Business process automation [BPA]: Definition & tips | Zapier
When I was in college, one of my more lucrative side hustles was preparing marketing mailers for a friend who ran a one-man insurance company. I’d come by his high-rise apartment in downtown Orlando once a week, print out 500 pre-addressed envelopes and corresponding marketing letters, stuff them one by one, seal them up, stamp them, and drive them to the post office.
Streamline work across departments with automation
I realize now I was essentially my friend’s business process automation in human form—the task was so repetitive I could do it while eating leftover pizza and watching anime at the same time. While actual automation would have put me out of a side hustle, that $75 worth of stupefyingly repetitive menial labor bought me about a month of groceries.
BPA is a little more sophisticated for today’s businesses, but no less useful.
Table of contents:
Zapier is the leader in no-code automation—integrating with 5,000+ apps from partners like Google, Salesforce, and Microsoft. Build secure, automated systems for your business-critical workflows across your organization’s technology stack. Learn more.
Mục Lục
What is business process automation (BPA)?
Business process automation (BPA) is the practice of using software to automatically execute repetitive tasks related to a company’s essential procedures. You can use BPA to streamline and optimize processes for everything from sales and marketing to HR, compliance, training, and beyond.
Business process automation (BPA) vs. business process management (BPM)
While you can use business process automation to optimize business processes, business process management (BPM) can involve tactics outside of automation to streamline and enhance procedures. In short, BPM may or may not include BPA, but BPA always contributes to improving BPM.
Business process automation (BPA) vs. robotic process automation (RPA)
Similarly, robotic process automation (RPA) can be used as part of a broad-level business processes automation strategy. Where BPA looks at automating an entire complex process, RPA involves the use of software-based bots and/or machine learning to mimic individual human actions. This way, it can play a role in improving efficiencies by automating tasks that would otherwise take up the attention of flesh-and-blood employees.
AI and business process automation
