Business Economics
Mục Lục
What is Business Economics?
Business economics is a field of study that reviews the implementation of the economic system in business operations. It assists in utilizing the nature and importance of financial analysis to clarify business problems. Moreover, the introduction to this definition helps balance between limited sources and unlimited aspirations.
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc., Please provide us with an attribution linkHow to Provide Attribution?Article Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: Business Economics (wallstreetmojo.com)
The nature and importance of business economics lie in the future prediction and drafting of several regulations for profit maximization. The relevant areas pertained to this discipline are demand analysis and forecasting, cost and production analysis, pricing decisions, profit management, and wealth governance.
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc., Please provide us with an attribution linkHow to Provide Attribution?Article Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: Business Economics (wallstreetmojo.com)
Key Takeaways
- The business economics definition implicates blending business processes with economic theories to simplify the decision-making procedure.
- It reviews the study of the firm’s financial, market-related, environmental, and organizational issues. Moreover, it is considered both an art and science.
- It covers demand analysis and forecasting, cost and production analysis, pricing decisions and strategies, profit management, and wealth management.
- Its objectives include future prediction, recognition, and clarification of business issues, drafting business policies, and establishing relations between different economic aspects.
Business Economics Explained
Business economics or managerial economics discusses the usage and importance of economic policies and concepts in business governance. Moreover, it analyzes economic models, approaches, and philosophies applied to solve rational business issues. The introduction to business economics is certainly both an art and a science.
It is a sphere of economicsEconomicsEconomics is an area of social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of limited resources within a society.read more analyzing the study of organizational, fiscal, environmental, and market-related problems. Therefore, this includes the topics of product factors, scarcity, consumption, and dissemination.
It is important to comprehend the nature of business economics, which is closely related to normative economicsNormative EconomicsNormative economics refers to economists’ opinions about what they believe. It may be true for some, but false for others. Furthermore, the statements mentioned under normative economics cannot be verified or tested.read more. Simply put, economic theory is utilized for administration in a doubtful situation to solve or elucidate difficulties in company management.
For instance, demand, profitProfitProfit refers to the earnings that an individual or business takes home after all the costs are paid. In economics, the term is associated with monetary gains. read more, pricing, competition, production, national income, business cycles, etc.
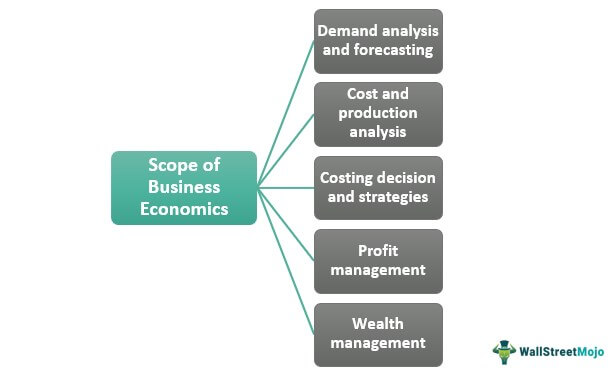
Scope Of Business Economics
In the same vein, the below-mentioned disciplines describe the scope of introduction to business economics:
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc., Please provide us with an attribution linkHow to Provide Attribution?Article Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: Business Economics (wallstreetmojo.com)
#1 – Demand Analysis and Forecasting
This aids in directing the organization to arrange production schedules and harness resources. Additionally, it assists the leadership preserve and boosting the revenueRevenueRevenue is the amount of money that a business can earn in its normal course of business by selling its goods and services. In the case of the federal government, it refers to the total amount of income generated from taxes, which remains unfiltered from any deductions.read more base and market position through discerning various factors affecting the product demand.
#2 – Cost And Production Analysis
The business economics definition entails the production of cost assessment of various outputs and recognizing elements behind the deviations in estimated costs. That is to say, the manager selects cost reduction output levels and also avoids the time and material wastage to attain the desired profit percentageProfit PercentageThe profit percentage formula calculates the financial benefits left with the entity after it has paid all the expenses. Profit percentage is of two types – markup expressed as a percentage of cost price or profit margin calculated using the selling price.read more. This also constitutes the implementation of Break-even analysisBreak-even AnalysisBreak-even analysis refers to the identifying of the point where the revenue of the company starts exceeding its total cost i.e., the point when the project or company under consideration will start generating the profits by the way of studying the relationship between the revenue of the company, its fixed cost, and the variable cost.read more.
#3 – Costing Decisions and Strategies
Valuation is the root of the company’s earningsEarningsEarnings are usually defined as the net income of the company obtained after reducing the cost of sales, operating expenses, interest, and taxes from all the sales revenue for a specific time period. In the case of an individual, it comprises wages or salaries or other payments.read more since its success is mostly based on the accuracy of costing decisions. Moreover, the key aspects incorporate pricing methods, price discovery in numerous market forms, product line pricing, and differential pricing.
