12 Best Network Security Tools for 2023 (Paid & Free)

Network security monitoring has become a complicated task because of the wide range of attack vectors that hackers now have at their disposal.
New attack strategies appear regularly, making traditional system defense software ineffective. A better strategy is to deploy security monitoring systems that don’t rely on a process of pattern matching.
Old security tools that just compare packet content to a list of known strategies quickly become outdated and need to be updated constantly. Smarter network security tools assess regular activities on a network and then lookout for anything that is different, which is called an anomaly. These AI-based tools are more sustainable in the ever-changing landscape of cybersecurity.
Mục Lục
Here is our list of the best network security tools:
- Endpoint Protector
EDITOR’S CHOICE
A cloud-based system that watches over endpoints, peripherals and applications to prevent the leak of sensitive data. Access a free demo.
- SolarWinds Security Event Manager
(FREE TRIAL)
A real-time incident detection and response system that is based on log file analysis. It installs on Windows Server.
- ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus
(FREE TRIAL)
A vulnerability scanner packaged together with a patch manager and configuration manager that also ensures secure password policies are established at the endpoints. It installs on Windows environments. - ManageEngine Log360
(FREE TRIAL)
This security package includes file integrity monitoring, a SIEM, and compliance reporting. Runs on Windows Server.
- OSSEC A free open-source host-based intrusion detection system that includes the option of automated threat remediation. It installs on Windows, Linux, macOS, and Unix.
- Intruder A SaaS automated vulnerability scanner with the option of on-demand scans and human penetration testing.
- CrowdStrike Falcon Insight A package that includes a cloud-based SIEM system and device-resident endpoint detection and response instances. Agents for Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- Nessus Vulnerability Scanner A security tool that seeks out vulnerabilities in hardware configurations and software versions. It installs on Windows, Linux, macOS, and Free BSD.
- OWASP ZAP A web application security system that scans web pages for known threats and examined web servers for configuration and access control weaknesses.
- Zscaler Cloud Firewall A cloud-based network security service that is ideal for virtual offices.
- Burp Suite A collection of penetration testing tools and a vulnerability scanner that attempts a range of simulated hacker attacks on a network. It installs on Windows, Linux, and macOS.
- Teramind DLP A data loss prevention system that scans for sensitive data and watches user activities to aid compliance with data security standards.
There are a number of different approaches that can be taken towards protecting a network and each strategy requires its own set of tools. These tools and strategies are:
- Firewall – block all known attacks at the boundary of the network.
- Reverse firewall – for data loss prevention.
- Intrusion prevention systems/SIEMs – catch anomalous behavior on the network that the firewall missed.
- VPN/edge services – protect all onsite resources by channeling internet traffic through an external proxy server.
- Endpoint Detection and Response – use endpoints as security monitoring stations to identify malicious activity on the network.
This shows that there are four physical locations that can be utilized to monitor network security:
- Offsite with an edge service
- At the network boundary with a firewall
- On the network by packet sniffing
- On endpoints with EDR software
Network security strategies
Thorough network managers are advised to use a combination of tactics. This is because even the most reliable security system can be bypassed. By implementing several strategies, you will cover every possible security threat. For example, a firewall will block known infected software from entering the network but it won’t stop a disgruntled employee from mailing out your client list to a rival.
Blended strategies require preparedness as well as blocks on malware, malicious activity monitoring, attack shutdown, and system reviews. You need to implement network security by:
- tightening up vulnerabilities to reduce risk
- controlling access to the network
- monitoring traffic to spot attacks in progress
- take action to stop an attack
- reviewing data to identify past attacks that slipped through the net
- and adjusting the security and monitoring systems according to past experience
As there are so many different network security tasks and tools for each of them, this review lists exceptional tools that fall into each of the defense strategies that you will need to deploy. None of them cover every aspect of system security, so you will need to implement several of them.
Our methodology for selecting a network security tool
We reviewed the market for network security systems and analyzed tools based on the following criteria:
- Network discovery to identify all paths and devices
- Activity baselining, preferably with Machine Learning
- Adaptable anomaly detection
- Alerts for suspicious activity to attract technicians
- Extensive reports and logging
- A free trial or a demo account that enables a cost-free assessment
- Value for money from a tool whose vigilance will save the expenses involved in system recovery
With these selection criteria in mind, we identified candidate network monitoring systems that are worth trialing. We looked for utilities that will install on Windows Server and Linux plus SaaS platforms.
You can read more about each of these security tools in the following sections.