As is the case with RPA, business process automation may or may not include AI solutions. Artificial intelligence—deployed as a solution like a chatbot—is an underlying technology that brings a big boost to BPA and RPA strategies. AI can perform human tasks like recognizing file types, synthesizing data, identifying patterns, and even making decisions—making it incredibly useful in handling tedious work tasks and conceiving dystopian sci-fi storylines.
What are the benefits of business process automation?
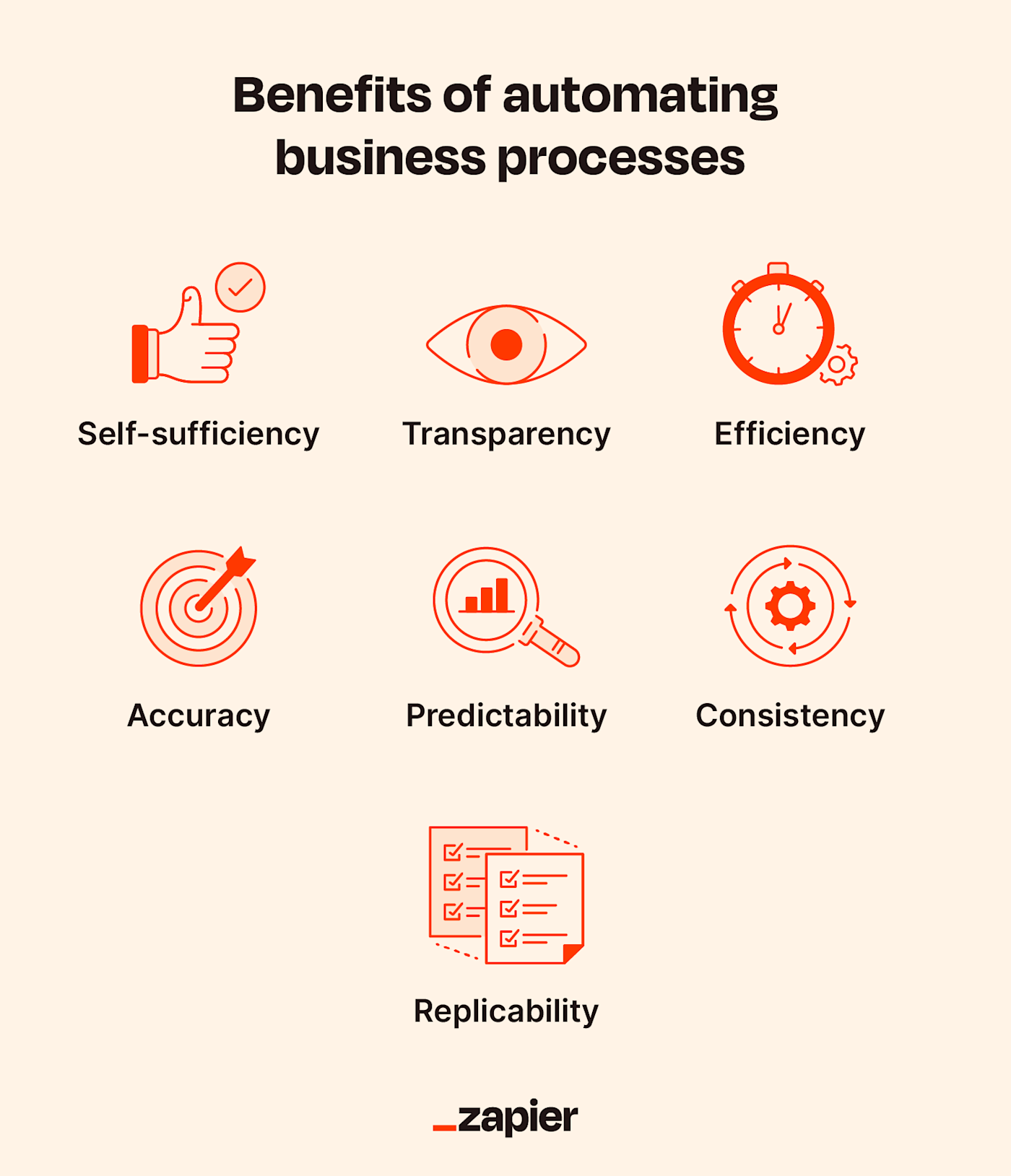
I’ll admit that business process automation isn’t the first thing that comes to mind when I see the acronym “BPA.” Given the benefits below, maybe it should be.
-
Self-sufficiency: Teams are better prepared to handle processes internally without the need to hire contractors, involve outside teams, or outsource labor.
-
Transparency: Team members at every level gain a clear idea of essential processes, values, and timelines.
-
Efficiency: Automatically handling repetitive tasks saves time, resources, and overhead.
-
Accuracy: Properly designed and executed automation eliminates the risk of human error.
-
Consistency: Since repeated tasks are fulfilled systematically and automatically, the results are always the same.
-
Predictability: Consistent results, set procedures, and instantaneous completion lead to predictable timelines and more reliable forecasting.
-
Replicability: Once they’re set, you can easily replicate processes across tasks, teams, and employees.
Identifying business processes to automate
Sometimes, knowing when to automate is pretty simple (like hiring your friends to stuff hundreds of envelopes while you run sales, customer service, and HR by yourself).
For those other times, here are a few questions you can ask about a given task—if the answer is “yes,” there’s a good chance it can benefit from automation.
-
Is it repetitive and/or menial?
-
Do you do it on a schedule?
-
Does it involve moving information?
-
Does it distract you from more valuable tasks?
Conversely, if you answer “yes” to any of these questions about a task, it’s probably not a great opportunity for automation.
-
Does it require creativity?
-
Does it require emotional intelligence?
-
Does it require problem-solving skills?
-
Does it require a human touch?
Still not sure when to automate a task? Zapier asked superusers and employees how they know when to automate a task.
Business process automation examples
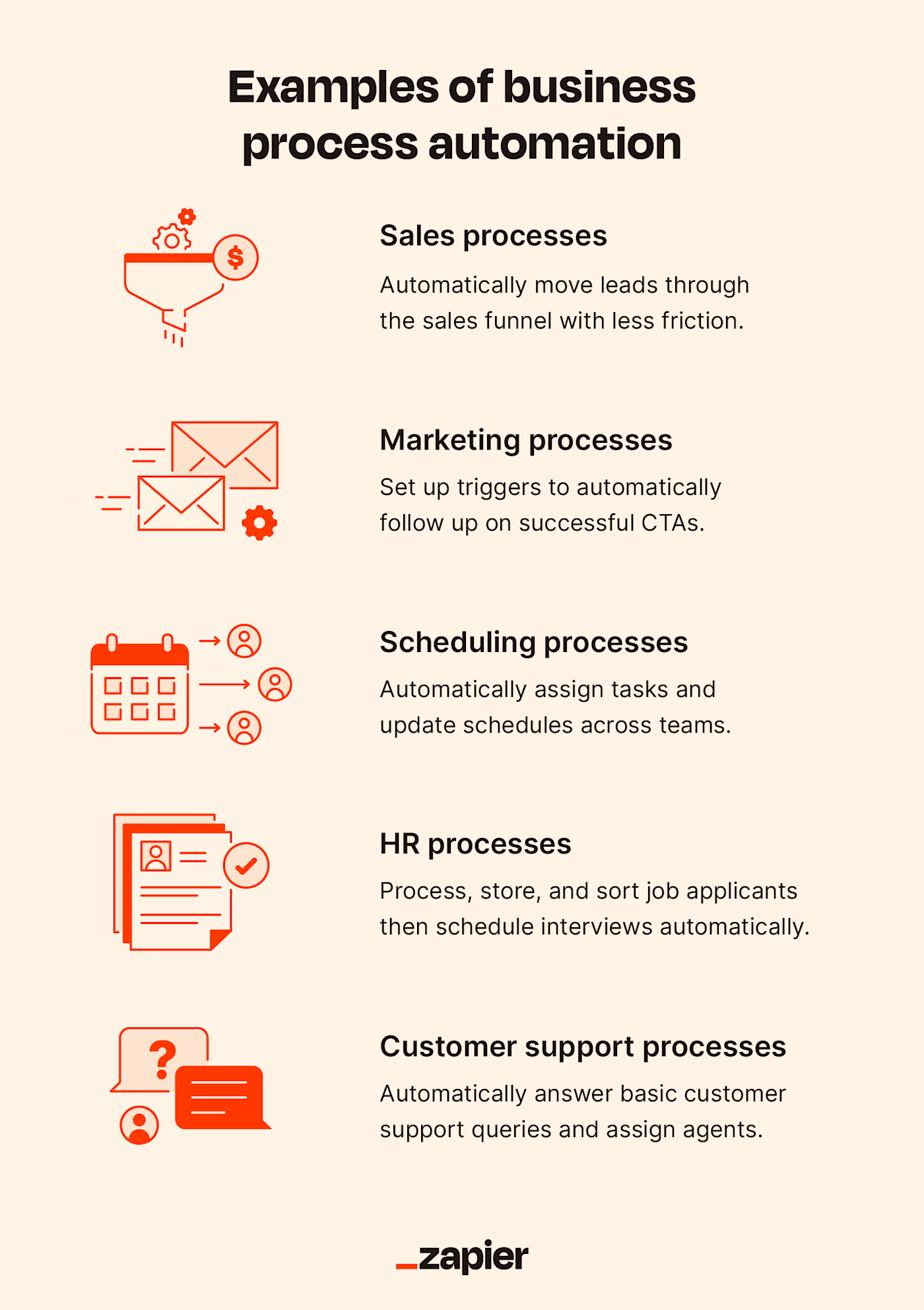
Business process automation is useful for more than insurance mailouts. Here are a few use cases to illustrate what it can look like across industries.
Sales processes
