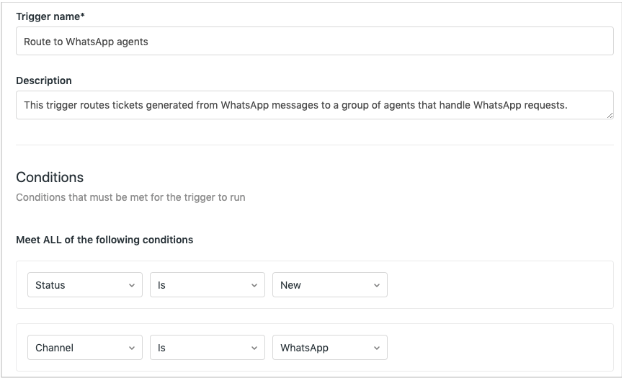
Channels organize your distribution of support tickets. Configure your channels based on how you want agents to speak with customers. For example, you can use channels to route experienced agents to more complicated tickets.
Note: All requests become tickets that agents manage in Zendesk, regardless of the channel they come through. See an example of channel routing below:
5. Leverage rich messages
Once agents move through the proper channels, they talk to the customer. Strong customer service skills and institutional knowledge will get the agent far, but rich messaging can help them go farther. Carousels let customers quickly swipe through a conversation, for instance, while multimedia messages help illustrate concepts.
6. Improve the experience with automation
Chatbots and automation can lighten agents’ workload and enhance the customer experience. With triggers based on key terms or support types, AI bots can step in and answer simple questions. This gives agents time to address more complex issues. And if automation tools can’t help a customer, agents can jump in anytime.
Tip: You can create conversational bot flows in Zendesk with a click-to-configure tool that doesn’t require any code. Responses can form FAQs, collect customer data, or surface relevant knowledge base material.
7. Track and measure performance
Integrating Zendesk with Messenger gives you the option to record analytics. Your software will compile data into reports that measure your support performance. Savvy managers leverage this data when adjusting their workflow or operations. These reports reveal:
- The number of tickets processed in a given time
- The ticket resolution rates for agents and bots
- The most common types of requests















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