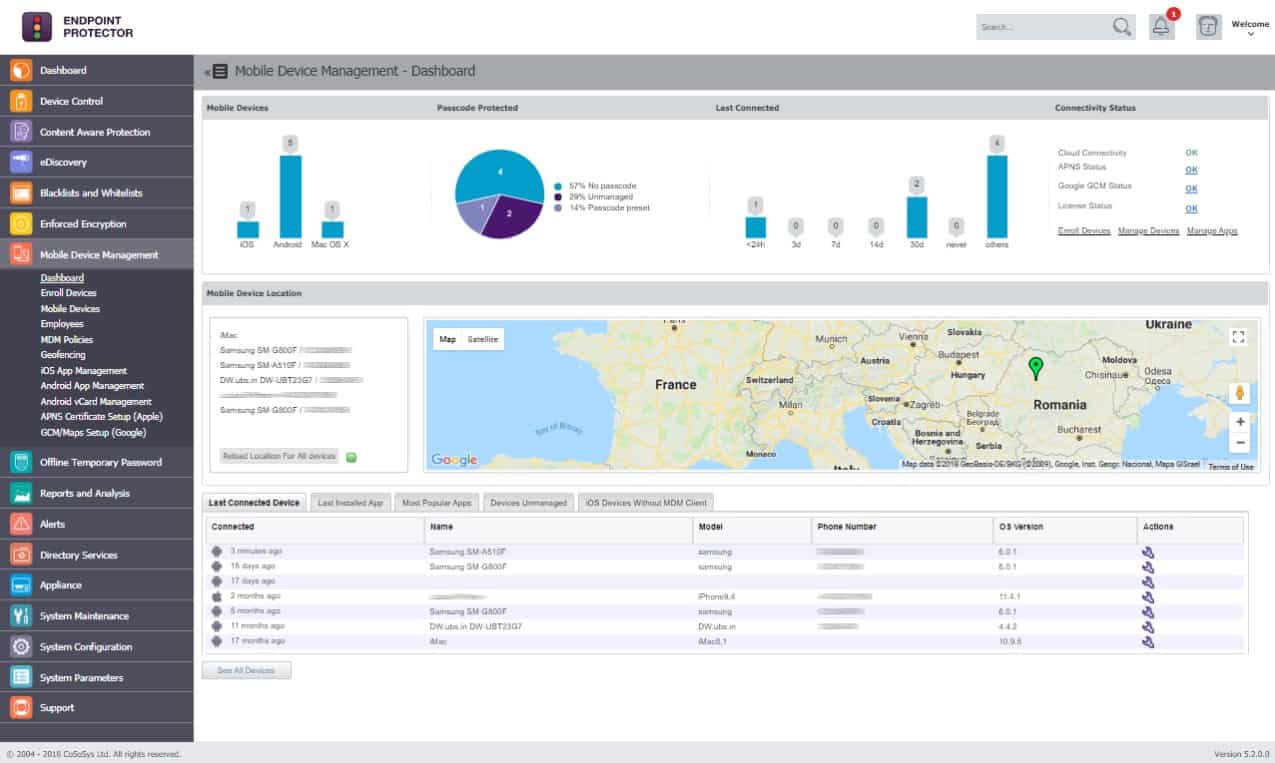
Endpoint Protector by CoSoSys watches over all of the devices on a network from its cloud location. The system requires that each monitored endpoint has an agent installed on it. With the agent in place, the system administrator can command a sweep of all devices for locations of data storage. The service then categorizes data by a sensitivity ranking.
Key Features
- A SaaS platform
- On-site agents
- Sensitive data discovery
- Data loss prevention
- Device control
The Endpoint Protector system allows system administrators to define security policies that vary the allowed actions of different user groups and employee statuses. The controls over data access can also be varied per department. Thus, different types of data can be access and/or changed in different ways according to the user. Inappropriate data access attempts will trigger alerts.
Utilities on the network can also be monitored. This extended to communication with printers and USB devices. Again, the degree of control over the movement of data over memory sticks or through printing can be varied according to the sensitivity rating of that information.
Endpoint Protector’s dashboard shows live events across the network. The extent of the systems data control is not limited to one LAN. The service can also monitor data flows in many locations, including in the homes of telecommuters.
Pros:
- Enroll endpoints anywhere
- Variable security policies
- Sensitive data discovery and classification
- Live activity monitoring
- Alerts for unauthorized data access or movement
Cons:
- Not available for self-hosting
The Endpoint Protector system is offered in a hosted package as a SaaS. The system can also be accessed as a service on AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform. It is possible to get the software for Endpoint Protector and install it on your site as a virtual appliance. There isn’t a free trial available for Endpoint Protector. However, you can access a free demo to assess the software for free.
EDITOR’S CHOICE
Endpoint Protector is our top pick for a network security tool because it is able to simultaneously monitor all endpoints, whether they run Windows, macOS, or Linux. It doesn’t matter where those endpoints are located, so you can be running a WAN or a virtual office and still get full control over sensitive data. The Endpoint Protector service offers live data access tracking and includes a system of alerts that will let you know if potentially damaging data access attempts are made.
Acess FREE Demo: endpointprotector.com/get-demo/
OS: Cloud-based
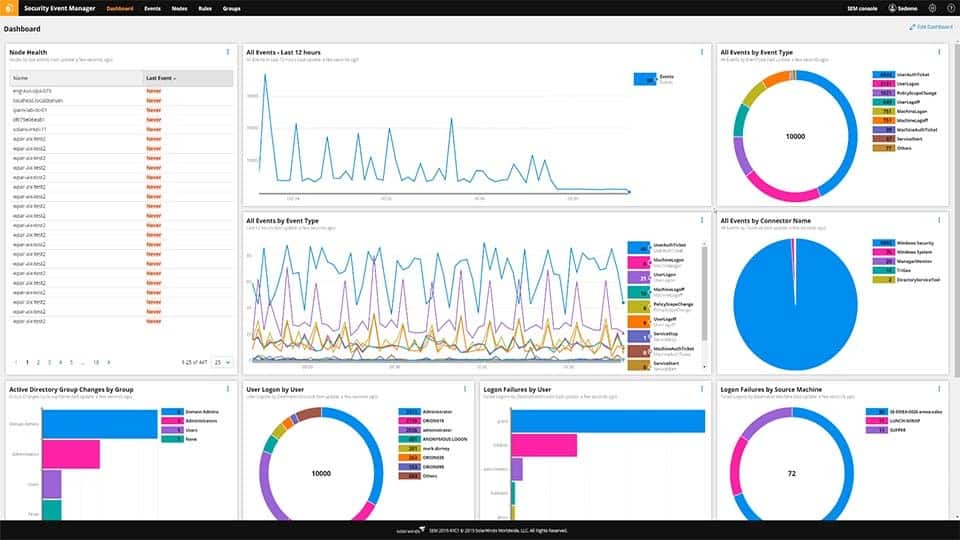
The Security Event Manager from SolarWinds is a SIEM system that scans events on a network and watches out for anomalies that are indicated by a live threat intelligence feed. This network security tool extends to all devices connected to the network. It collects all log messages and manages their layout, creating a common format. Those records are then filed while also being analyzed by the tool.
