Electric Field: Concept of a Field Revisited
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe a force field and calculate the strength of an electric field due to a point charge.
- Calculate the force exerted on a test charge by an electric field.
- Explain the relationship between electrical force (F) on a test charge and electrical field strength (E).
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
For example, a charged rubber comb attracts neutral bits of paper from a distance via the Coulomb force. It is very useful to think of an object being surrounded in space by a force field. The force field carries the force to another object (called a test object) some distance away.
Concept of a Field
A field is a way of conceptualizing and mapping the force that surrounds any object and acts on another object at a distance without apparent physical connection. For example, the gravitational field surrounding the earth (and all other masses) represents the gravitational force that would be experienced if another mass were placed at a given point within the field.
In the same way, the Coulomb force field surrounding any charge extends throughout space. Using Coulomb’s law,
F=k∣q1q2∣r2F=k\frac{\mid{q_1q_2}\mid}{r^2}\\
F
=
k
r
2
∣
q
1
q
2
∣
, its magnitude is given by the equation
F=k∣qQ∣r2F=k\frac{\mid{qQ}\mid}{r^2}\\
F
=
k
r
2
∣
∣
, for a point charge (a particle having a charge Q) acting on a test charge q at a distance r (see Figure 1). Both the magnitude and direction of the Coulomb force field depend on Q and the test charge q.
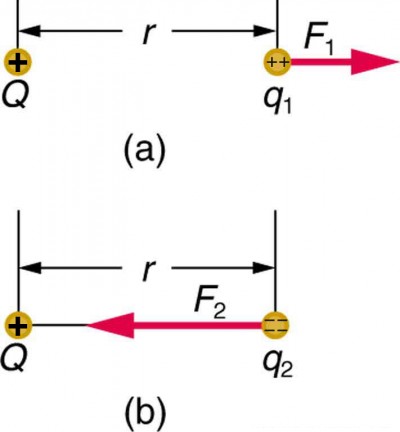 Figure 1. The Coulomb force field due to a positive charge Q is shown acting on two different charges. Both charges are the same distance from Q. (a) Since q1 is positive, the force F1 acting on it is repulsive. (b) The charge q2 is negative and greater in magnitude than q1, and so the force F2 acting on it is attractive and stronger than F1. The Coulomb force field is thus not unique at any point in space, because it depends on the test charges q1 and q2 as well as the charge Q.
Figure 1. The Coulomb force field due to a positive charge Q is shown acting on two different charges. Both charges are the same distance from Q. (a) Since q1 is positive, the force F1 acting on it is repulsive. (b) The charge q2 is negative and greater in magnitude than q1, and so the force F2 acting on it is attractive and stronger than F1. The Coulomb force field is thus not unique at any point in space, because it depends on the test charges q1 and q2 as well as the charge Q.
Figure 1. The Coulomb force field due to a positive charge Q is shown acting on two different charges. Both charges are the same distance from Q. (a) Since qis positive, the force Facting on it is repulsive. (b) The charge qis negative and greater in magnitude than q, and so the force Facting on it is attractive and stronger than F. The Coulomb force field is thus not unique at any point in space, because it depends on the test charges qand qas well as the charge Q.
To simplify things, we would prefer to have a field that depends only on Q and not on the test charge q. The electric field is defined in such a manner that it represents only the charge creating it and is unique at every point in space. Specifically, the electric field E is defined to be the ratio of the Coulomb force to the test charge:
Contact forces, such as between a baseball and a bat, are explained on the small scale by the interaction of the charges in atoms and molecules in close proximity. They interact through forces that include the Coulomb force. Action at a distance is a force between objects that are not close enough for their atoms to “touch.” That is, they are separated by more than a few atomic diameters.For example, a charged rubber comb attracts neutral bits of paper from a distance via the Coulomb force. It is very useful to think of an object being surrounded in space by a force field. The force field carries the force to another object (called a test object) some distance away.A field is a way of conceptualizing and mapping the force that surrounds any object and acts on another object at a distance without apparent physical connection. For example, the gravitational field surrounding the earth (and all other masses) represents the gravitational force that would be experienced if another mass were placed at a given point within the field.In the same way, the Coulomb force field surrounding any charge extends throughout space. Using Coulomb’s law,, its magnitude is given by the equation, for a point charge (a particle having a charge Q) acting on a test charge q at a distance r (see Figure 1). Both the magnitude and direction of the Coulomb force field depend on Q and the test charge q.To simplify things, we would prefer to have a field that depends only on Q and not on the test charge q. The electric field is defined in such a manner that it represents only the charge creating it and is unique at every point in space. Specifically, the electric field E is defined to be the ratio of the Coulomb force to the test charge:
