Board of Directors (BOD)
Mục Lục
Board of Directors Definition
Board of Directors (BOD) refers to a corporate body comprising a group of elected people who represent the interest of a company’s stockholders. The board forms the top layer of the hierarchy and focuses on ensuring that the company efficiently achieves its goals.
One crucial job of the board is to keep a firm on its feet even during a crisis. Other jobs include policy formation, corporate decision-making, the firm’s overall management and law abidance. It also allows answerability amongst the concerned parties.
Key Takeaways
- The board of directors is an elected panel in a company representing the company’s shareholders and includes high-level corporate position holders.
- The BOD’s composition differs as per organizations. Usually, there is a CEO, board’s chairman, directors, non-executive director, CFO, vice-president, zonal heads, etc.
- By law, a public company is obligated to have a BOD while it is optional for the non-profit or private entities.
- BOD aims to stand for the rights and interests of the stakeholders and investors while taking care of their assets invested in the business.
- A board is the supreme governing authority in an organization that takes strategic corporate decisions by participating in the board meetings.

You are free to use this image on your website, templates etc, Please provide us with an attribution linkHow to Provide Attribution?Article Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: Board of Directors (BOD) (wallstreetmojo.com)
Understanding Board of Directors
A board of directors is a group of officials who the shareholders of a firm elect. State laws obligate public corporations to keep a BOD. In the case of non-profit or private entities, it is optional to have a board of directors. The idea behind a BOD is to have a body that safeguards shareholders’ interests as they are the firm’s owner.
The relationship between a BOD and shareholdersShareholdersA shareholder is an individual or an institution that owns one or more shares of stock in a public or a private corporation and, therefore, are the legal owners of the company. The ownership percentage depends on the number of shares they hold against the company’s total shares.read more flows from the theory of the principal-agent relationship. Here the shareholders are the principal or the owners. The BOD is the agent that ensures the safety of shareholders’ investments. As such, the board needs to ensure organizational efficiency to allow profit maximization, which will add to the shareholders’ wealth.
In the process, the BOD as a governance body also needs to work in the best interest of other stakeholders apart from shareholders. This is because a business needs to cater to its stakeholders for continued existence. For instance, the BOD needs to ensure that the company functions as per the laws to avoid drawing negative attention from the law enforcement agencies.
Structure of Board of Directors
BOD members hold different positions within the panel. The composition of the board varies as per the company and state laws. For example, Amazon’s board of directors contains official positions such a chairman, directors, CFOs, segment-wise CEOs and VPs, etc.
The board size is limited by a company specifying the minimum and maximum limit in its Articles of AssociationArticles Of AssociationArticles of association is a legally binding document that states the corporate rules, regulations, and purpose. It serves as a user’s guide for executing the organizational tasks, directors’ appointment and recording the financial information.read more. Organizations commonly have 3 to 31 directors. Let us look at some designations and positions common to a BOD in public corporations.
Roles and Responsibilities of Board of Directors

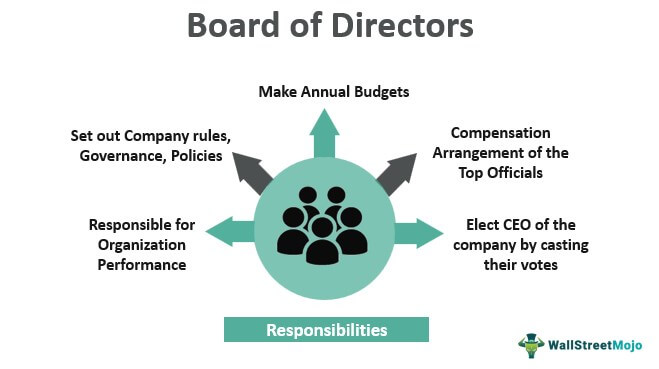
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc., Please provide us with an attribution linkHow to Provide Attribution?Article Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: Board of Directors (BOD) (wallstreetmojo.com)
Immediately after receiving the news of deaths, the company warned and urged customers not to take Tylenol. The company removed its capsules from the market, costing it over $100 million. A year later, Tylenol bounced back. In the $1.2 billion drug market, Tylenol shares had fallen to $7 from $37 but after the crisis was averted, they came back to $30.
Interesting BOD Aspects
Liability: Since a company pertains to a separate legal entity, the directors cannot be held personally liable for the corporate debts. Although, they are responsible for the losses incurred.
Tenure: The director’s tenure on the board can be between 5-10 years, but this differs amongst companies. Extensions to tenure in a board of directors are sometimes allowed after a special resolution.
Remuneration: Board of directors are usually liable to receive an annual salary and stock options. As per a study, in 2017, half of the large US companies paid over $300,000 compensation to board members. Sometimes, the members are also given additional compensation for participating in meetings.
Directors’ Information: The company’s directors’ information can be acquired from various sources as discussed below:
Disqualification of a BOD
A board member can be disqualified from the panel for a specific period or banned permanently for the following reasons:
As an example of disqualification, readers can refer to the case of Buckinghamshire-based company Masstech Ltd. The company’s sole director Ulhaque Lone Ahtamad was found guilty of a VAT fraud. He was disqualified and banned for 15 years as a penalty of the fraud.
FAQs
What is a board of directors?
A board of directors is a corporate panel of elected members who represent shareholders of a company. The board participates in board meetings, ensures that the company runs efficiently, and protects the interest of shareholders and other stakeholders of the company.
What is the role of the board of directors?
The significant functions performed by a board of directors include • Protecting company’s assets and shareholders’ interest; • Forming corporate policies such as for dividend and payouts; • Monitoring, making policies and controlling the organization to ensure maximum efficiency • Crisis management • Strategic decision making like executives’ compensation; • Hiring high-level managers and executives, and the auditor.
Who is the more powerful CEO or board of directors (BOD)?
The BOD holds more powers when compared to the company’s chief executive officer (CEO). The CEO is appointed by the board and can even be sacked by the board members. Thus, the CEO needs to take the approval of the chairman before taking crucial corporate decisions.
Who elects the board of directors (BOD)?
Corporate shareholders vote for the BOD in the company’s annual shareholders’ meeting. However, the nominees for the shareholders’ voting are elected by a special nomination committee (comprising the independent directorsIndependent DirectorsThe term “independent director” refers to a member of the board who is not associated with the organization and who provides a neutral opinion because he or she is not tied to the current management.read more).
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to what is a Board of Directors and its definition. Here we discuss the structure along with the roles & responsibilities of directors of the board. You can learn more from the following articles –















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