Key Features
- On-premises software for Windows Server
- Collects system logs
- Searches for suspicious activities
The message checking service receives live reporting information from all points on the system. As these records are processed, the Security Event Manager scans for signs of intrusion or other malicious activity. Some typical attacks can be spotted by looking at one event, while others are only made apparent by a pattern of seemingly unrelated incidences. So, in order to provide a full network security service, the tool works both on live data and historical records.
In order to reduce the incidences of “false positive” reporting, the Security Event Manager makes a record of normal traffic patterns and activities. This is an AI-based machine learning technique known as User and Entity Behavior Analysis (UEBA).
As well as detecting suspicious activity, the Security Event Manager is able to implement actions to close it down. This service takes the form of blocking communications from specified IP addresses or suspending a user account that appears to have been hijacked. The mitigation automation is activated by the user, so it can be left to just an alert if you want to investigate a problem before implementing a solution manually.
SolarWinds Security Event Manager is a great choice for a network security tool because it covers all elements of IT infrastructure by exploiting the built-in reporting features of each component. Threat intelligence feeds, combined with machine learning ensure that this system will trap all of the latest threats without impairing system availability to genuine users.
Pros:
- Log-based SIEM
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics for baselining
- Anomaly detection
Cons:
- No SaaS version
SolarWinds Security Event Manager runs on Windows Server and it is available on a 30-day free trial.
SolarWinds Security Event Manager
Download 30-day FREE Trial

Vulnerability scanning is an essential preventative network security task. There are many ongoing maintenance tasks that network managers need to conduct and some of these are necessary in order to keep the system secure.
Key Features
- System hardening
- Automated patching
- Access rights management assessment
Apart from vulnerability scans, you need to keep all operating systems patched and software updates applied. These patches and updates are often written in order to address newly discovered “exploits”. ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus includes a Patch Manager to keep your software secure. It also has a Configuration Manager that standardizes the setup of network devices and blocks unauthorized changes. Configuration management is another important task to keep a network secure.
Vulnerability Manager Plus combines vulnerability scanning with tools to address issues that the scan identifies. These extend to access rights analysis and password management features. Other tools include firewall auditing and service hardening, such as browser security enhancements.
ManageEngine offers Vulnerability Manager Plus in three editions: Free, Professional, and Enterprise. The Free version will manage networks connecting up to 25 computers. The Professional edition doesn’t have the system limit and it also has specialized processes for managing the security of servers. That version only covers the network on one site; the Enterprise edition is designed to serve WANs.
Pros:
- Combines vulnerability scanning with tools to fix discovered problems
- Automated remediation playbooks
- Configuration Protection
Cons:
- This is a bundle of many tools that are available individually
The software for Vulnerability Manager Plus installs on Windows and Windows Server and you can get it on a 30-day free trial.
ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus
Download 30-day FREE Trial
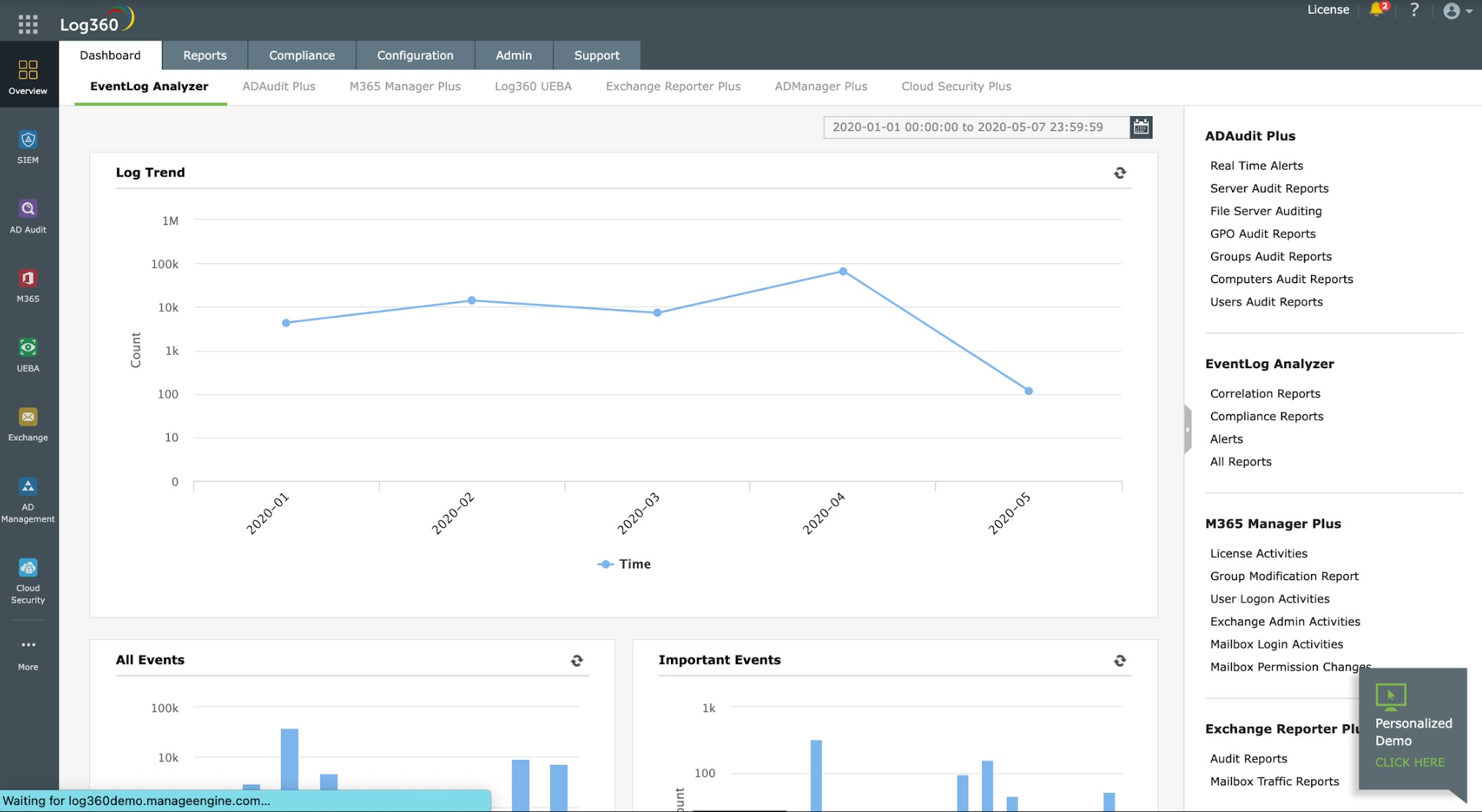
ManageEngine Log360 is a SIEM system that also performs file integrity monitoring and provides compliance reporting for HIPAA, PCI DSS, FISMA, SOX, GDPR, and GLBA. The package includes a central log server and a library of data collection agents. Install one agent on each device on your system – there are also agents for cloud platforms.
