10 Different Types of Computer Networks in Today’s World
Written By
Computer networks keep changing the way we live and do things in the 21st century. This is because virtually every computing activity or information sharing we do today depends on one form of network or another.
The Internet is a very good example of a computer network that allows users to get information from any part of the world, using an internet-enabled device.
Depending on the type of communication you want to achieve, a networking device such as a router or switch is often used when designing a computer network.
There are several types of computer networks that can be used for the purpose of data communication and information sharing. Let us take a look at the most popular types of networks available today.
1) Personal Area Network (PAN)
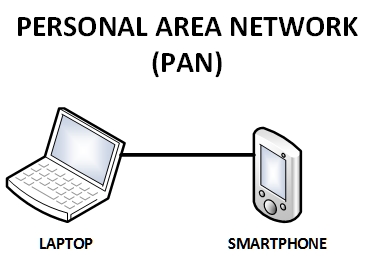
A Personal Area Network or PAN has been around for quite sometime and this type of network focuses on a person’s workspace. A Personal Area Network handles data transmission within devices such as tablets, personal digital assistants, smartphones, and computers. Note that single users in most cases basically use this type of network. People make use of these types of networks commonly in situations where they need to connect wearable or mobile devices.
2) Local Area Network (LAN)
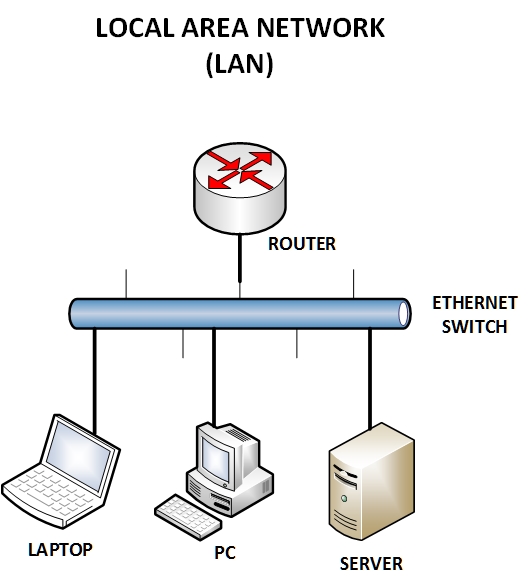
A Local Area Network or LAN as it’s commonly known is a network that connects devices usually in the same building or local area. This could be computers or other devices that are within an office building, which are connected together to share resources.
Most people make use of this network type to share files and other business-related documents in an organization. A router is often used when multiple Local Area Networks need to be connected to each other. A LAN is probably the most commonly used computer network nowadays. A major component of a LAN network is a Layer2 Ethernet Switch which provides the actual communication between devices.
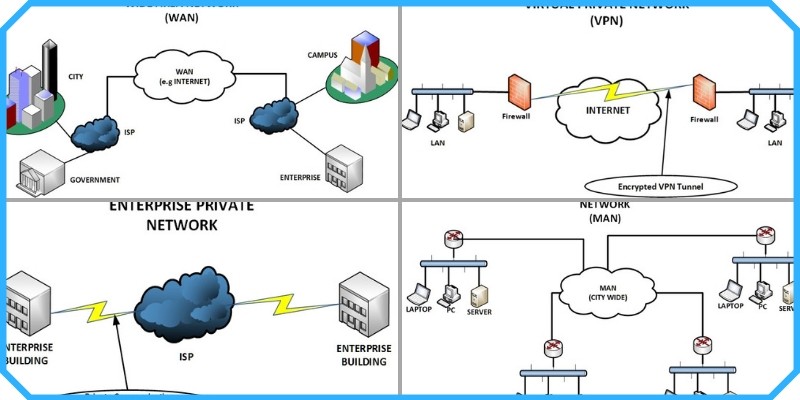
3) Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
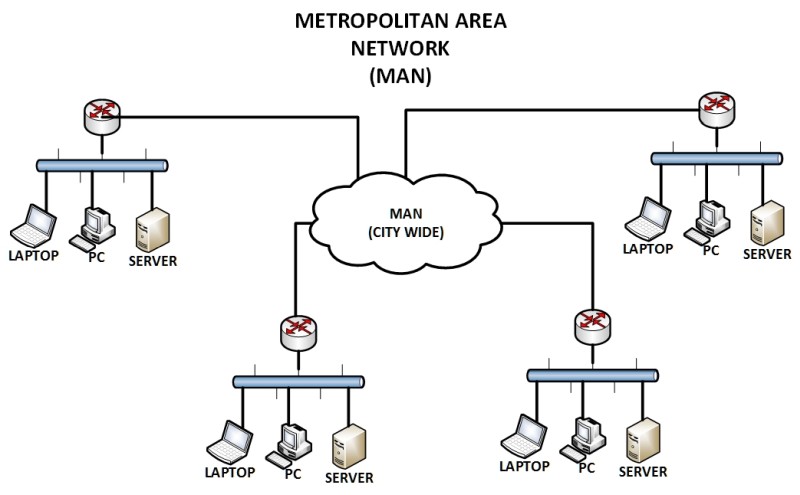
When it comes to the MAN network type, know that it is usually a large computer network on a large geographical area that includes several buildings and LANs, or even the entire city or metropolitan area. The geographical area of the MAN is larger than LAN, but smaller than WAN, which makes it fall in between a Local Area Network and a Wide Area Network.
