6 Ways to Fix “Windows Could Not Find a Driver for Your Network Adapter”
“Windows Could Not Find a Driver for Your Network Adapter” is a common error message in the Network Adapter troubleshooter if your network driver is missing. Or, for some reason, your computer thinks it’s missing. It could be because of defective and disabled NIC, malfunctioning power management settings, and corrupted driver.
Many people use Network Adapter troubleshooters to fix any issues they find in their network connection. From no internet access to intermittent network connection, the Network Adapter troubleshooter is a handy tool for any network-related issue.
However, sometimes even the Network Adapter troubleshooter cannot fix the issue and shows this error message.
How to Fix Windows Could Not Find a Driver for Your Network Adapter Error?
There are several methods to fix this error, and not all of them may work according to the cause of the issue. Before trying the fixes on this list, make sure to power cycle your device.
Here are the methods to fix this particular error message showing up.
Reinstall The Driver
The most common and effective fix for this issue is reinstalling the driver. The error message directly states that the network adapter driver is missing, and more often than not, it is the cause.
However, with the network adapter driver missing, your PC has no way of connecting to the internet. So, you have to take a few extra steps to manually download and reinstall the driver.
Here’s how to reinstall a driver without internet access.
- Press Windows key + R to open the run box.
- Type
devmgmt.mscand press Enter.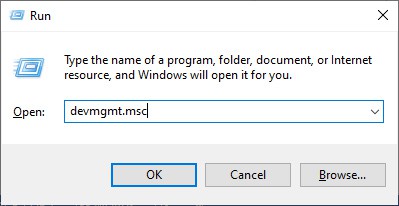
- In Device Manager, click on Network adapter.
- Locate your network driver and right-click it. (If you can’t find your network driver, right-click Network adapter and press Scan for hardware changes.)
- Click on Uninstall device. (Remember the driver’s name before uninstalling.)

After a restart, your device should automatically reinstall the network driver. It is only possible if your device has a copy of the driver pre-loaded to its driver list.
If the network driver didn’t automatically get reinstalled after a restart, here’s how to manually reinstall the network driver.
- On a different device, connect to the internet and download the latest version of the driver from the official website. (The one named in Device Manager.)
- Transfer it to your PC through USB or any method you like.
- Run the setup or executable file of the driver on your PC.
- Restart your PC.
If you have an ethernet cable, you can connect to the internet and reinstall your driver following the same process on your PC.
Change Power Management Settings
The Windows power management settings have a default option of turning off the driver to save power. This means the driver usually gets turned off when the computer is in sleep mode. However, this setting can cause some errors and conflict with your settings.
Furthermore, what your device considers sleep mode may change due to bugs and user input, and it arbitrarily turns off the driver.
To disable this setting, follow the steps below.
- Press Windows key + R to open the run box.
- Type
devmgmt.mscand press Enter. - In Device Manager, double click on Network adapter.
- Locate your network driver and right-click it.
- Click on Properties.
- Go to the Power Management tab and deselect Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power.

- Click OK.
Enable NIC From BIOS
While not common, your PC can automatically disable the network interface card after some changes in your system. It is common if you have recently upgraded your Windows OS or made major changes to your computer.
Here’s how to check and enable your network interface card from BIOS.
- Shut down your computer.
- Turn on your PC, and immediately and repeatedly press the F10 or Esc key. You will enter the BIOS setup. Different computers have different keys or key combinations to enter BIOS setup. Check what your computer’s keys are on a different device with an internet connection.
- Go to System configuration
- Select Boot Options, and press Enter. (Navigate with the arrow keys.)
- In Boot Options, select Internal Network Adapter Boot and press F5 to enable the NIC. (If it is already enabled, disable it and enable it again.)

- Press F10 to exit and save changes.
- Select Yes.
Note: The above steps are for Intel BIOS setup. You may need different steps for other motherboard BIOS.
Perform a System Restore
System Restore is a widely used method to troubleshoot and fix various issues. Performing a system restore rolls back the changes made to your computer to a determined restore point.
If the error message started showing up just recently, you could try performing a system restore.
Follow the steps below to perform a system restore:
- Search the Control panel in the search bar and open it.
- On the top right, next to View by, select Large icons.
- Select Recovery and click on Open System Restore
- Click on Next.
- Select a restore point where the NIC worked properly and click on Next.

Perform a Network Reset
A network reset will wipe your configured settings and data and restore your settings to their default state. It is like a hard reset but only for your network settings. A network reset helps fix several kinds of network issues in your PC.
Follow the steps below to perform a network reset:
- Open settings from the start menu.
- Go to Network & Internet.
- Scroll down and click on the Network Reset option.

- Click on Reset now and hit Yes.
- Restart your PC.
After your device restarts, check if your internet connection has been restored.
Perform a Winsock Reset
You can also try performing a Winsock reset if a network reset doesn’t fix the issue. Winsock reset is similar to network reset as it wipes and restores default configuration. However, it only targets the Winsock Catalog in Windows.
Here’s how to perform a Winsock reset.
- Search Command prompt in the search bar.
- Right-click the Command prompt and select Run as administrator.
- Type
netsh winsock resetand press Enter.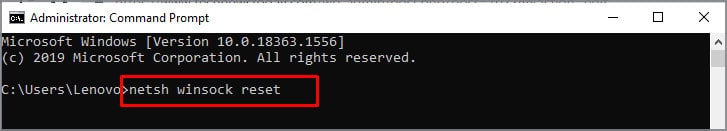
- Restart your PC.
Lastly, if all the methods didn’t work, your network interface card may be malfunctioning or defective. You would have to replace your NIC if this is a hardware issue.















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