Key Features:
- Consolidates different log message standards
- Threat intelligence feed
- Compliance reporting
The log server of Log360 shows messages live in the console as they arrive and also stores them to file. The system gets a threat intelligence feed of the latest hacker strategies and that improves the Log360 threat detection process.
The Log360 system raises an alert when it identifies suspicious activity. You can get those alerts forwarded to your technicians through a service desk tool. Log360 works with ManageEngine ServiceDesk Plus, Jira, and Kayoko.
Pros:
- A SIEM tool with log management extras
- Can feed alerts into a ticketing system for technician attention
- Monitors cloud platforms as well as on-premises systems
Cons:
- No SaaS option
The ManageEngine Log360 server runs on Windows Server. You can assess the package with a 30-day free trial.
ManageEngine Log360
Download 30-day FREE Trial
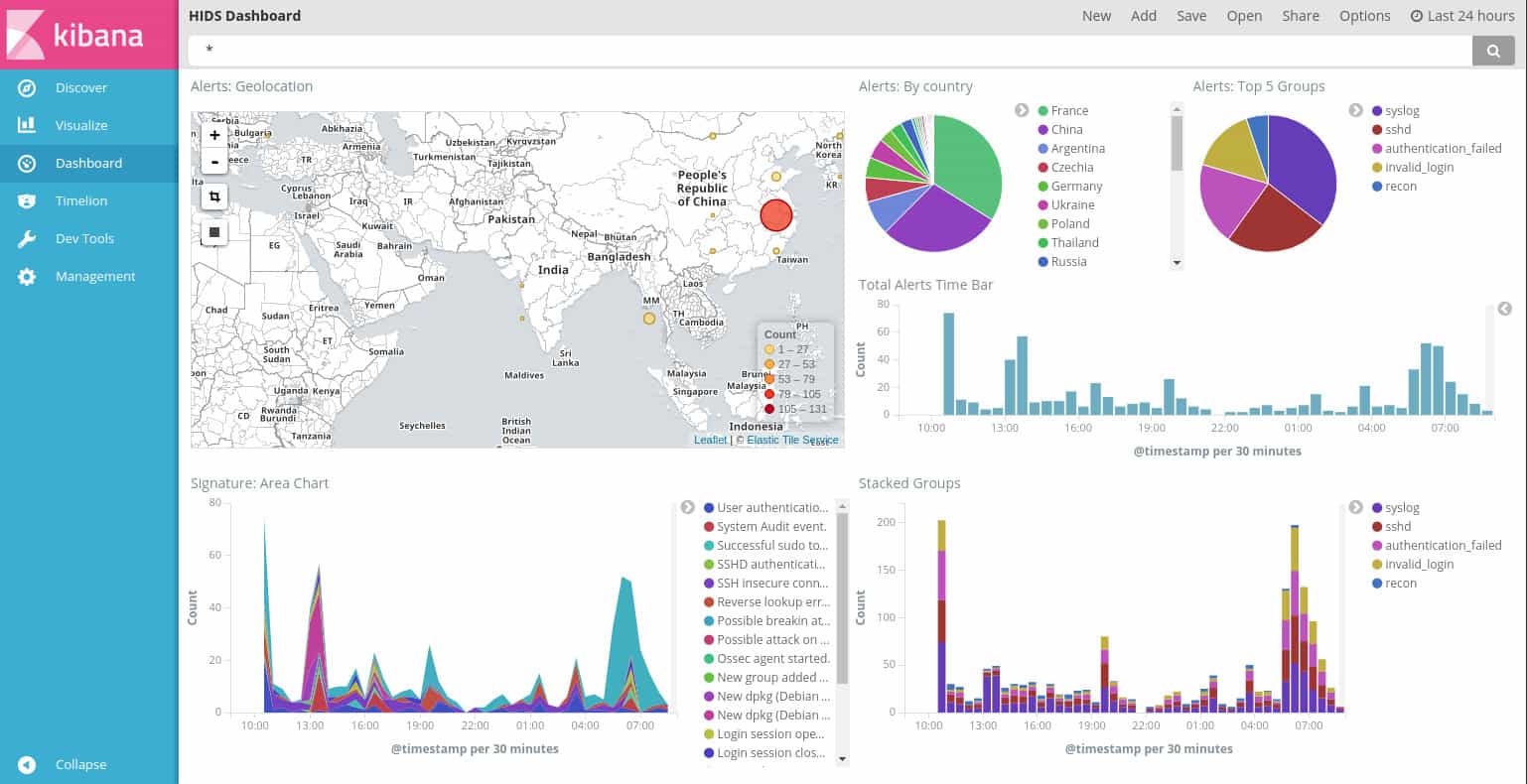
OSSEC is a Host-based Intrusion Detection System (HIDS). This type of security strategy examines log files for signs of malicious activity. OSSEC stands for “Open Source HIDS Security.” It is a free system but is owned by TrendMicro.