4) Wide Area Network (WAN)
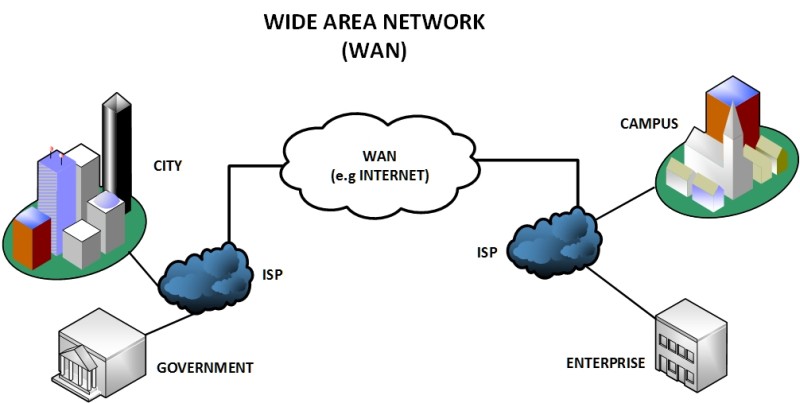
Unlike Local Area Networks and Metropolitan Area Networks, Wide Area Networks or WAN are networks that span over wide geographical locations, which could be multiple buildings or even multiple cities or countries.
This kind of network is suitable for providing Internet access to Local Area Networks or some other kinds of networks. Wide area network communications often require networking devices such as routers and modems for effective data communication.
Moreover, WANs are usually provided by ISPs which are interconnected to offer communication to wider areas. A WAN link is usually referring to a network interface that provides connection of the smaller network towards the bigger WAN network. A WAN link can be fiber optic, Ethernet Layer2 VPN, Layer 3 MPLS vpn etc.
5) Wireless LAN (WLAN)
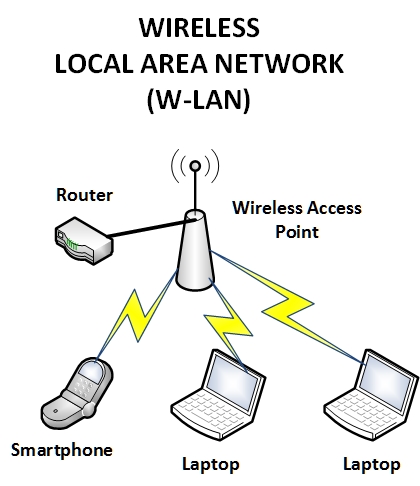
Unlike Local Area Network, a Wireless LAN network doesn’t make use of a cable for end-to-end connectivity. A WLAN makes use of a Wireless Access Point (WAP) device, which serves as the point of connectivity for wireless clients on the network.
Keep in mind that this kind of network can support other devices such as smartphones and tablets. One of the advantages of using a WLAN network is the flexibility it offers users, since there is are cable restrictions.
6) Virtual Private Network (VPN)
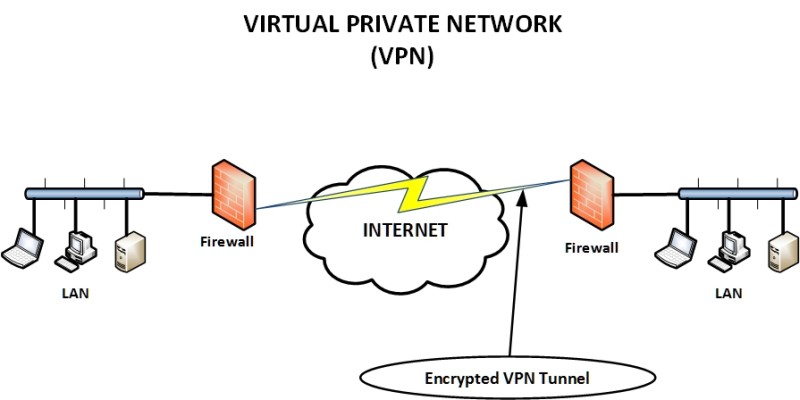
A Virtual Private Network is a type of network that makes use of existing private or public network infrastructure (e.g the Internet) to provide a secured network connection. This is often achieved by creating an encrypted tunnel for secured end-to-end connectivity. A Virtual Private Network uses data encryption techniques to provide security for files that are sent or received over the network. This is often used by organizations that have highly sensitive data to transfer.
Have in mind that a VPN is also used to connect LAN networks that are far away between them. For example, a company has different buildings (with LAN networks) in different Cities and wants to interconnect the buildings over the Internet. A VPN will provide an ideal and cheap solution for such a case.
