4G LTE explained (Long Term Evolution) – Updated
Last updated 12 January 2022
Mục Lục
What is LTE?
It’s a worldwide standard for 4G wireless transmission data, the fourth generation of mobile network technology initiated in 2008.

4G LTE networks are the next generation from the existing 3G networks – Universal Mobile Telecommunications System UMTS or 3rd generation.
LTE full form – What does LTE stands for?
LTE stands for Long Term Evolution.
Why?
It was indeed a “long-term evolution” for mobile networks (based on 3G tech at that time) when 4G came out in 2008.
The evolution took many years.
1G (First generation)
1980’s
Let us talk to each other on mobile phones
2G
1990’s
Let us send SMS and travel (roaming)
3G
2000’s
Introduced some mobile internet experience
4G
2010’s
Brought fast internet experience
5G
2020’s
Brings super-fast Internet and much more
What does LTE mean on my phone? It means fast-internet connection. Mobile network generations: from 1G to 5G – Source Thales 2021
4G LTE is a global standard and success.
Who’s in charge of defining and maintaining this technology?
The 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) standards group has developed and maintains LTE high-speed wireless technology.
3GGP unites telecom standard development organizations so that everybody uses the same technology.
And 4G LTE is a global success.
66% of mobile users have 4G LTE in Jan. 2022
LTE is a success worldwide, with 6.6 billion subscriptions connecting two-thirds of mobile users globally, according to the Global mobile Suppliers’ Associations (GSA – January 2022 report).
- 791 telecom operators are running LTE networks in 240 countries and territories across the globe.
- 336 have rolled out LTE-Advanced networks.
- 227 have initiated VoLTE networks.
4G LTE is today the most current cell phone technology.
LTE vs 3G
Is 4G LTE the same as 3G?
No. LTE means 4G, and the visible difference is speed!
- 3G (third generation of mobile communications introduced in 2001) theoretically delivers 7.2Mbps and up to 3Mbps in practice.
- 3G HSPA+ (the advanced version – High-Speed Packet Access+) or 3G++ delivers up to 42Mps and up to 6Mbps in practice.
4G LTE data rates with 100Mbps are 2,5 times faster than 3G HSPA+ and 15 times faster than 3G.
LTE vs 4G: who’s better?
What’s the difference between LTE and 4G?
Well, they are not competing. LTE is the technology behind 4G (the fourth generation of mobile communications – an architecture).
All 4G phones utilize LTE technology in 2022. It brings high speed to mobile and broadband data.
How fast is 4G LTE?
In theory, LTE’s maximum speed is 100Mbps. In practice, it tops at 15Mbps. Of course, it all depends on where you’re located.
But what is LTE-A?
LTE-A, LTE-Advanced, 4G+, and LTE+
LTE-A, LTE-Advanced, 4G+, and LTE+ are all acronyms for the same 4G service. It’s a faster version of LTE.
How fast is LTE-A? Again, in theory, LTE-A data rates are up to 300Mbps. In practice, you can expect between 40 to 90Mbps.
LTE-A is three times faster than LTE.
4G LTE features at a glance
LTE – often called 4th generation LTE or 4G LTE – have an all-IP flat networking structure. LTE is used for mobile, fixed, and portable broadband access.
LTE is designed for lower latency (the time it takes for data to travel in the network) and increased bandwidth – very interesting for the Internet of Things.
In fact, bandwidth increases can be as high as 100 Mbps on the downlink and up to 50 Mbps on the uplink.
- The higher bandwidth enables faster access to content and applications, particularly video applications that can only be offered today on fixed systems.
- The low latency enables time-sensitive applications like voice services.
- The all-IP architecture enables new converging services based on the IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS).
There’s more.
Voice over LTE (VoLTE)
What is VoLTE on your phone?
VoLTE means voice-over LTE. It’s an improved version of 4G LTE for voice and video calls.
In essence, you get HD voice and video calls, and it’s a great experience overall with better coverage and battery life increase.