Key Features
- A free tool
- Extensible with free detection rules
- Automated remediation actions
The OSSEC system works on a databank of detection rules. These are called “policies” and they can be written by the user or acquired from other users for free through a community listing website and message board. The user community is also the primary source for help and tips on using OSSEC. The lack of a professional support system for the tool might put off some corporate users. However, Trend Micro offers support contracts for a fee.
Existing policies can be adapted and set up to trigger actions, which gives the service the power to automate attack mitigation. Typical actions include interfacing to firewalls in order to block access to specific IP addresses or update the access rights manager to block user accounts. This possibility makes OSSEC an Intrusion Prevention System (IPS).
Pros:
- One of the first SIEM systems to be created
- Highly respected and built to enable customization
- Supported by TrendMicro
Cons:
- No frontend
A big problem with OSSEC is that it doesn’t have a user interface. However, it is easy to set it up to feed data to Kibana or Graylog. OSSEC installs on Windows, Linux, macOS, and Unix.
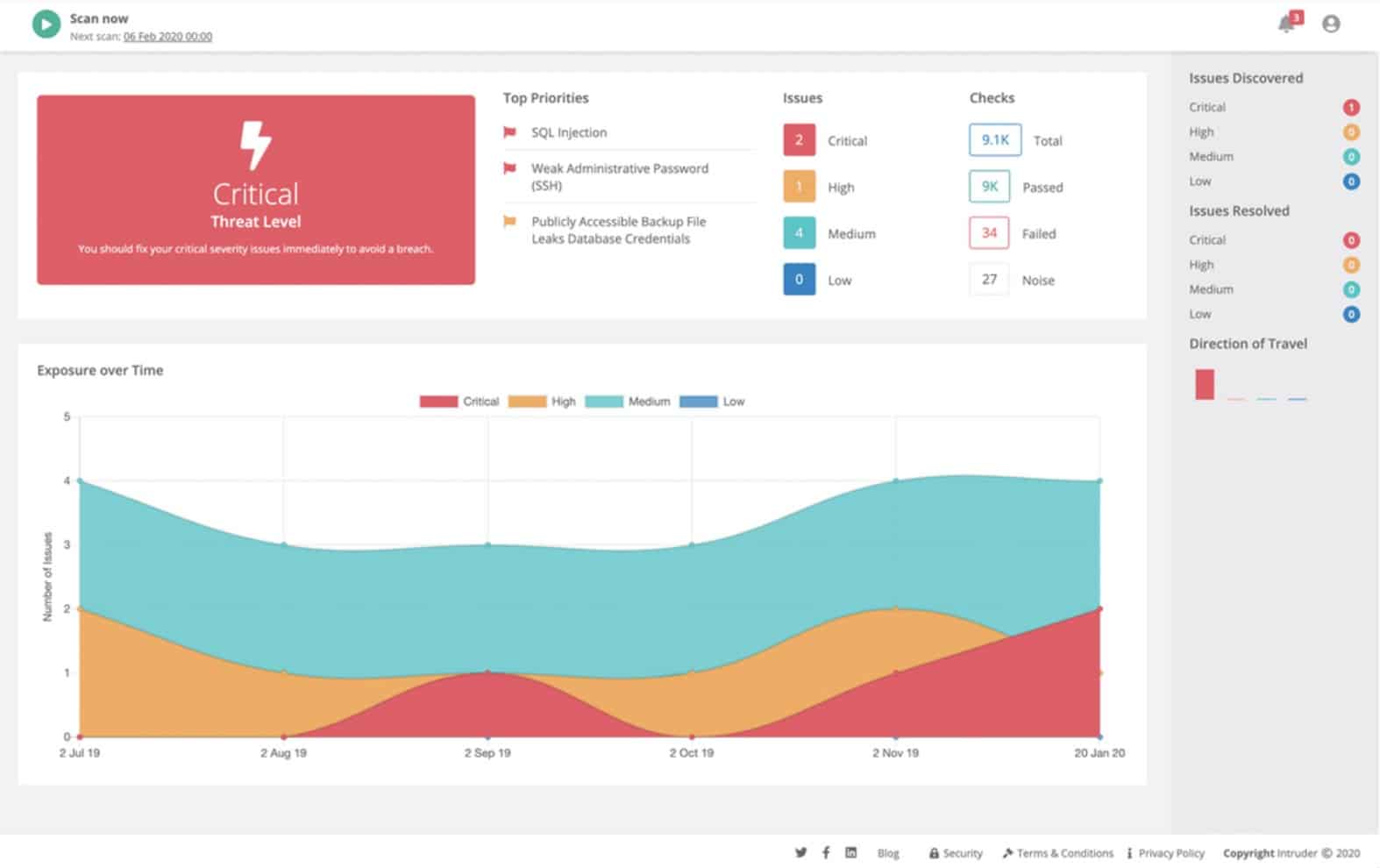
Intruder is a cloud-based security tool that performs constant vulnerability checks on a monitored system. On enrollment, Intruder performs an extensive system sweep, highlighting security issues. Thereafter, the service will recheck the monitored system whenever it receives updated threat information, which occurs once a month.
Key Features
- Cloud-based
- Vulnerability scanning
- Automated patch management
Threat updates trigger new sweeps automatically. However new hardware or software in the system does not get detected, so those system tests need to be launched manually.
Pros:
- Choice of regular or monthly scans
- Emergency checks on the discovery of a new threat
- Customizable automation rules
Cons:
- You would need the top plan for full protection
Intruder is charged for by subscription and is available in three editions: Essential, Pro, and Vanguard. The Essential plan doesn’t include on-demand testing, so administrators who add new software or hardware will need to wait for the monthly scan in order to get those new services checked. The Pro plan includes both automatic and on-demand scans and the Vanguard edition includes the services of human penetration testers.
Intruder is offered on a 30-day free trial.