To ramp up revenue, a consulting company decides to automate sales processes to move potential clients through their sales funnel with less friction. They set up a webform to automatically separate requests for quotes by type. Based on the parameters of their request, the company’s CRM automatically emails a quote to qualified leads the following day. If they don’t respond, the CRM sends a follow-up email five days later. If leads take the next step to set up a consultation, the CRM syncs to a relevant consultant and schedules a meeting based on availability.
Marketing processes
An eCommerce company starts automating marketing operations to improve ROI on Facebook ads. They set up triggers so when a user clicks on an ad and follows through with a CTA, Gmail automatically populates their name into a template and sends them a personalized follow-up email with a coupon code. Meanwhile, the company is able to automatically have their contact information stored in a dedicated list based on which ad they interacted with.
Scheduling processes
A design firm improves overall efficiency by scheduling collaborative tasks instantaneously. When new projects come in, they’re immediately assigned to a team member with availability. As they move their project through to its next phase, the firm’s CRM automatically assigns it to another team member, blocks their schedule, and alerts them.
HR processes
To streamline the recruiting process, a large marketing firm brings automation to their HR processes by synching their job board account with their applicant tracking system. As applications come in, candidate profiles are automatically logged as software scrapes their resumes. Candidates who don’t meet essential requirements get segmented to one list, while candidates who do meet requirements are segmented to another. The internal hiring team then sorts through profiles and sends the top picks through automatic scheduling funnels to set up interviews.
Customer support processes
A SaaS company uses automation to help their customer support team. They deploy a chatbot that directs simple customer questions to relevant help pages. For more complex customer needs, the chatbot gives users the option of staying on the chat or receiving an email. The bot then assigns the query to the next available support agent. If the agent needs to involve additional team members, they can notify that team member and have the ticket transferred automatically.
5 steps to implement business process automation
If you’re ready to set up automation for your business processes, here’s a high-level rundown of how you can put it into action.