If you upgrade to 4G LTE, make sure you also get 4G VoLTE.
4G LTE and India: massive expansion in 2020
Around 100m new 4G users were added in 2020, and 4G data consumption alone contributed to 99% of the total traffic in the country with a +60% annual growth, according to
were added in 2020, and 4G data consumption alone contributed to 99% of the total traffic in the country with a +60% annual growth, according to Times of India . Data traffic grew by x60 from 2015 to 2020. Early 2021, India is now a full 4G market with 99% of the 700m mobile internet subscribers using 4G LTE for going online.
But 4G LTE is also decisive for IoT devices (connected things).
4G LTE for the IoT (Internet of Things)
There are three broad categories within 4G – which is mainstream to connect industry-grade IoT devices today.
- The LPWAN, low powered wide area network, has two variants, which are category M (Machine to Machine) (Cat-M or LTE-M) and category NB-IoT (Cat NB-IoT).
- The mid-range bandwidth is category LTE-1 (LTE Cat 1).
- The high bandwidth applications typically use networks called LTE Advanced (LTE-A) or LTE Advanced Pro.
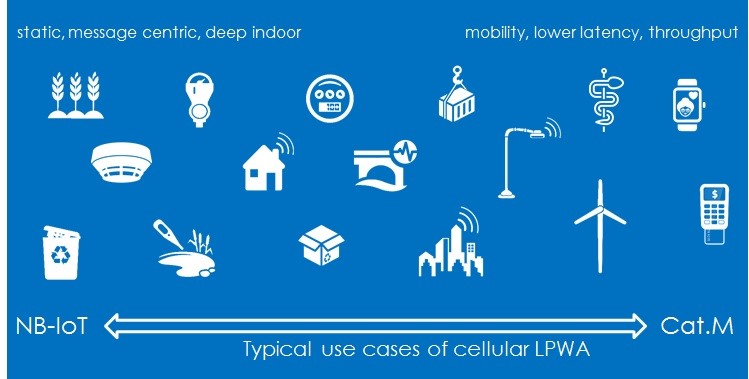
4G comes in different flavors for connected objects. Here are some examples of IoT devices and their specific bandwidth needs. The suitable 4G LTE module can then be selected according to the need.
LTE back-ward compatibility
LTE is compatible with existing mobile networks to provide maximum flexibility.
This feature encompasses formerly deployed network technology, including GSM, cdmaOne, W-CDMA (UMTS), and CDMA2000.
Wi-Fi vs LTE
Wi-Fi was created in 2000 by the Wi-Fi Alliance. It is a set of wireless local (limited range) area network (LAN) protocols for short-distance connectivity.
Access to the Internet is most commonly done via a wireless router.
Wi-Fi is based on IEEE 802.11.
LTE is a broadband (unlimited range) wireless network technology.
First, Wi-Fi-certified products came with IEEE 802.11b (yes, b came before a).
How fast is Wi-Fi?
The theoretical speed for version b is 11Mbps and 5.5Mps actual. Version a offers 54Mbps in theory and about 20Mps in reality. The maximum range is 10m for version b and 140m for version a.
Wi-Fi comes in many flavors now, and speed performance continues to improve with each new generation.
Before wireless – If you’re old enough to remember – network connections on a LAN or over the Internet were done via Ethernet wired connections or a modem over phone lines.
Wi-Fi works best for line-of-sight use, and walls, pillars, or TV screens (obstacles) may seriously reduce range. Practical performance is also related to distance from the router.
Wi-Fi speed continues to improve with each new generation.
Is 5G the same as 4G LTE?
No, it’s not. LTE is a 4G technology.
5G is the fifth generation of mobile network technology. 5G does not replace 4G LTE. 4G and 5G work together.
5G network technology, 5G services, and 5G-enabled smartphones have started their roll-out.
Needless to say, there’s no such thing as 5G LTE.
4G – 5G milestones
- 4G (2008) networks brought all-IP services (Voice and Data), a fast internet experience, with unified network architectures and protocols.
- 4 G LTE ( for Long Term Evolution), starting in 2009, is doubling data speeds.
- 5G (starting in 2019) networks expand broadband wireless services beyond mobile Internet to IoT and critical communications segments with speed up to X10 compared to 4G LTE.

When will 5G take over?
In short, 2019 was when 5G lifts off, and 2020 onward is when 5G networks and 5G phones will be available en masse.
ABI Research sees 5G overtake 4G by 2025.
5G with 10Gbps is up to 100 times faster than 4G LTE.
But there’s more in 5G than speed.
Discover key facts and more about 5G technology and worldwide roll-outs in our 5G web dossier.
Now it’s your turn.
If you’ve something to say on 4G LTE, a question to ask, or have found this article helpful; please leave a comment in the box below. We’d also welcome any suggestions on how it could be improved.
We look forward to hearing from you.















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