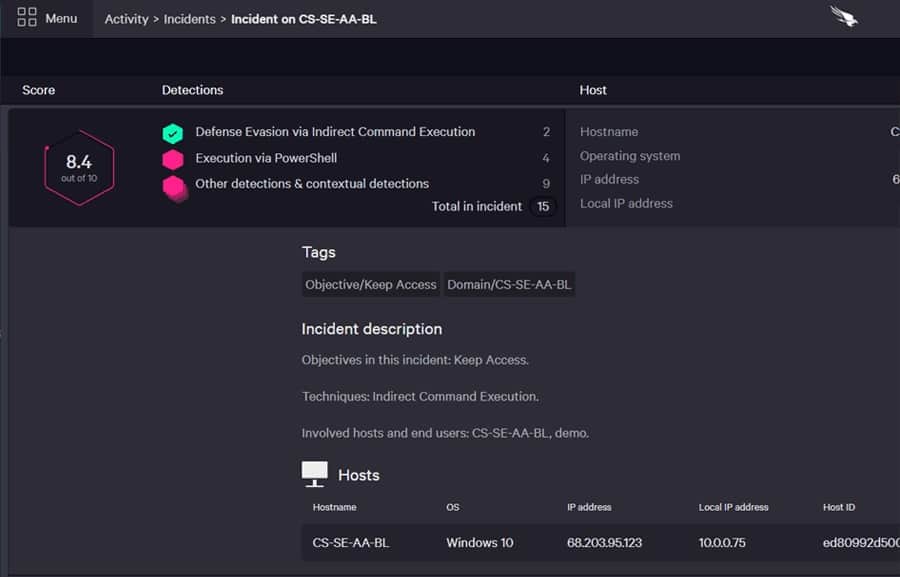
CrowdStrike Falcon Insight
is a combination of a SIEM system and endpoint detection and response (EDR). The EDR part of the system is fulfilled by instances of Falcon Prevent. By opting for Falcon Insight instead, you get a fully coordinated enterprise-wide security system rather than a collection of endpoints with individual AVs to manage.
Key Features
- Cloud service with on-site agents
- Combines SIEM with endpoint detection and response
- Remediation actions
The central service is cloud resident and it makes sure that each endpoint agent is kept up to date. Not only does it ensure that the software is fully updated but it constantly updates those instances with new detection strategies.
The endpoint agents offer full protection and will continue to operate even when they are disconnected from the network and unable to communicate with the central controller. Those agents assess the activities on the endpoint and all of the user accounts that are active on them. This is a UEBA service that establishes a baseline of normal behavior and raises an alert when it encounters an activity that deviates from that standard. The agents also upload log messages and activity reports to the central controller.
The central unit searches through the received data for indicators of compromise. The service also receives a threat intelligence feed that shares the attack experiences of other CrowdStrike customers. The coordinating function of the cloud module acts like an in-house threat intelligence feed, sharing activity summaries between agents.
Pros:
- Unifies endpoint activity tracking
- Implements triage to home in on suspicious activities
- Centralized threat hunting that can cover multiple sites
Cons:
- The Falcon XDR package adds on interaction with third-party tools, which is better
The endpoint agents for CrowdStrike Falcon Insight are available for Windows, macOS, and Linux. You can get a 15-day free trial of Falcon Prevent, which gives you all of the functionality of the endpoint agents.
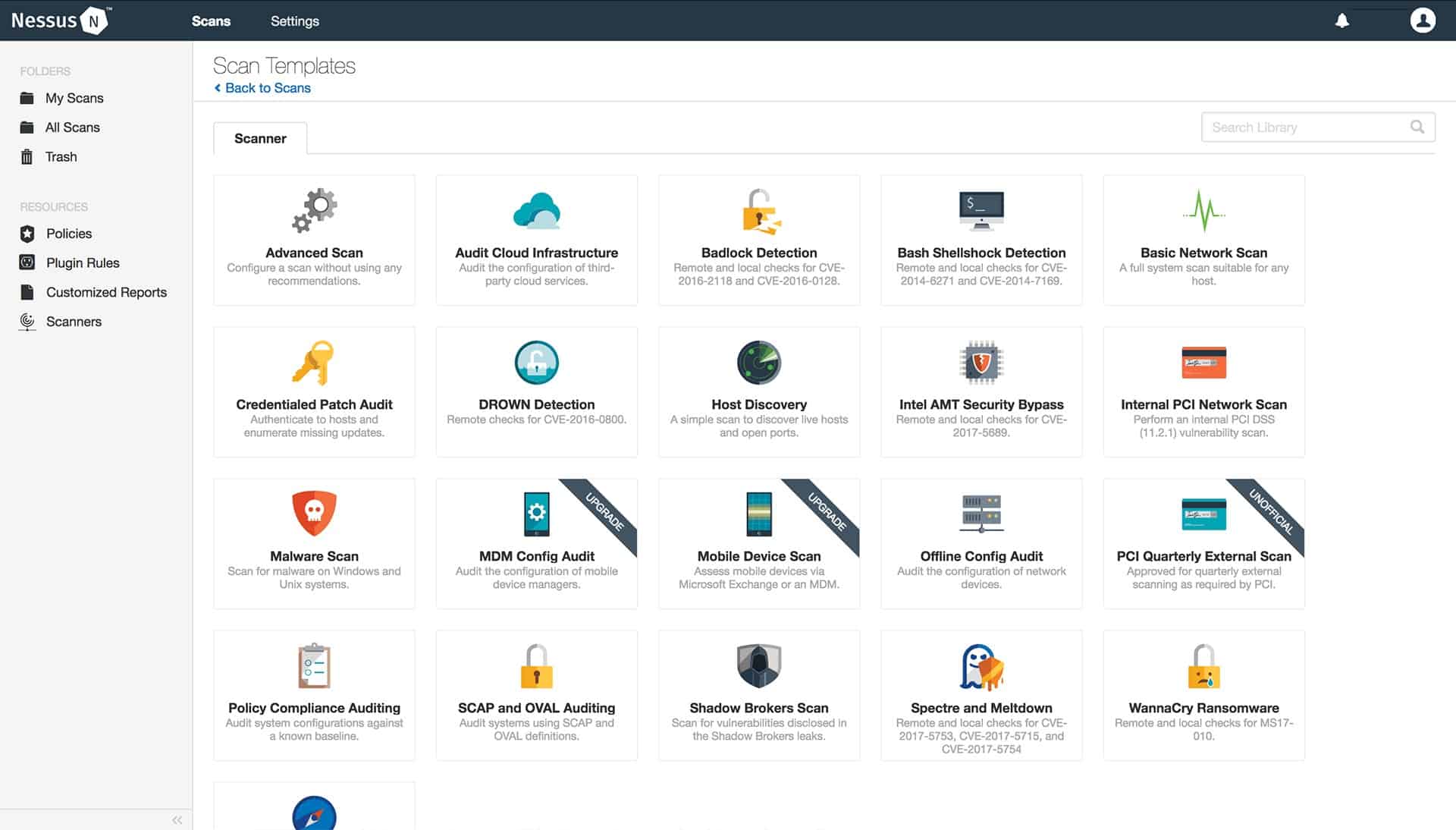
Nessus is one of the leading vulnerability scanners. Its system sweeps check both hardware and software. The tool particularly focuses on device configurations, open ports, and password controls. The system monitors server processes and network traffic, looking for abnormalities.