#4 – Profit Management
The manager must be able to devise a more or less precise evaluation of the company’s expected gains and pricing at distinct output levels. To clarify, uncertainty reduction assists the firm in achieving higher revenues. While comprehending the importance of business economics, profit calculation and profit planning are the most difficult concepts.
#5 – Wealth Management
It infers regulation and drafting of capital expenses due to the involvement of a huge amount. Disposing of the capital assets is quite complicated and hence, demands a substantial amount of labor and time. Subsequently, this requires the business to manage current assetsCurrent AssetsCurrent assets refer to those short-term assets which can be efficiently utilized for business operations, sold for immediate cash or liquidated within a year. It comprises inventory, cash, cash equivalents, marketable securities, accounts receivable, etc.read more and current liabilitiesCurrent LiabilitiesCurrent Liabilities are the payables which are likely to settled within twelve months of reporting. They’re usually salaries payable, expense payable, short term loans etc.read more properly.
Examples
Here are some examples of introduction to business economics for better comprehension.
Example #1
Suppose that an enterprise named XYZ Corp. deals in manufacturing home furnishings. Now, it performs demand forecasting to evaluate its market penetrationMarket PenetrationMarket penetration is calculated as how much the customers are using the product or service compared to the total market for that product or service.read more rate. Next, the firm computes estimated equipment and labor costs and executes production analysis to exploit the available resources.
Adopting smart pricing tactics and product line pricing aids the enterprise in avoiding overspending. Then, it determines the opportunity costOpportunity CostThe difference between the chosen plan of action and the next best plan is known as the opportunity cost. It’s essentially the cost of the next best alternative that has been forgiven.read more and profit planning to ensure goal attainment within the stipulated period. Lastly, the company designs and controls capital expendituresCapital ExpendituresCapex or Capital Expenditure is the expense of the company’s total purchases of assets during a given period determined by adding the net increase in factory, property, equipment, and depreciation expense during a fiscal year.read more to maintain and enhance its market stature.
So, the process mentioned above implies the application of economic theories to the corporate decision-making process.
Example #2
During its initial phase, Uber didn’t strategize to be high on the fixed investment aspect owing to its doubts about market penetration. Instead, it began with an aggregator business model responsible for connecting riders to drivers.
The latter drove the cars as and when deemed feasible and were paid weekly according to the terms of the ride. Then, with an increased market horizon, Uber started connecting drivers permanently to the car fleet owners and hired drivers. This helped the firm satisfy all the rider requests without relying on the availability of drivers.
Needlessly, this transformation is a clear testament to the definition and importance of business economics. After the intensive market assessment, Uber then decided to soar the supply. It conducted the cost-benefit evaluation and expanded its employee base for fulfilling the surging ride demands.
Business Economics Objectives
The following points explain the objectives of business economics:

You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc., Please provide us with an attribution linkHow to Provide Attribution?Article Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: Business Economics (wallstreetmojo.com)
#1 – Identification And Resolution of Business Problems
Managerial economics involves many significant concepts like short-run and long-run costs, demand and supply analysis, and the law of diminishing marginal utilityLaw Of Diminishing Marginal UtilityThe law of diminishing marginal utility states that the amount of satisfaction provided by consuming every additional unit of goods decreases as we increase that goods consumption. Marginal utility is the change in the contentment derived from consuming an extra unit of goods.read more. This certainly aids the business manager in recognizing and clarifying the business issues.
#2 – Designing Numerous Profitable Business Policies
Keeping profit maximization in mind aids in drafting several business policies like cost policies and pricing policies. Please note that the depiction of these regulations is done as per economic assessment and data.
#3 – Future Prediction
The intensive evaluation of multiple economic variables, including business capital and cost production, assists firms in future prediction. Subsequently, it permits the enterprise to detect and avert any unwanted situation by capitalizing on the available resources.
#4 – Building Relations Between Distinct Financial Aspects
Managerial economics assists build relations between diverse economic factorsEconomic FactorsEconomic factors are external, environmental factors that influence business performance, such as interest rates, inflation, unemployment, and economic growth, among others.read more such as profits, income, market structure, and losses. This certainly aids in supervising the managers for efficient decision-making and seamless business administration.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Is the Scope of Business Economics?
The scope of business economics is extensive and covers the below-mentioned fields:
1. Demand analysis and prediction
2. Pricing and production analysis
3. Pricing plans and decisions
4. Profit management
5. Wealth management
What Is the Nature of Business Economics?
Generally, the nature of business economics is normative. It provides insights into the exercise of economic concepts during decision-making, policy formation, and future planning. Nonetheless, companies must completely understand the atmosphere for establishing decision policies.
What Are the Two Components of Business Economics?
The two major components of business economics introduction are supply and demand and the effect of scarcity. Other subjects included in this discipline are product factors, consumption, and dissemination.
Precisely put, managerial economics aims at the factors and components throughout business activities and their relation to the economy. Additionally, it involves assessing external financial factors and their impact on company decisions.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Business Economics & its Definition. Here we explain the introduction of business economics, its scope, importance, and nature. You may learn more about our articles below on Economics –















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