E=Eq\mathbf{E}=\frac{\mathbf{E}}{q}\\
E
=
q
E
,
where F is the electrostatic force (or Coulomb force) exerted on a positive test charge q. It is understood that E is in the same direction as F. It is also assumed that q is so small that it does not alter the charge distribution creating the electric field. The units of electric field are newtons per coulomb (N/C). If the electric field is known, then the electrostatic force on any charge q is simply obtained by multiplying charge times electric field, or F = qE. Consider the electric field due to a point charge Q. According to Coulomb’s law, the force it exerts on a test charge q is
F=k∣qQ∣r2F=k\frac{\mid{qQ}\mid}{r^2}\\
F
=
k
r
2
∣
∣
. Thus the magnitude of the electric field, E, for a point charge is
, whereis the electrostatic force (or Coulomb force) exerted on a positive test charge q. It is understood that E is in the same direction as. It is also assumed that q is so small that it does not alter the charge distribution creating the electric field. The units of electric field are newtons per coulomb (N/C). If the electric field is known, then the electrostatic force on any charge q is simply obtained by multiplying charge times electric field, or= q. Consider the electric field due to a point charge Q. According to Coulomb’s law, the force it exerts on a test charge q is. Thus the magnitude of the electric field, E, for a point charge is
E=∣Fq∣=k∣qQqr2∣=k∣Q∣r2E=\left|\frac{F}{q}\right|=k\left|\frac{qQ}{qr^2}\right|=k\frac{\left|Q\right|}{r^2}\\
E
=
∣
∣
q
F
∣
∣
=
k
∣
∣
q
r
2
∣
∣
=
k
r
2
∣
Q
∣
.
Since the test charge cancels, we see that
. Since the test charge cancels, we see that
E=k∣Q∣r2E=k\frac{\left|Q\right|}{r^2}\\
E
=
k
r
2
∣
Q
∣
.
The electric field is thus seen to depend only on the charge Q and the distance r; it is completely independent of the test charge q.
Example 1. Calculating the Electric Field of a Point Charge
Calculate the strength and direction of the electric field E due to a point charge of 2.00 nC (nano-Coulombs) at a distance of 5.00 mm from the charge.
Strategy
We can find the electric field created by a point charge by using the equation
E=kQr2E=\frac{kQ}{r^2}\\
E
=
r
2
k
Q
.
Solution
Here Q = 2.00 × 10−9 C and r = 5.00 × 10−3 m. Entering those values into the above equation gives
Calculate the strength and direction of the electric field E due to a point charge of 2.00 nC (nano-Coulombs) at a distance of 5.00 mm from the charge.We can find the electric field created by a point charge by using the equationHere Q = 2.00 × 10C and r = 5.00 × 10m. Entering those values into the above equation gives
E=kQr2 =(8.99×109N⋅m2C2)×(2.00×10−9 C)(5.00×10−3 m)2 =7.19×105 N/C\begin{array}{lll}E&=&k\frac{Q}{r^2}\\\text{ }&=&\left(8.99\times10^9\frac{\text{N}\cdot\text{m}^2}{\text{C}^2}\right)\times\frac{\left(2.00\times10^{-9}\text{ C}\right)}{\left(5.00\times10^{-3}\text{ m}\right)^2}\\\text{ }&=&7.19\times10^5\text{ N/C}\end{array}\\
E
=
=
=
k
r
2
Q
(
8.99
×
1
0
9
C
2
N
⋅
m
2
)
×
(
5.00
×
1
0
−
3
m
)
2
(
2.00
×
1
0
−
9
C
)
7.19
×
1
0
5
N/C
Discussion
This electric field strength is the same at any point 5.00 mm away from the charge Q that creates the field. It is positive, meaning that it has a direction pointing away from the charge Q.
This electric field strength is the same at any point 5.00 mm away from the charge Q that creates the field. It is positive, meaning that it has a direction pointing away from the charge Q.
Example 2. Calculating the Force Exerted on a Point Charge by an Electric Field
What force does the electric field found in the previous example exert on a point charge of −0.250 μC?
Strategy
Since we know the electric field strength and the charge in the field, the force on that charge can be calculated using the definition of electric field
E=Fq\mathbf{E}=\frac{\mathbf{F}}{q}\\
E
=
q
F
rearranged to F = qE.