Key Features
- System security hardening
- Cloud-based
- Free version available
Nessus is available in three editions: Nessus Essentials, Nessus Professional, and Tenable.io. The Essentials version is free to use; it will monitor up to 16 IP addresses and it is community supported. Nessus Professional has no limit on the number of devices that it will scan; it adds configuration assessments and a reporting module. This edition is community supported but has a professional support add-on.
Pros:
- The most widely-used vulnerability scanner in the world
- Checks configuration weaknesses and software versions
- On-site and cloud options
Cons:
- Most installations of this tool are the free version
Tenable.io is a cloud-based managed service and includes full support. The two paid versions are charged for by subscription. You can get a 7-day free trial of Nessus Professional or a 30-day free trial of Tenable.io.
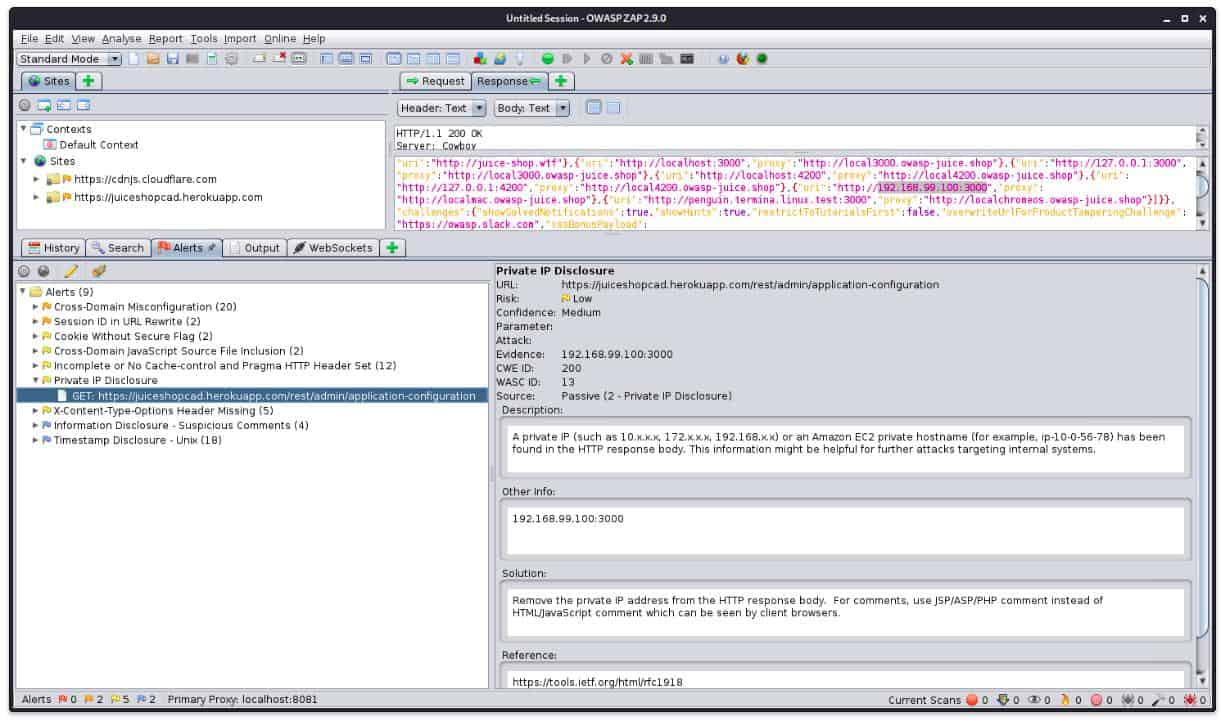
OWASP ZAP is an open-source project that is a fork of Paros Proxy – another very popular network security tool. OWASP stands for Open Web Security Project and ZAP is short for Zed Attack Proxy.
Key Features
- Free to use
- Works as a penetration testing tool
- Checks for Web application vulnerabilities
Despite acting as a proxy, this system is a remote service. It is downloadable software that you need to host yourself. The purpose of the system is to protect a web system from hacker interference. The method of this service is to analyze a web page, looking for SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and cross-site request forgery (CSRF) attacks. It also scans for faulty authentication and session management, system configuration weaknesses, poor access control, unprotected APIs, known vulnerabilities, and sensitive data exposure.