-
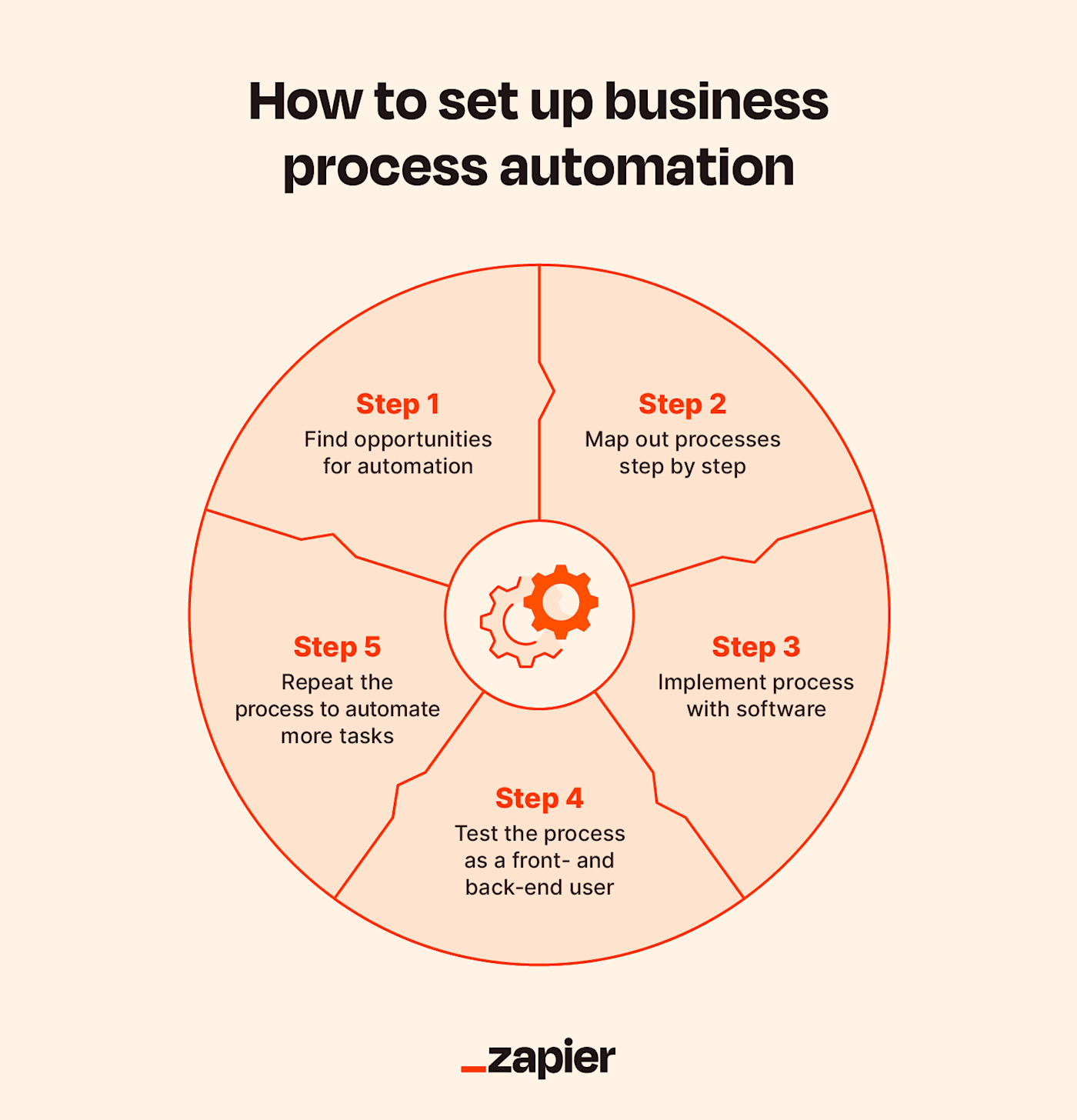
Step 1: Find opportunities for automation. Look for low-level tasks that are repetitive, scheduled, and distract employees from more valuable work.
-
Step 2: Map out processes step-by-step. When you’ve found a process that ticks the above boxes, map out every step and every involved party.
-
Step 3: Implement process with software. Use your workflow manager or your app’s automation capabilities or set up triggers with third-party software (like Zapier) that integrates with your CRM and apps.
-
Step 4: Test the process as a front- and back-end user. Try out your automation process to see how it looks from both internal and external perspectives. Tweak as necessary until you feel confident that the process runs without a hitch.
-
Step 5: Repeat the process to automate more tasks. Once you’ve got the hang of automating one task, you’ll start seeing more and more tasks that you can automate. Keep repeating the process and looking for new automation opportunities.
Automate your business processes with Zapier
If your essential procedures could use efficiency boosts, you can do one better than hiring a broke college kid to fumble through the menial tasks. Zapier can help set up business process automation, so you can cut out wasted time and frustration for customers and employees alike.
Here are a few more ways you can bring automation to your business:















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