Solution
The magnitude of the force on a charge q = −0.250 μC exerted by a field of strength E = 7.20 × 105 N/C is thus,
What force does the electric field found in the previous example exert on a point charge of −0.250 μC?Since we know the electric field strength and the charge in the field, the force on that charge can be calculated using the definition of electric fieldrearranged to= qThe magnitude of the force on a charge q = −0.250 μC exerted by a field of strength E = 7.20 × 10N/C is thus,
F=−qE =(0.250×10−6 C)(7.20×105 N/C) =0.180 N\begin{array}{lll}F&=&-qE\\\text{ }&=&\left(0.250\times10^{-6}\text{ C}\right)\left(7.20\times10^5\text{ N/C}\right)\\\text{ }&=&0.180\text{ N}\end{array}\\
F
=
=
=
−
qE
(
0.250
×
1
0
−
6
C
)
(
7.20
×
1
0
5
N/C
)
0.180
N
Because q is negative, the force is directed opposite to the direction of the field.
Discussion
The force is attractive, as expected for unlike charges. (The field was created by a positive charge and here acts on a negative charge.) The charges in this example are typical of common static electricity, and the modest attractive force obtained is similar to forces experienced in static cling and similar situations.
Because q is negative, the force is directed opposite to the direction of the field.The force is attractive, as expected for unlike charges. (The field was created by a positive charge and here acts on a negative charge.) The charges in this example are typical of common static electricity, and the modest attractive force obtained is similar to forces experienced in static cling and similar situations.
PhET Explorations: Electric Field of Dreams
Play ball! Add charges to the Field of Dreams and see how they react to the electric field. Turn on a background electric field and adjust the direction and magnitude.
 Click to download the simulation. Run using Java.
Click to download the simulation. Run using Java.
Click to download the simulation. Run using Java.
Play ball! Add charges to the Field of Dreams and see how they react to the electric field. Turn on a background electric field and adjust the direction and magnitude.
Section Summary
- The electrostatic force field surrounding a charged object extends out into space in all directions.
- The electrostatic force exerted by a point charge on a test charge at a distance r depends on the charge of both charges, as well as the distance between the two.
- The electric field E is defined to be
E=Fq\mathbf{\text{E}}=\frac{\mathbf{\text{F}}}{q}\\
E
=
q
F
, where F is the Coulomb or electrostatic force exerted on a small positive test charge q. E has units of N/C.
- The magnitude of the electric field E created by a point charge Q is
E=k∣Q∣r2\mathbf{\text{E}}=k\frac{\left|Q\right|}{{r}^{2}}\\
E
=
k
r
2
∣
Q
∣
, where r is the distance from Q. The electric field E is a vector and fields due to multiple charges add like vectors.
Conceptual Questions
- Why must the test charge q in the definition of the electric field be vanishingly small?
- Are the direction and magnitude of the Coulomb force unique at a given point in space? What about the electric field?
Problems & Exercises
- What is the magnitude and direction of an electric field that exerts a 2.00 × 10−5 N upward force on a −1.75 μC charge?
- What is the magnitude and direction of the force exerted on a 3.50 μC charge by a 250 N/C electric field that points due east?
- Calculate the magnitude of the electric field 2.00 m from a point charge of 5.00 mC (such as found on the terminal of a Van de Graaff).
- (a) What magnitude point charge creates a 10,000 N/C electric field at a distance of 0.250 m? (b) How large is the field at 10.0 m?
- Calculate the initial (from rest) acceleration of a proton in a 5.00 × 106 N/C electric field (such as created by a research Van de Graaff). Explicitly show how you follow the steps in the Problem-Solving Strategy for electrostatics.
- (a) Find the direction and magnitude of an electric field that exerts a 4.80 × 10−17 N westward force on an electron. (b) What magnitude and direction force does this field exert on a proton?
Glossary
field: a map of the amount and direction of a force acting on other objects, extending out into space
point charge: A charged particle, designated Q, generating an electric field
test charge: A particle (designated q) with either a positive or negative charge set down within an electric field generated by a point charge
Selected Solutions to Problems & Exercises
2. 8.75 × 10−4 N
4. (a) 6.94 × 10−8 C; (b) 6.25 N/C
6. (a) 300 N/C (east); (b) 4.80 × 10−17 N (east)
Licenses and Attributions
CC licensed content, Original
- PhET Interactive Simulations . Provided by: University of Colorado Boulder . Located at: https://phet.colorado.edu/. License: CC BY: Attribution
CC licensed content, Shared previously
- College Physics. Authored by: OpenStax College. Located at: https://openstax.org/books/college-physics/pages/1-introduction-to-science-and-the-realm-of-physics-physical-quantities-and-units. License: CC BY: Attribution. License terms: Located at License
. The electric field is thus seen to depend only on the charge Q and the distance r; it is completely independent of the test charge q.a map of the amount and direction of a force acting on other objects, extending out into spaceA charged particle, designated Q, generating an electric fieldA particle (designated q) with either a positive or negative charge set down within an electric field generated by a point charge















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