Pros:
- Created by the people who defined the OWASP Top 10
- Offers lots of customizations through plug-ins
- Good for ensuring the security of Web-based assets
Cons:
- No professional support
This network security software is free to use and is extensible by plug-ins, which are also available for free. Those add-ons as well as tips and support are available from the user community. The software runs on Windows, macOS, Linux, and BSD Unix.
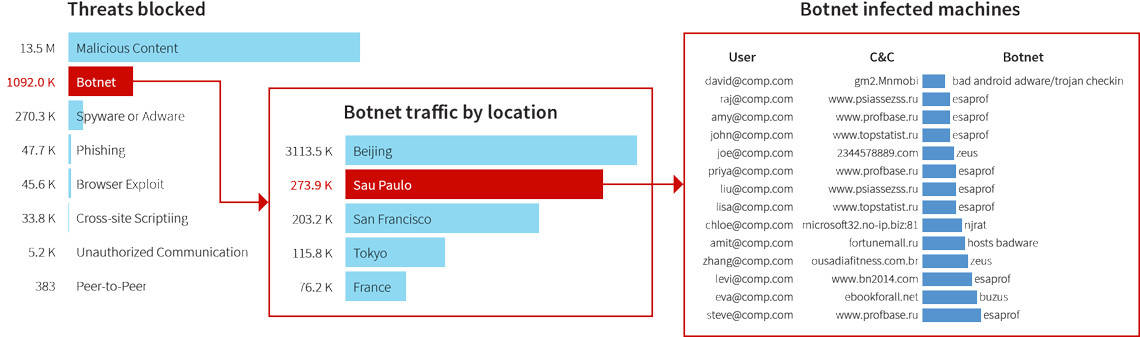
Zscaler is a “firewall as a service” (FWaaS). It runs as an edge service and can monitor a distributed fleet of devices. You don’t need to limit the application of this service to one network in one building. The service creates a virtual network that can extend across the internet to reach its users wherever they are.
Key Features
- Comprehensive defense
- Can cover multiple sites
- SaaS service
The Zscaler methodology is to protect the connections between a community of users. It doesn’t need those connections to be over a single network – it will protect communications over the internet to anywhere, so it is great for companies that use a lot of home-based telecommuters. It is also very easy to grant system access to BYOD users with the Zscaler service.
Pros:
- Secure multiple sites and include individual remote computers
- Easy to set up and use
- Offers a range of secure virtual networking options
Cons:
- The full capabilities of the Zscaler stable are much greater than this one product
All of the processing and anomaly detection of the Zscaler system is run on the service’s host; only a small agent program needs to be installed on protected devices. Essentially, Zscaler creates a virtual network through a series of VPNs. However, the service is more complicated than a VPN because it implements security policies as well as enforcing connection privacy.
Burp Suite is a collection of cybersecurity tools that are useful for penetration testing (pen testing). The suite also features a vulnerability scanner for automated network security sweeps. The key strategy of Burp Suite is to simulate an attack on a network and then list the access attempts that proved successful. The results of this exercise can then be investigated further.
Key Features
- Penetration testing tool
- Free version available
- On-premises package for Windows, macOS, and Linux
There is a Community Edition of Burp Suite that is free to use. This version of the software does not include access to a professional support team, so users have to rely on the community for advice. The Community Edition doesn’t include automated tools, such as the vulnerability scanner.
There are two paid versions of Burp Suite. The Professional Edition includes more sophisticated tools for pen testing and also the web vulnerability scanner. The highest version is called Enterprise. This includes repeated vulnerability scanning and scheduling for network security sweeps. This version can also be used for software testing during development.
Pros:
- Use this package for automated vulnerability scanning or manual penetration testing
- Investigation screens can copy over discovered data into attack utilities
- Can be used for development testing
Cons:
- The paid version is very expensive
Burp Suite is available for installation on Windows, Linux, and macOS. There is no free trial of the vulnerability scanner, but you could access the Community Edition to get a feel for the style of operations of Burp Suite before buying.
Teramind DLP is a data security tool that is an important data protection system for those businesses that need to get standards accreditation. The Teramind data loss prevention system is written to the PCI DSS, HIPAA, ISO 27001, and GDPR standards.
Key Features
- Data loss prevention
- Compliance reporting
- Scans outgoing emails
The Teramind system aims to spot insider threats and block data disclosure. The type of data that has been selected from the settings will be searched across the network to find all instances of that data type. Those data stores are then tracked very closely.
Pros:
- Identifies, categorizes, and protects sensitive data
- Compliance with PCI DSS, HIPAA, ISO 27001, and GDPR
- User activity tracking
Cons:
- No on-premises version
Insider threat protection involves a constant scan of user activities on the network and company-provided applications. The system monitors emails and other communications, looking for data disclosures. Users that are identified as potential data leakers can then be monitored more closely with extra tools, such as a keystroke logger.
Network Security FAQs
What are the types of network security tools?
Three are many types of network security tools
-
Network Access Control (including multifactor authentication)
-
Gateway security (including firewalls)
-
Web security (including VPNs)
-
Wireless security
-
Network security policies
-
Vulnerability management
-
Network penetration testing
-
Data loss prevention
-
Threat prevention (includes insider threat management, intrusion detection systems and SIEMs)
-
Address controls
-
Endpoint security (including anti-malware)
-
Application Security
-
Email security
How does the CVE standard make network security devices and tools more effective?
The Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures program (CVE) is a list of commonly-known system weaknesses. Sharing this information allows network security software to be written in order to catch vulnerabilities and the CVE standard also gives network managers a yardstick by which to measure the effectiveness of network security tools.
Which two basic functions are performed by network security tools?
The two basic purposes of network security tools are to block unauthorized access and to prevent unauthorized actions.















![Toni Kroos là ai? [ sự thật về tiểu sử đầy đủ Toni Kroos ]](https://evbn.org/wp-content/uploads/New-Project-6635-1671934592.jpg)