7) Storage Area Network (SAN)
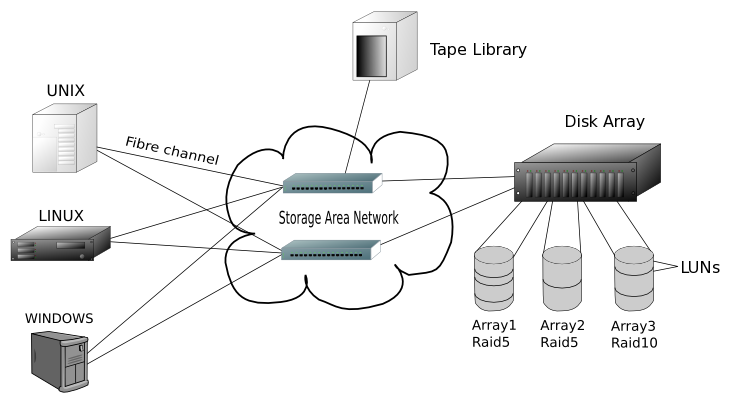
A Storage Area Network or SAN is a network that has been designed for storing and transferring files. This network setup is often made up of servers with large storage capacity and special switches and interface cards.
There are many reasons why any organization would make use of a Storage Area Network, and one of them is to provide a safe place for storing important files and for providing a fast network for backing up files.
Storage Area Networks are often designed to have high availability, because files must be accessible at any given time. Also, a SAN might not use the classical TCP/IP used in other computer networks but some special protocols such as Fiber Channel Protocol, SCSI over FCP etc.
8) Enterprise Internal Private Network
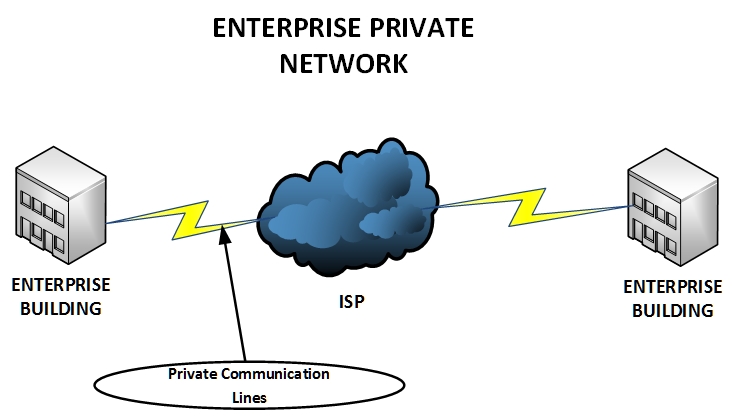
An Enterprise Internal Private Network is a type of network that is designed for private communication within an organization. This type of network is only accessible from within the enterprise since its major goal is to provide security for users within the organization. A firewall is often used when users need to access information on the Internet.
Although it’s a private network, it does not mean that its only available within a building. It can span several buildings using private communication lines.
9) Campus Area Network
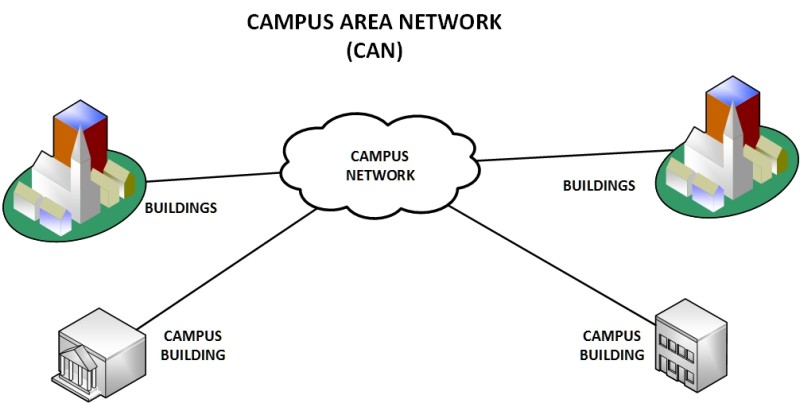
Campus Area Networks are basically made up of several Local Area Networks, which are often within a campus area. Campus Area Networks are used in places such as hospitals, schools, universities or any organization that has multiple LANs and buildings that need to connect to each other to share resources.
10) System Area Network
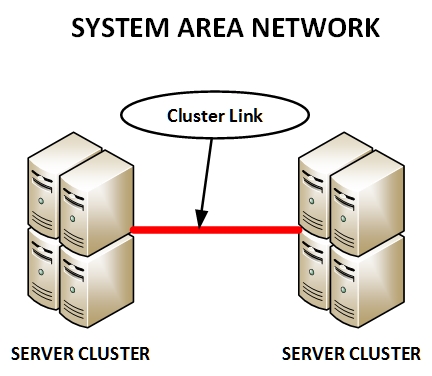
A System Area Network is a network that is designed to work in parallel computing environments; it connects computers that are in a High Performance Computing setting. These are often used where high processing is needed. Computer clusters make use of System Area Networks to achieve connectivity. The major difference here is the distance in between the computers on the network, which is often a short distance.















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


